数据结构—图邻接表存储基本运算算法图的遍历
Posted 之墨_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构—图邻接表存储基本运算算法图的遍历相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
邻接表概念
邻接表(Adjacency List)顾名思义,就是通过链表或者利用数组模拟链表的方式将图的相连接关系表示的一种方法,存储方法跟树的孩子链表示法相类似,是一种顺序分配和链式分配相结合的存储结构。 如这个表头结点所对应的顶点存在相邻顶点,则把相邻顶点依次存放于表头结点所指向的单向链表中


邻接表存储代码实现
typedef struct ANode
int adjvex;///邻接点编号
struct ANode *nextarc;///指向下一条边的指针
int weight;///边的相关信息
ArcNode;///边结点类型
typedef struct Vnode
InfoType info;///顶点的其他信息
int degree; /// 存放顶点入度,仅用于拓扑排序
ArcNode *firstArc;///指向第一条边
VNode; /// 邻接表头结点类型
typedef struct
VNode adjList(MAXV);///邻接表头结点数组
int n,e;///图中顶点数n和边数e
AdjGraph;///完整的图邻接表类型
邻接表基本运算算法
void CreateAdj(AdjGraph *&G,int A[MAXV][MAXV],int n,int e)
int i, j;
ArcNode *p;
G = (AdjGraph *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
for(i = 0;i<n;i++)
G->adjList[i].firstArc = NULL;
for(i = 0;i<n;i++)
if(A[i][j] != 0&& A[i][j] != INF)///存在一条边
p = (AdjGraph *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));///创建一个结点
p->adjvex = j;
p->weight = A[i][j];
p->nextarc = G->adjList[i].firstArc;///头插法插入结点p
G->adjList[i].firstArc = p;
G->n = n;
g->e = n;
void DispAdj(AdjGraph *G)
///输出邻接表G
ArcNode *p;
for(int i - 0;i<G->n;i++)
p = G->adjList[i].firstArc;
cout<<i;
while(p != NULL)
cout<<p->adjvex<<p->weight;
p = p->nextarc;
cout<<"^"<<endl;
void DestroyAdj(AdjGraph *&G)
ArcNode *pre ,*p;
for(int i = 0;i<G->n;i++)///扫描所有单链表
pre = G->adjList[i].firstArc;///pre指向第i个单链表的首结点
if(pre != NULL)
p = pre->nextarc;
while(p!=NULL)///释放第i个单链表 的所有边结点
free(pre);
pre = p;
