BERT实战——基于Keras
Posted dogecheng
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了BERT实战——基于Keras相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.keras_bert 和 kert4keras
keras_bert 是 CyberZHG 大佬封装好了Keras版的Bert,可以直接调用官方发布的预训练权重。
github:https://github.com/CyberZHG/keras-bert
快速安装:pip install keras-bert
kert4keras 是 苏剑林 大佬参考 keras-bert 重新编写的一个 keras 版的 bert,所以使用体验差不多,但 kert4keras 可以适配 albert
github:https://github.com/bojone/bert4keras
快速安装:pip install git+https://www.github.com/bojone/bert4keras.git
2.keras_bert
2.1.Tokenizer
在 keras-bert 里面,使用 Tokenizer 会将文本拆分成字并生成相应的id。
我们需要提供一个字典,字典存放着 token 和 id 的映射。字典里还有 BERT 里特别的 token。
[CLS],[SEP],[UNK]等
在下面的示例中,如果文本拆分出来的字在字典不存在,它的 id 会是 5,代表 [UNK],即 unknown
from keras_bert import Tokenizer #字典 token_dict = ‘[CLS]‘: 0, ‘[SEP]‘: 1, ‘un‘: 2, ‘##aff‘: 3, ‘##able‘: 4, ‘[UNK]‘: 5, tokenizer = Tokenizer(token_dict) # 拆分单词实例 print(tokenizer.tokenize(‘unaffable‘)) # [‘[CLS]‘, ‘un‘, ‘##aff‘, ‘##able‘, ‘[SEP]‘] # indices是字对应索引 # segments表示索引对应位置上的字属于第一句话还是第二句话 # 这里只有一句话 unaffable,所以segments都是0 indices, segments = tokenizer.encode(‘unaffable‘) print(indices) # [0, 2, 3, 4, 1] print(segments) # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
我们用同样的字典,拆分不存在 字典 中的单词,结果如下,可以看到英语中会直接把不存在字典中的部分直接按字母拆分。
print(tokenizer.tokenize(‘unknown‘)) # [‘[CLS]‘, ‘un‘, ‘##k‘, ‘##n‘, ‘##o‘, ‘##w‘, ‘##n‘, ‘[SEP]‘] indices, segments = tokenizer.encode(‘unknown‘) # [0, 2, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 1] # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
下面是输入两句话的例子,encode 函数中 我们可以带上参数 max_len,只看文本拆分出来的 max_len 个字
如果拆分完的字不超过max_len,则用 0 填充
print(tokenizer.tokenize(first=‘unaffable‘, second=‘钢‘)) # [‘[CLS]‘, ‘un‘, ‘##aff‘, ‘##able‘, ‘[SEP]‘, ‘钢‘, ‘[SEP]‘] indices, segments = tokenizer.encode(first=‘unaffable‘, second=‘钢‘, max_len=10) print(indices) # [0, 2, 3, 4, 1, 5, 1, 0, 0, 0] print(segments) # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]
注意这个 max_len 包括 BERT 中的特殊 token,比如下面的代码
tokenizer.encode(‘unaffable‘, max_len=3)
# [0, 2, 1]我们得到的结果是 [0, 2, 1],0 和 1 分别代表 [CLS] 和 [SEP]
2.2.模型的训练和使用
2.2.1.函数介绍
keras_bert 中我们可以使用 get_model() 来取得 BERT 模型,它有以下参数可供选择
- token_num:token 的数量
- pos_num:最大 position 。默认512
- seq_len:输入序列的最大长度,为 None 时不限制。默认512
- embed_dim:嵌入维度,默认768
- transformer_num:transformer的个数,默认12
- head_num:每个 transformer 中 multi-head attention 中 heads 的个数,默认12
- feed_forward_dim:每个 transformer 中 feed-forward 层的维度,默认3072
- dropout_rate:dropout 的概率
- attention_activation:attention 层的激活函数
- feed_forward_activation:feed forward 层使用的激活函数,默认是gelu
- training:如果为True,则将返回带有 MLM 和 NSP输出的模型;否则,将返回输入层和最后一个特征提取层。默认 True
- trainable:模型是否是可训练的,默认和 training 一样的设置
