Keras深度学习实战——基于ResNet模型实现性别分类
Posted 盼小辉丶
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Keras深度学习实战——基于ResNet模型实现性别分类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Keras深度学习实战——基于ResNet模型实现性别分类
0. 前言
从 VGG16 到 VGG19,最显著的变化在于网络层数的增加,通常而言,神经网络越深,其模型性能就越好。但如果仅通过增加网络层数就可以获得更高的模型性能,事情就变得简单了,我们可以通过不断向模型添加更多层直到其达到最佳性能。
但不幸的是,事实并非如此,随着网络层数的增加,梯度消失的问题也浮出水面——随着层数的增加,网络中的梯度就会变得很小,以至于难以调整权重,同时网络性能也会下降。
深度残差网络 (ResNet) 的提出就是为了解决上述问题。在 ResNet 中,如果模型没有什么要学习的,那么卷积层可以什么也不做,只是将上一层的输出传递给下一层。但是,如果模型需要学习其他一些特征,则卷积层将前一层的输出作为输入,并学习完成目标任务所需的其它特征。
1. ResNet 架构简介
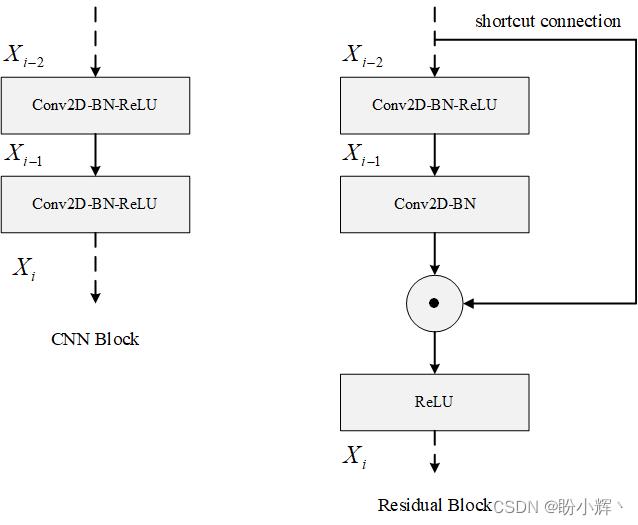
残差 (Residual) 在数理统计中是指实际观察值与估计值(拟合值)之间的差值。经典的 ResNet 架构如下所示:

在上图中,可以看出,模型中具有跳跃连接,该连接将前一层与该网络中的传统卷积层一起连接到线路的下一层。更正式的讲,输入 x x x 通过卷积层,得到特征变换后的输出 F ( x ) F(x) F(x),与输入 x x x 进行逐元素的相加运算,得到最终输出 H ( x ) H(x) H(x):
H ( x ) = x + F ( x ) H(x) = x + F(x) H(x)=x+F(x)
VGG 模块和残差模块对比如下:
2. 基于预训练的 ResNet50 模型实现性别分类
在《迁移学习》中,我们了解了利用迁移学习,只需要少量样本即可训练得到性能较好的模型;并基于迁移学习利用预训练的 VGG16 模型进行了性别分类的实战。在本节中,我们同样使用预训练的 ResNet50 进行性别分类实战,其中 ResNet50 中的 50 表示网络中共有 50 个网络层。
2.1 训练性别分类模型
首先导入所需库,并下载预训练的 ResNet50 模型:
from keras.applications import ResNet50
from keras.applications.resnet50 import preprocess_input
from glob import glob
from skimage import io
import cv2
import numpy as np
model = ResNet50(include_top=False, weights='imagenet', input_shape=(256, 256, 3))
创建输入和输出数据集,需要注意的是,ResNet50 的输入图像的尺寸至少为 224 x 224,以保证 ResNet50 预训练模型能够正常工作。我们重用在《卷积神经网络进行性别分类》中使用的数据集以及数据加载代码:
x = []
y = []
for i in glob('man_woman/a_resized/*.jpg')[:800]:
try:
image = io.imread(i)
x.append(image)
y.append(0)
except:
continue
for i in glob('man_woman/b_resized/*.jpg')[:800]:
try:
image = io.imread(i)
x.append(image)
y.append(1)
except:
continue
x_resnet50 = []
for i in range(len(x)):
img = x[i]
img = preprocess_input(img.reshape((1, 256, 256, 3)))
img_feature = model.predict(img)
x_resnet50.append(img_feature)
构建输入和输出 numpy 数组,同时将数据集划分为训练和测试集:
x_resnet50 = np.array(x_resnet50)
x_resnet50 = x_resnet50.reshape(x_resnet50.shape[0], x_resnet50.shape[2], x_resnet50.shape[3], x_resnet50.shape[4])
y = np.array(y)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x_resnet50, y, test_size=0.2)
在预训练的 ResNet50 模型得到的输出基础上构建微调模型:
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten, Dropout, Dense
model_fine_tuning = Sequential()
model_fine_tuning.add(Conv2D(2048,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
activation='relu',
input_shape=(x_train.shape[1], x_train.shape[2], x_train.shape[3])))
model_fine_tuning.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model_fine_tuning.add(Flatten())
model_fine_tuning.add(Dense(1024, activation='relu'))
model_fine_tuning.add(Dropout(0.5))
model_fine_tuning.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model_fine_tuning.summary()
该模型的简要架构信息如下:
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 6, 6, 2048) 37750784
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d (MaxPooling2D) (None, 3, 3, 2048) 0
_________________________________________________________________
flatten (Flatten) (None, 18432) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 1024) 18875392
_________________________________________________________________
dropout (Dropout) (None, 1024) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 1) 1025
=================================================================
Total params: 56,627,201
Trainable params: 56,627,201
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
编译并拟合构建的微调模型:
model_fine_tuning.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',optimizer='adam',metrics=['acc'])
history = model_fine_tuning.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=32,
epochs=20,
verbose=1,
validation_data = (x_test, y_test))
在训练期间,模型在训练数据集和测试数据集上准确率和损失值的变化如下:
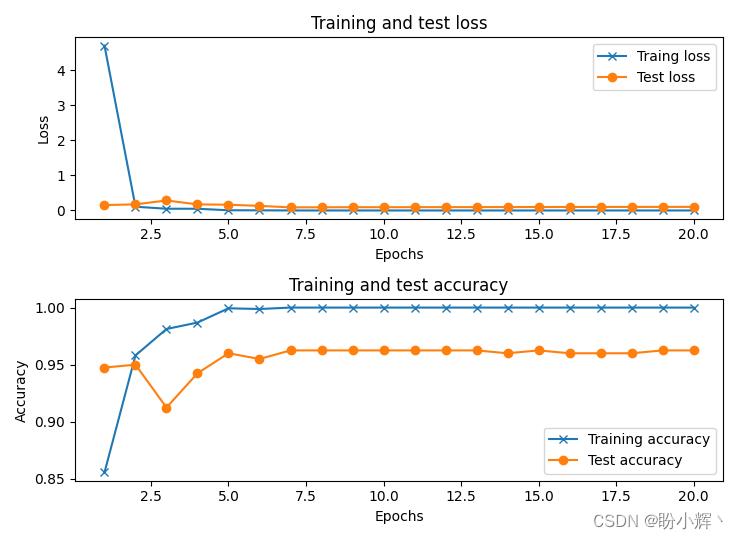
可以看到,使用预训练 ResNet50 的实现的性别分类模型准确率可以达到 95% 左右。
2.2 错误分类图像示例
错误分类的图像示例如下:
x = np.array(x)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2)
x_test_resnet50 = []
for i in range(len(x_test)):
img = x_test[i]
img = preprocess_input(img.reshape((1, 256, 256, 3)))
img_feature = model.predict(img)
x_test_resnet50.append(img_feature)
x_test_resnet50 = np.array(x_test_resnet50)
x_test_resnet50 = x_test_resnet50.reshape(x_test_resnet50.shape[0], x_test_resnet50.shape[2], x_test_resnet50.shape[3], x_test_resnet50.shape[4])
y_pred = model_fine_tuning.predict(x_test_resnet50)
wrong = np.argsort(np.abs(y_pred.flatten()-y_test))
print(wrong)
y_test_char = np.where(y_test==0,'M','F')
y_pred_char = np.where(y_pred>0.5,'F','M')
plt.subplot(221)
plt.imshow(x_test[wrong[-1]])
plt.title('Actual: '+str(y_test_char[wrong[-1]])+', '+'Predicted: '+str((y_pred_char[wrong[-1]][0])))
plt.subplot(222)
plt.imshow(x_test[wrong[-2]])
plt.title('Actual: '+str(y_test_char[wrong[-2]])+', '+'Predicted: '+str((y_pred_char[wrong[-2]][0])))
plt.subplot(223)
plt.imshow(x_test[wrong[-3]])
plt.title('Actual: '+str(y_test_char[wrong[-3]])+', '+'Predicted: '+str((y_pred_char[wrong[-3]][0])))
plt.subplot(224)
plt.imshow(x_test[wrong[-4]])
plt.title('Actual: '+str(y_test_char[wrong[-4]])+', '+'Predicted: '+str((y_pred_char[wrong[-4]][0])))
plt.show()
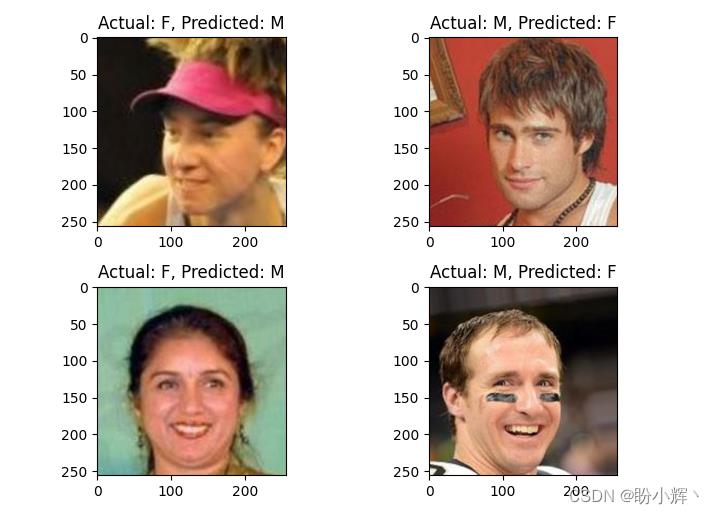

对比 VGG16、VGG19 和 Inception v3,在多个预先训练的性别分类模型的准确率并没有显着差异,因为可能这些预训练模型所提取的图像特征是更加通用的一般特征,并没有针对提取性别特征进行优化,我们可以从头训练一个 RestNet50,查看网络性能表现。
相关链接
Keras深度学习实战(7)——卷积神经网络详解与实现
Keras深度学习实战(9)——卷积神经网络的局限性
Keras深度学习实战(10)——迁移学习
Keras深度学习实战——使用卷积神经网络实现性别分类
Keras深度学习实战——基于VGG19模型实现性别分类
Keras深度学习实战——基于Inception v3实现性别分类
以上是关于Keras深度学习实战——基于ResNet模型实现性别分类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Keras深度学习实战——基于Inception v3实现性别分类
PyTorch深度学习实战 | 基于ResNet的人脸关键点检测