p = p->nextarc;
free(pre);
free(G);///释放头结点数组
完整代码
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define INF 32767 ///定义∞
#define MAX 100
using namespace std;
typedef char InfoType;
typedef struct
int no; ///顶点的编号
InfoType info ; ///顶点的其他信息
VertexType; ///顶点的类型
typedef struct
int edges[MAX][MAX]; ///邻接矩阵数组
int n,e; ///顶点数、边数
VertexType vexs[MAX]; ///顶点的类型
MatGraph; ///完整的图邻接矩阵类型
typedef struct ANode
int adjvex;///邻接点编号
struct ANode *nextarc;///指向下一条边的指针
int weight;///边的相关信息
ArcNode;///边结点类型
typedef struct Vnode
InfoType info;///顶点的其他信息
int degree; /// 存放顶点入度,仅用于拓扑排序
ArcNode *firstArc;///指向第一条边
VNode; /// 邻接表头结点类型
typedef struct
VNode adjList[MAX];///邻接表头结点数组
int n,e;///图中顶点数n和边数e
AdjGraph;///完整的图邻接表类型
void CreateMat(MatGraph &g,int A[MAX][MAX],int n,int e)
///创建图的邻接矩阵
int i,j;
g.n = n;
g.e = e;
for(i = 0;i<g.n;i++)
for(j = 0;j<g.n;j++)
g.edges[i][j] = A[i][j];
void DispMat(MatGraph g)
///输出邻接矩阵
int i,j;
for(i = 0;i<g.n;i++)
for(j = 0;j<g.n;j++)
if(g.edges[i][j] != INF)
cout<<g.edges[i][j]<<" ";
else
cout<<"∞"<<" ";
cout<<endl;
void CreateAdj(AdjGraph *&G,int A[MAX][MAX],int n,int e)
///创建邻接表
int i, j;
ArcNode *p;
G = (AdjGraph *)malloc(sizeof(AdjGraph));
for(i = 0;i<n;i++)
G->adjList[i].firstArc = NULL;
for(i = 0;i<n;i++)
for(int j = n-1;j>=0;j--)
if(A[i][j] != 0&& A[i][j] != INF)///存在一条边
p = (ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));///创建一个结点
p->adjvex = j;
p->weight = A[i][j];
p->nextarc = G->adjList[i].firstArc;///头插法插入结点p
G->adjList[i].firstArc = p;
G->n = n;
G->e = n;
void DispAdj(AdjGraph *G)