- output_layer_num:多少个FeedForward-Norm层的输出被连接为单个输出。仅在 training 为 False 时可用。默认1
- use_task_embed:是否将 task embedding 加到现有的 embedding 中,默认 False
- task_num:任务数,默认10
- use_adapter:是否在每个残差网络前使用 feed-forward adapter,默认 False
- adapter_units:feed-forward adapter 中第一个 transformation 的维度
关于adapter可以参考这篇论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.00751.pdf
gen_batch_inputs() 函数可以产生我们用于训练的数据,可用参数如下
- sentence_pairs:列表,这个包含了许多 token 组成的句子对。
- token_dict:包括 BERT 所用的特殊符号在内的字典
- token_list:包括所有 token 的列表
- seq_len:序列的长度,默认512
- mask_rate:随机 token 被替换为 [MASK] 的概率,然后预测这个被替换的 token。默认0.15
- mask_mask_rate:如果一个 token 要被替换为 [MASK],真正替换为 [MASK] 的概率。默认0.8
- mask_random_rate:如果一个 token 要被替换为 [MASK],替换成一个随机的 token。默认0.1
- swap_sentence_rate:交换第一个句子和第二个句子的概率。默认0.5
- force_mask:至少一个位置的 token 被 masked,默认 True
compile_model() 函数用来编译我们的模型,可用参数如下
- model:要编译的模型
- weight_decay:权重衰减率,默认0.01
- decay_steps:学习率会在这个步长中线性衰减至0,默认100000
- warmup_steps:学习率会在预热步长中线性增长到设置的学习率,默认10000
- learning_rate:学习率,默认1e-4
warmup可以参考这篇文章:https://yinguobing.com/tensorflowzhong-de-xue-xi-lu-re-shen/
当step小于warm up setp时,学习率等于基础学习率×(当前step/warmup_step),由于后者是一个小于1的数值,因此在整个warm up的过程中,学习率是一个递增的过程!当warm up结束后,学习率开始递减。
load_trained_model_from_checkpoint() 函数用来加载官方训练好的模型,可用参数如下
- config_file:JSON 配置文件路径
- checkpoint_file:checkpoint 文件路径
- training:True 的话,会返回整个模型,否则会忽略 MLM 和 NSP 部分。默认 False
- trainable:模型是否可训练,默认和 training 设置一样
- output_layer_num:多少个FeedForward-Norm层的输出被连接为单个输出。仅在 training 为 False 时可用。默认1
- seq_len:如果这个数值比配置文件中的长度小,position embeddings 会被切成适用于这个长度。默认1e9
2.2.2.构建和训练模型
这个例子里面,我们的不用 Tokenizer 将文本拆分成 “字”,而是使用 “词” 级别作为模型的输入
这里跟 keras 的文本处理很像,可以参考下面这篇文章
import keras from keras_bert import get_base_dict, get_model, compile_model, gen_batch_inputs # 输入示例 sentence_pairs = [ [[‘all‘, ‘work‘, ‘and‘, ‘no‘, ‘play‘], [‘makes‘, ‘jack‘, ‘a‘, ‘dull‘, ‘boy‘]], [[‘from‘, ‘the‘, ‘day‘, ‘forth‘], [‘my‘, ‘arm‘, ‘changed‘]], [[‘and‘, ‘a‘, ‘voice‘, ‘echoed‘], [‘power‘, ‘give‘, ‘me‘, ‘more‘, ‘power‘]], ] # 构建 token 字典 # 这个字典存放的是【词】 token_dict = get_base_dict() # get_base_dict()返回一个字典 # 字典预置了一些特殊token,具体内容如下 # ‘‘: 0, ‘[UNK]‘: 1, ‘[CLS]‘: 2, ‘[SEP]‘: 3, ‘[MASK]‘: 4 for pairs in sentence_pairs: for token in pairs[0] + pairs[1]: if token not in token_dict: token_dict[token] = len(token_dict) # token_dict 是由词组成的字典,大致如下 # ‘‘: 0, ‘[UNK]‘: 1, ‘[CLS]‘: 2, ‘[SEP]‘: 3, ‘[MASK]‘: 4, ‘all‘: 5, ‘work‘: 6,..., ‘me‘: 26, ‘more‘: 27 token_list = list(token_dict.keys()) # 构建和训练模型 model = get_model( token_num=len(token_dict), head_num=5, transformer_num=12, embed_dim=25, feed_forward_dim=100, seq_len=20, pos_num=20, dropout_rate=0.05, ) compile_model(model) model.summary() def _generator(): while True: yield