图的邻接表存储表示,图的深度优先和广度优先遍历
Posted robin_X
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了图的邻接表存储表示,图的深度优先和广度优先遍历相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
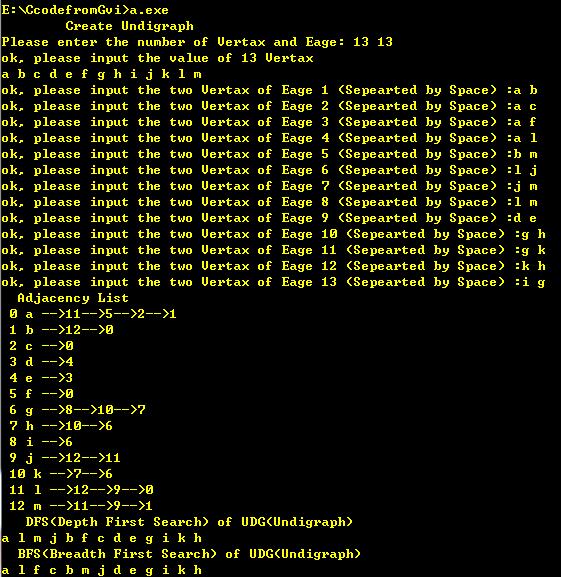
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 #define MAX_VERTAX_SIZE 20 5 #define OK 1 6 #define ERROR 0 7 8 typedef int Status; 9 typedef char ElemType; 10 11 typedef struct EageNode{ 12 int adjacentVertax; 13 struct EageNode* nextAdjacentVertax; 14 }EageNode, *EageNodePtr; 15 16 typedef struct VertaxNode{ 17 ElemType data; 18 EageNodePtr firstEage; 19 }VertaxNode; 20 21 typedef struct GraphAL{ 22 VertaxNode VertaxArray[MAX_VERTAX_SIZE]; 23 int vertaxNum; 24 int eageNum; 25 }GraphAL; 26 27 //定义队列结构,用于图的广度优先遍历 28 typedef struct QueueNode{ 29 ElemType data; 30 struct QueueNode* next; 31 }QueueNode, *QueueNodePtr; 32 typedef struct Queue{ 33 QueueNodePtr front; 34 QueueNodePtr rear; 35 }Queue; 36 Status InitQueue(Queue* Q){ 37 Q->front = (QueueNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct QueueNode)); 38 if( !Q->front ) 39 return ERROR; 40 Q->rear = Q->front; 41 Q->rear->next = NULL; 42 return OK; 43 } 44 Status EnterQueue(Queue *q, ElemType value){ 45 QueueNode* n; 46 n = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct QueueNode)); 47 if( !n ) 48 return ERROR; 49 n->data = value; 50 n->next = q->rear->next; 51 q->rear->next = n; 52 q->rear = n; 53 return OK; 54 } 55 Status DeleteQueue(Queue* q,ElemType* value){ 56 if( q->front == q->rear ) 57 return ERROR; 58 QueueNode* p; 59 p = q->front->next; 60 *value = p->data; 61 q->front->next = p->next; 62 free(p); 63 if( p == q->rear ) 64 q->rear = q->front; 65 return OK; 66 } 67 int IsQueueEmpty(Queue q){ 68 return q.front == q.rear ? OK : ERROR; 69 } 70 /* 71 int main(){ 72 Queue q; 73 ElemType c; 74 InitQueue(&q); 75 EnterQueue(&q,‘a‘); 76 EnterQueue(&q,‘f‘); 77 EnterQueue(&q,‘g‘); 78 EnterQueue(&q,‘e‘); 79 DeleteQueue(&q,&c); 80 printf("%c \n", c); 81 printf("&&&&%d", IsQueueEmpty(q)); 82 DeleteQueue(&q,&c); 83 printf("%c \n", c); 84 return 0; 85 } 86 */ 87 88 //返回顶点v在G中的下标 89 int LocateVertax(GraphAL G, ElemType v){ 90 int i; 91 for( i = 0; i < G.vertaxNum; i++ ){ 92 if( G.VertaxArray[i].data == v ) 93 return i; 94 } 95 return -1; 96 } 97 //通过下标得到元素的值 98 ElemType GetValueFromIndex(GraphAL G, int index){ 99 return G.VertaxArray[index].data; 100 } 101 //创建邻接表无向图 102 Status CreateUDG_AdjacencyList(GraphAL* G){ 103 int i; 104 ElemType v,w; 105 int index_v, index_w; 106 EageNodePtr vPtr,wPtr; 107 printf(" Create Undigraph\n"); 108 printf("Please enter the number of Vertax and Eage: "); 109 scanf("%d %d%*c", &(G->vertaxNum), &(G->eageNum)); 110 111 printf("ok, please input the value of %d Vertax\n", G->vertaxNum); 112 for( i = 0; i < G->vertaxNum; i++ ){ 113 scanf("%c%*c", &(G->VertaxArray[i].data)); 114 G->VertaxArray[i].firstEage = NULL; 115 } 116 117 for( i = 0; i < G->eageNum; i++ ){ 118 printf("ok, please input the two Vertax of Eage %d (Sepearted by Space) :", i+1); 119 scanf("%c %c%*c", &v,&w); //一条边的两个顶点v w 120 index_v = LocateVertax(*G, v); 121 index_w = LocateVertax(*G, w); 122 wPtr = (EageNode*)malloc(sizeof(EageNode)); 123 if( !wPtr ) 124 return ERROR; 125 wPtr->adjacentVertax = index_w; 126 wPtr->nextAdjacentVertax = G->VertaxArray[index_v].firstEage; 127 G->VertaxArray[index_v].firstEage = wPtr; 128 129 vPtr = (EageNode*)malloc(sizeof(EageNode)); 130 if( !vPtr ) 131 return ERROR; 132 vPtr->adjacentVertax = index_v; 133 vPtr->nextAdjacentVertax = G->VertaxArray[index_w].firstEage; 134 G->VertaxArray[index_w].firstEage = vPtr; 135 } 136 return OK; 137 } 138 //在图G中找v的第一个邻接顶点,找到则返回该顶点在邻接表中的位置,若没有则返回-1 139 int FirstAdjacentVertax(GraphAL G, ElemType v){ 140 int index_v; 141 index_v = LocateVertax(G, v); 142 if( G.VertaxArray[index_v].firstEage == NULL ) 143 return -1; 144 else 145 return (G.VertaxArray[index_v].firstEage)->adjacentVertax; 146 } 147 //在图G中找v的从w开始的下一个相邻的顶点 148 int NextAdjacentVertax(GraphAL G, ElemType v, ElemType w ){ 149 int index_v,index_w; 150 EageNodePtr p; 151 index_v = LocateVertax(G, v); 152 index_w = LocateVertax(G, w); 153 if( G.VertaxArray[index_v].firstEage == NULL ) 154 return -1; 155 p = G.VertaxArray[index_v].firstEage; //p pointer to first node 156 while( p->nextAdjacentVertax != NULL ){ 157 if( p->adjacentVertax == index_w ) 158 return p->nextAdjacentVertax->adjacentVertax; 159 p = p->nextAdjacentVertax; 160 } 161 return -1; 162 } 163 164 //DFS深度优先遍历图:使用递归算法,算法思想: 165 // 1:从v顶点开始,visit(v),将其设置为已遍历 166 // 2: 获得v的第一个邻接顶点w,若其存在并且没有访问过,递归遍历; 167 // 3: 获得v的从w之后的邻接点,若其存在并且没有访问过,递归遍历;直到所有都访问过 168 int visitedArray[MAX_VERTAX_SIZE]; 169 void visit(ElemType c){ 170 printf("%c ", c); 171 } 172 Status DFS(GraphAL G, ElemType v){ 173 ElemType w; 174 visit(v); 175 visitedArray[LocateVertax(G, v)] = 1; 176 for( w = GetValueFromIndex(G, FirstAdjacentVertax(G, v)); LocateVertax(G, w) != -1; w = GetValueFromIndex(G, NextAdjacentVertax(G, v, w))){ 177 if( visitedArray[LocateVertax(G, w)] != 1 ) 178 DFS(G, w); 179 } 180 return OK; 181 } 182 Status DFSTraverse(GraphAL G){ 183 int i; 184 for( i = 0; i < G.vertaxNum; i++ ) 185 visitedArray[i] = 0; 186 for( i = 0; i < G.vertaxNum; i++ ) 187 if( visitedArray[i] != 1 ) 188 DFS(G, GetValueFromIndex(G, i)); 189 return OK; 190 } 191 192 193 //BFS(Breadth First Search) 194 Status BFS(GraphAL G){ 195 int i,j; 196 Queue q; 197 ElemType c; 198 InitQueue(&q); 199 for(i = 0; i < G.vertaxNum; i++) 200 visitedArray[i] = 0; 201 for(i = 0; i < G.vertaxNum; i++){ //这个for实际执行的次数是连通分量的个数 202 if( visitedArray[i] == 0 ){ 203 EnterQueue(&q, G.VertaxArray[i].data); 204 visitedArray[i] = 1; 205 while( IsQueueEmpty(q) != OK ){ 206 DeleteQueue(&q, &c); 207 visit(c); 208 for( j = FirstAdjacentVertax(G, c); j != -1; j = NextAdjacentVertax(G, c, GetValueFromIndex(G, j))){ 209 if( visitedArray[j] == 0 ){ 210 EnterQueue(&q, GetValueFromIndex(G, j)); 211 visitedArray[j] = 1; 212 } 213 } 214 } 215 } 216 } 217 } 218 219 220 //打印无向图的邻接表 221 void PrintUDG_AdjacentList(GraphAL G){ 222 int i; 223 EageNodePtr p; 224 printf(" Adjacency List \n"); 225 for( i = 0; i < G.vertaxNum; i++ ){ 226 printf(" %d %c ",i, G.VertaxArray[i]); 227 p = G.VertaxArray[i].firstEage; 228 while( p != NULL ){ 229 printf("-->%d", p->adjacentVertax); 230 p = p->nextAdjacentVertax; 231 } 232 printf("\n"); 233 } 234 } 235 int main(){ 236 GraphAL G; 237 CreateUDG_AdjacencyList(&G); 238 PrintUDG_AdjacentList(G); 239 240 printf(" DFS(Depth First Search) of UDG(Undigraph)\n"); 241 DFSTraverse(G); 242 243 printf("\n BFS(Breadth First Search) of UDG(Undigraph)\n"); 244 BFS(G); 245 return 0; 246 }
以上是关于图的邻接表存储表示,图的深度优先和广度优先遍历的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章