///输出邻接表G
ArcNode *p;
for(int i = 0;i<G->n;i++)
p = G->adjList[i].firstArc;
printf("%3d:",i);
while(p != NULL)
printf("%3d[%d]→",p->adjvex,p->weight);
p = p->nextarc;
printf("^\\n");
void DestroyAdj(AdjGraph *&G)
ArcNode *pre ,*p;
for(int i = 0;i<G->n;i++)///扫描所有单链表
pre = G->adjList[i].firstArc;///pre指向第i个单链表的首结点
if(pre != NULL)
p = pre->nextarc;
while(p!=NULL)///释放第i个单链表 的所有边结点
free(pre);
pre = p;
p = p->nextarc;
free(pre);
free(G);///释放头结点数组
int main()
MatGraph g;
AdjGraph *G;
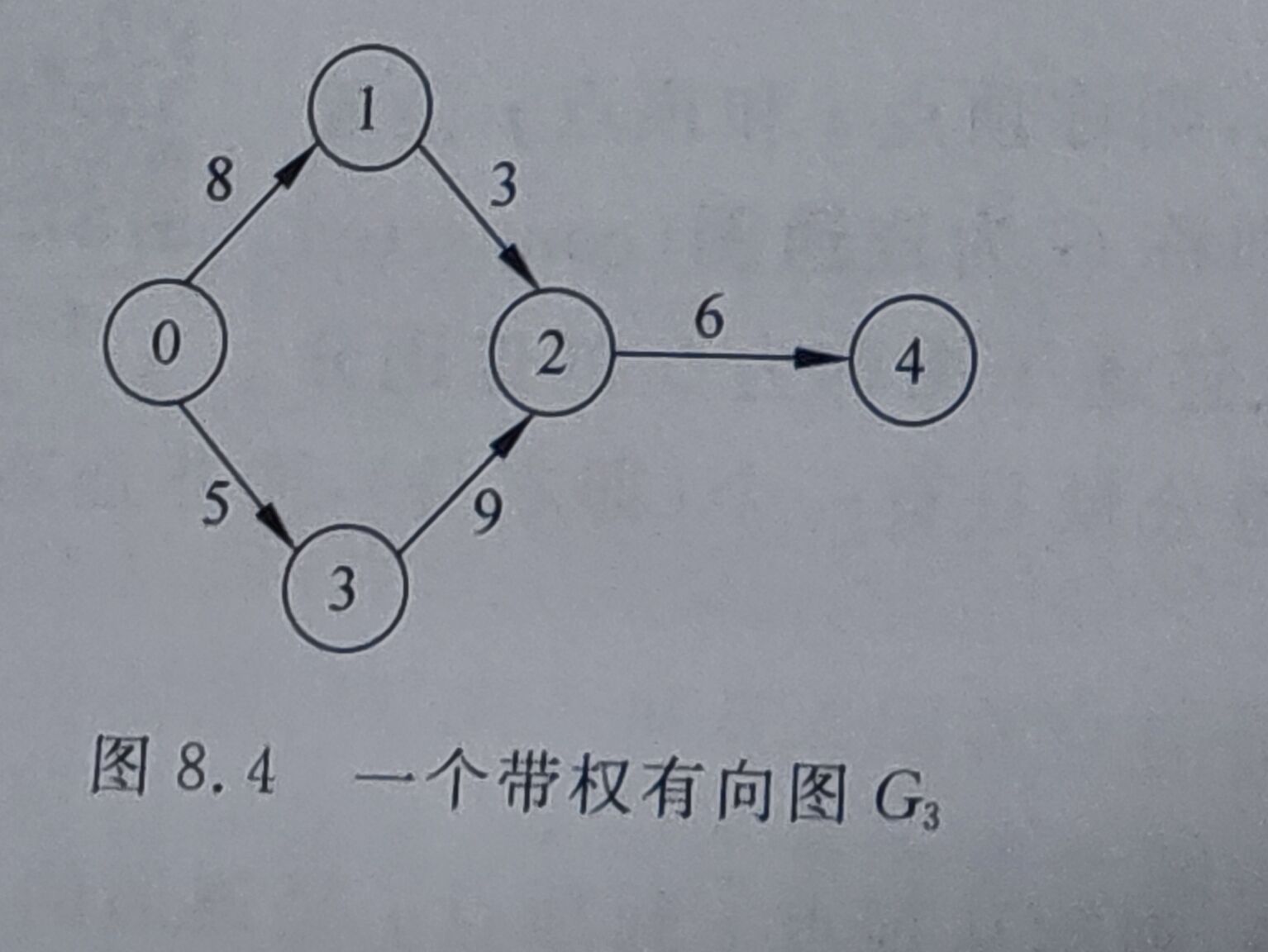
int A[MAX][MAX] = 0,5,INF,7,INF,INF,INF,0,4,INF,INF,INF,
8,INF,0,INF,INF,9, INF,INF,5,0,INF,6,
INF,INF,INF,5,0,INF,3,INF,INF,INF,1,0;
int n =6,e=10;
CreateMat(g,A,n,e);
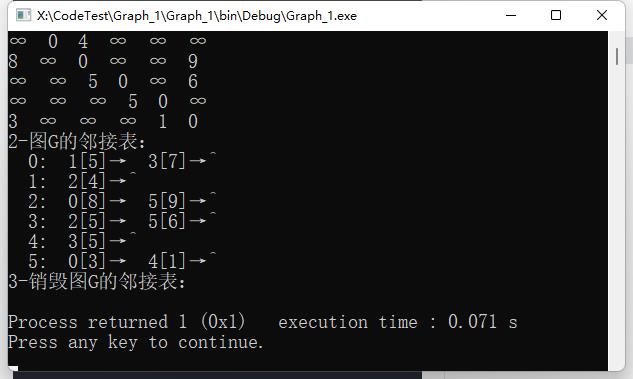
cout<<"1-图G的邻接矩阵"<<endl;
DispMat(g);
CreateAdj(G,A,n,e);
cout<<"2-图G的邻接表:"<<endl;
DispAdj(G);
cout<<"3-销毁图G的邻接表:"<<endl;
DestroyAdj(G);
return 1;
运行结果
图的遍历
图的遍历
从给定图中任意指定的顶点(称为初始点)出发,按照某种搜索方法沿着图的边访问图中的所有顶点,每个顶点被访问一次且仅访问一次,这个过程称为图的遍历。
如果给定图是连通的无向图或者是强连通的有向图,则遍历过程一次就能完成,并可按访问的先后顺序得到由该图的所有顶点组成的一个序列
图的遍历比树的遍历更复杂,因为从树根到达树中的任意结点只有一条路径,而从图的初始点到达图中的每个顶点可能存在着多条路径
当沿着图中的一条路径访问过某一顶点之后,可能还沿着另一条路径回到该顶点,即存在回路
为了避免同一个顶点被重复访问,必须记住每个被访问过的顶点
为此,可设置一个访问标记数组 visited,当顶点 i 被访问过时,数组中的元素 visited[i]置为 1,否则置为 0
根据搜索方法的不同,图的遍历方法有两种:一种叫深度优先遍历(Depth First Search,DFS),另一种叫广度优先遍历(Breadth First Search,BFS)。
深搜示意图
深度优先搜索生成树: 对于无向连通生成图,如果将第一次深度优先搜索时前进操作经过的边保留下来则可以构成一棵深度优先搜索生成树

以上是关于数据结构—图邻接表存储基本运算算法图的遍历的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
数据结构与算法图 ( 图的存储形式 | 图的基本概念 | 图的表示方式 | 邻接矩阵 | 邻接表 | 图的创建 | 代码示例 )