gen_batch_inputs( sentence_pairs, token_dict, token_list, seq_len=20, mask_rate=0.3, swap_sentence_rate=1.0, ) model.fit_generator( # 这里测试集和验证集使用了同样的数据 # 实际中使用时不能这样 generator=_generator(), steps_per_epoch=1000, epochs=100, validation_data=_generator(), validation_steps=100, callbacks=[ keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor=‘val_loss‘, patience=5) ], ) # 使用训练好的模型 # 取出 输入层 和 最后一个特征提取层 inputs, output_layer = get_model( token_num=len(token_dict), head_num=5, transformer_num=12, embed_dim=25, feed_forward_dim=100, seq_len=20, pos_num=20, dropout_rate=0.05, training=False, trainable=False, output_layer_num=4, )
2.2.3下载和使用预训练模型
参考地址:https://github.com/CyberZHG/keras-bert/tree/master/demo
我们可以使用 load_trained_model_from_checkpoint() 函数使用本地已经下载好的预训练模型,可以从 BERT 的 github 上获取下载地址
下面是使用预训练模型提取输入文本的特征
import os # 设置预训练模型的路径 pretrained_path = ‘chinese_L-12_H-768_A-12‘ config_path = os.path.join(pretrained_path, ‘bert_config.json‘) checkpoint_path = os.path.join(pretrained_path, ‘bert_model.ckpt‘) vocab_path = os.path.join(pretrained_path, ‘vocab.txt‘) # 构建字典 # 也可以用 keras_bert 中的 load_vocabulary() 函数 # 传入 vocab_path 即可 # from keras_bert import load_vocabulary # token_dict = load_vocabulary(vocab_path) import codecs token_dict = with codecs.open(vocab_path, ‘r‘, ‘utf8‘) as reader: for line in reader: token = line.strip() token_dict[token] = len(token_dict) # 加载预训练模型 from keras_bert import load_trained_model_from_checkpoint model = load_trained_model_from_checkpoint(config_path, checkpoint_path) # Tokenization from keras_bert import Tokenizer tokenizer = Tokenizer(token_dict) text = ‘语言模型‘ tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(text) # [‘[CLS]‘, ‘语‘, ‘言‘, ‘模‘, ‘型‘, ‘[SEP]‘] indices, segments = tokenizer.encode(first=text, max_len=512) print(indices[:10]) # [101, 6427, 6241, 3563, 1798, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0] print(segments[:10]) # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # 提取特征 import numpy as np predicts = model.predict([np.array([indices]), np.array([segments])])[0] for i, token in enumerate(tokens): print(token, predicts[i].tolist()[:5])
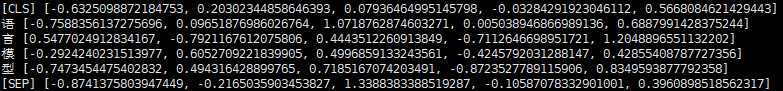
下面我们用预训练模型预测句子中被 MASKED 掉的词语是什么
token_dict = with codecs.open(vocab_path, ‘r‘, ‘utf8‘) as reader: for line in reader: token = line.strip() token_dict[token] = len(token_dict) token_dict_rev = v: k for k, v in token_dict.items() model = load_trained_model_from_checkpoint(config_path, checkpoint_path, training=True) text = ‘数学是利用符号语言研究数量、结构、变化以及空间等概念的一门学科‘ tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(text) tokens[1] = tokens[2] = ‘[MASK]‘# [‘[CLS]‘, ‘[MASK]‘, ‘[MASK]‘, ‘是‘, ‘利‘,..., ‘学‘, ‘科‘, ‘[SEP]‘] indices = np.array([[token_dict[token] for token in tokens] + [0] * (512 - len(tokens))]) segments = np.array([[0] * len(tokens) + [0] * (512 - len(tokens))]) masks = np.array([[0, 1, 1] + [0] * (512 - 3)]) predicts = model.predict([indices, segments, masks])[0].argmax(axis=-1).tolist() print(‘Fill with: ‘, list(map(lambda x: token_dict_rev[x], predicts[0][1:3]))) # Fill with: [‘数‘, ‘学‘]
3.albert 和 keras4bert
使用示例:https://github.com/bojone/bert4keras/tree/master/examples
albert中文预训练模型:https://github.com/brightmart/albert_zh
3.1.基本使用
keras4bert 是基于 keras-bert 重新编写的一个 keras 版的 bert,可以适配 albert,只需要在load_pretrained_model函数里加上albert=True。
使用体验和 keras_bert 差不多,下面是 github 提供的使用例子。
SimpleTokenizer是一个简单的分词器,直接将文本分割为单字符序列,专为中文处理设计,原则上只适用于中文模型。
load_pretrained_model 可用参数如下
- config_path:JSON 配置文件路径
- checkpoint_file:checkponit 文件路径
- with_mlm:是否包含 MLM 部分,默认 False
- seq2seq:True 则用来做seq2seq任务的Bert,默认 False
- keep_words:要保留的词ID列表
- albert:是否是 ALBERT 模型
from bert4keras.bert import load_pretrained_model from bert4keras.utils import SimpleTokenizer, load_vocab import numpy as np config_path = ‘./albert/albert_config_large.json‘ checkpoint_path = ‘./albert/albert_model.ckpt‘ dict_path = ‘./albert/vocab.txt‘ token_dict = load_vocab(dict_path) tokenizer = SimpleTokenizer(token_dict) # 使用ALBERT model = load_pretrained_model(config_path, checkpoint_path, albert=True) # 编码测试 token_ids, segment_ids = tokenizer.encode(u‘语言模型‘) print(model.predict([np.array([token_ids]), np.array([segment_ids])]))
预测 MASKED 掉的词汇
# 建立ALBERT模型,加载权重
# 预测 MASKED 掉的词汇,需要 MLM 层 model = load_pretrained_model(config_path, checkpoint_path, with_mlm=True, albert=True) token_ids, segment_ids = tokenizer.encode(u‘科学技术是第一生产力‘) # mask掉“技术” token_ids[3] = token_ids[4] = token_dict[‘[MASK]‘] # 用mlm模型预测被mask掉的部分 probas = model.predict([np.array([token_ids]), np.array([segment_ids])])[0] print(tokenizer.decode(probas[3:5].argmax(axis=1))) # 技术
3.2.情感分析实例
数据集:https://github.com/bojone/bert4keras/tree/master/examples/datasets
测试环境:
Ubuntu 16.04.6
Anaconda Python 3.7.3
数据集是两个 excel 表,分别存放着正面和负面评价,下面是负面评价的内容

先设置预训练模型的路径,并读取原始数据
import json import numpy as np import pandas as pd import os import codecs from bert4keras.bert import load_pretrained_model, set_gelu from bert4keras.utils import SimpleTokenizer, load_vocab set_gelu(‘tanh‘) # 切换gelu版本 # 配置文件路径 config_path = ‘./albert/albert_config_large.json‘ checkpoint_path = ‘./albert/albert_model.ckpt‘ dict_path = ‘./albert/vocab.txt‘ # 读取数据 neg = pd.read_excel(‘./learn_data/neg.xls‘, header=None) pos = pd.read_excel(‘./learn_data/pos.xls‘, header=None)
构建字典并建立分词器
# 字出现的次数 chars = # 数据集 data = [] for d in neg[0]: data.append((d, 0)) for c in d: chars[c] = chars.get(c, 0) + 1 for d in pos[0]: data.append((d, 1)) for c in d: chars[c] = chars.get(c, 0) + 1 # 保留出现次数大于 4 次的字 chars = i: j for i, j in chars.items() if j >= 4 # 读取字典 _token_dict = load_vocab(dict_path) # 构造字典 # token_dict 里是存放的都是本任务里用得到的字 # keep_words 存放的是索引 token_dict, keep_words = , [] for c in [‘[PAD]‘, ‘[UNK]‘, ‘[CLS]‘, ‘[SEP]‘, ‘[unused1]‘]: token_dict[c] = len(token_dict) keep_words.append(_token_dict[c]) for c in chars: if c in _token_dict: token_dict[c] = len(token_dict) keep_words.append(_token_dict[c]) okenizer = SimpleTokenizer(token_dict) # 建立分词器
构建训练数据和测试数据
if not os.path.exists(‘./random_order.json‘): random_order = list(range(len(data))) np.random.shuffle(random_order) json.dump( random_order, open(‘./random_order.json‘, ‘w‘), indent=4 ) else: random_order = json.load(open(‘./random_order.json‘)) # 按照9:1的比例划分训练集和验证集 train_data = [data[j] for i, j in enumerate(random_order) if i % 10 != 0] valid_data = [data[j] for i, j in enumerate(random_order) if i % 10 == 0] def seq_padding(X, padding=0): # 用 0 填充序列 # 让所有输入序列长度一致 L = [len(x) for x in X] ML = max(L) return np.array([ np.concatenate([x, [padding] * (ML - len(x))]) if len(x) < ML else x for x in X ]) class data_generator: def __init__(self, data, batch_size=32): self.data = data self.batch_size = batch_size self.steps = len(self.data) // self.batch_size if len(self.data) % self.batch_size != 0: self.steps += 1 def __len__(self): return self.steps def __iter__(self): while True: idxs = list(range(len(self.data))) np.random.shuffle(idxs) X1, X2, Y = [], [], [] for i in idxs: d = self.data[i] text = d[0][:maxlen] # x1 是字对应的索引 # x2 是句子对应的索引 x1, x2 = tokenizer.encode(first=text) y = d[1] X1.append(x1) X2.append(x2) Y.append([y]) if len(X1) == self.batch_size or i == idxs[-1]: X1 = seq_padding(X1) X2 = seq_padding(X2) Y = seq_padding(Y) yield [X1, X2], Y [X1, X2, Y] = [], [], [] # 允许序列的最大长度 maxlen = 100 train_D = data_generator(train_data) valid_D = data_generator(valid_data)
构建模型并训练
from keras.layers import * from keras.models import Model import keras.backend as K from keras.optimizers import Adam model = load_pretrained_model( config_path, checkpoint_path, keep_words=keep_words, albert=True ) output = Lambda(lambda x: x[:, 0])(model.output) output = Dense(1, activation=‘sigmoid‘)(output) model = Model(model.input, output) model.compile( loss=‘binary_crossentropy‘, optimizer=Adam(1e-5), # 用足够小的学习率 # optimizer=PiecewiseLinearLearningRate(Adam(1e-5), 1000: 1e-5, 2000: 6e-5), metrics=[‘accuracy‘] ) model.summary() model.fit_generator( train_D.__iter__(), steps_per_epoch=len(train_D), epochs=10, validation_data=valid_D.__iter__(), validation_steps=len(valid_D) )
以上是关于BERT实战——基于Keras的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章