C++数据结构与算法:布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)原理与实现
Posted linux大本营
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++数据结构与算法:布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)原理与实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文本代码下载地址:Github:
https://github.com/dongyusheng/csdn-code/tree/master/BloomFilter
一、什么是布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)是1970年由布隆提出的
它实际上是一个很长的二进制向量和一系列随机映射函数。布隆过滤器可以用于检索一个元素是否在一个集合中
优点:
- 可以高效地进行查询,可以用来告诉你“某样东西一定不存在或者可能存在”
- 可以高效的进行插入
- 相比于传统的List、Set、Map等数据结构,它占用空间更少,因为其本身并不存储任何数据(重点)
缺点:
- 其返回的结果是概率性(存在误差)的
- 一般不提供删除操作
布隆过滤器一般使用在数据量特别大的场景下,一般不会使用
用的使用场景:
- 使用word文档时,判断某个单词是否拼写正确。例如我们在编写word时,某个单词错误那么就会在单词下面显示红色波浪线
- 网络爬虫程序,不去爬相同的url页面
- 垃圾邮件的过滤算法
- 缓存崩溃后造成的缓存击穿
- 集合重复元素的判别
- 查询加速(比如基于key-value的存储系统,如redis等)
二、什么时候选择布隆过滤器,而不使用其他数据结构
如果想要判断一个元素是不是在一个集合里,一般想到的是将所有元素保存起来,然后通过比较确定。链表,树、哈希表等数据结构都是这种思路(如下图所示)

上面这些数据结构面对数据量特别大的时候显现的缺点:
- 存储容量占比高,考虑到负载因子的存在,通常空间是不能被用满的
- 当数据量特别大时,会占用大量的内存空间。如果存储了类似于URL这样的key,那么内存消费太严重
- 如果使用hashmap,如果已有元素超过了总容量的一半之后,一般就需要考虑扩容了,因为元素多了之后哈希冲突就会增加,退化为链表存储的效率了
下面是两个测试程序,分别测试hashmap和红黑树,当元素特别多时,其查询和占用的内存会非常大
测试map(内部使用红黑树)
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <utility>
#include <iomanip>
#define MAP_ITEMS 100000
using namespace std;
int main()
std::map<std::string, bool> mp;
timeval startTime, endTime;
//1.插入MAP_ITEMS个元素到map中
gettimeofday(&startTime, NULL);
std::string key = "https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285";
for(int i = 0; i < MAP_ITEMS; ++i)
string sub_key = to_string(i);
mp.insert(std::make_pair(key + sub_key, 1));
gettimeofday(&endTime, NULL);
long insert_time = (endTime.tv_sec - startTime.tv_sec)*1000 + (endTime.tv_usec-startTime.tv_usec)/1000;
//2.在map中查找一个元素
gettimeofday(&startTime, NULL);
if( mp.find(key + "10000") == mp.end())
std::cout << "not found!" << std::endl;
gettimeofday(&endTime, NULL);
long find_time = endTime.tv_usec - startTime.tv_usec;
//3.估算当前key的平均大小
double key_size = key.size() + to_string(MAP_ITEMS).size()/2;
//4.打印相关信息
std::cout << "Number of members " << "key size " << "insert time(ms) " << "find time(us) " << std::endl;
std::cout << left << setw(19) << MAP_ITEMS;
std::cout << left << setw(10) << key_size;
std::cout << left << setw(17) << insert_time;
std::cout << left << setw(15) << find_time << std::endl;
代码中的MAP_ITEMS常量代表当前map中存储的元素的个数
当MAP_ITEMS为100000时,结果如下:

当MAP_ITEMS为1000000时,结果如下:

当MAP_ITEMS为10000000时,结果如下:

相关视频推荐
redis、布隆过滤器、分布式一致性hash中hash的妙用
需要C/C++ Linux服务器架构师学习资料加qun812855908获取(资料包括C/C++,Linux,golang技术,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK,ffmpeg等),免费分享
测试unordered_map(内部使用hashmap)
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <utility>
#include <iomanip>
#define MAP_ITEMS 100000
using namespace std;
int main()
unordered_map<string, bool> unordermp;
timeval startTime, endTime;
//1.插入MAP_ITEMS个元素到map中
gettimeofday(&startTime, NULL);
std::string key = "https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285";
for(int i = 0; i < MAP_ITEMS; ++i)
string sub_key = to_string(i);
unordermp.insert(std::make_pair(key + sub_key, 1));
gettimeofday(&endTime, NULL);
long insert_time = (endTime.tv_sec - startTime.tv_sec)*1000 + (endTime.tv_usec-startTime.tv_usec)/1000;
//2.在map中查找一个元素
gettimeofday(&startTime, NULL);
if( unordermp.find(key + "10000") == unordermp.end())
std::cout << "not found!" << std::endl;
gettimeofday(&endTime, NULL);
long find_time = endTime.tv_usec - startTime.tv_usec;
//3.估算当前key的平均大小
double key_size = key.size() + to_string(MAP_ITEMS).size()/2;
//4.打印相关信息
std::cout << "Number of members " << "key size " << "insert time(ms) " << "find time(us) " << std::endl;
std::cout << left << setw(19) << MAP_ITEMS;
std::cout << left << setw(10) << key_size;
std::cout << left << setw(17) << insert_time;
std::cout << left << setw(15) << find_time << std::endl;
代码中的MAP_ITEMS常量代表当前unordered_map中存储的元素的个数
当MAP_ITEMS为100000时,结果如下:

当MAP_ITEMS为1000000时,结果如下:
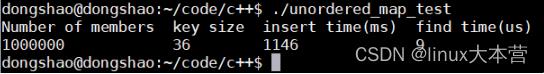
当MAP_ITEMS为10000000时,结果如下:
三、布隆过滤器的数据结构与实现原理
数据结构
布隆过滤器是一个bit向量或者说是一个bit数组(下面的数字为索引)。如下所示:

其最小单位为bit,初始化时全部置为0
添加、查询原理
布隆过滤器添加原理:利用K个Hash函数,将元素传入到这K个Hash函数中,并且映射到bit向量的K个点中,并且将映射到的K个点置为1
布隆过滤器查询原理:
- 利用K个Hash函数,将元素传入到这K个Hash函数中,并且映射到bit向量的K个点中
- 如果这些点中有任何一个为0,则被检测的元素一定不存在
- 如果这些点都返回1,则被检测的元素很可能(因为布隆过滤器存在误差)存在,但是不一定百分百存在
上面添加、查询使用的Hash函数一般都是相同的,实现设计好的
为什么布隆过滤器要使用多个Hash函数?
- Hash面临的问题就是冲突。假设Hash函数是良好的,如果我们的位阵列长度为m个点,那么如果我们想将冲突率降低到例如 1%,这个散列表就只能容纳 m/100个元素
- 解决方法较简单,使用K>1的布隆过滤器,即K个函数将每个元素改为对应于K个bits,因为误判度会降低很多,并且如果参数k和m选取得好,一半的m可被置为1
一个重要的概念:针对于一个特定的哈希函数和一个特定的值,那么该哈希函数返回的值每次都是固定的,不可能出现多次调用之间出现哈希函数返回值不同的情况
演示说明
假设我们的布隆过滤器有三个哈希函数,分别名为hash1、hash2、hash3
①添加元素:针对于“baidu”这个元素,我们调用三个哈希函数,将其映射到bit向量的三个位置(分别为1、4、7),并且将对应的位置置为1

②添加元素:现在针对于“tencent”这个元素,我们也调用三个哈希函数,将其映射到bit向量的三个位置(分别为3、4、8),并且将对应的位置置为1
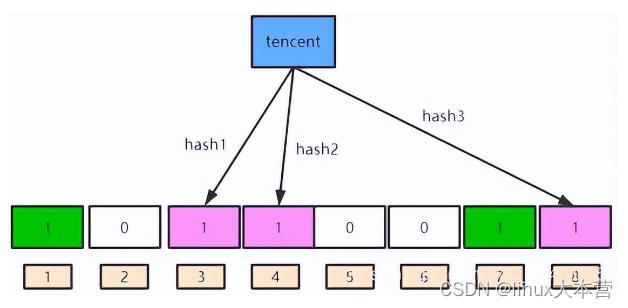
③此时,整个bit向量的1、3、4、7、8这几个位置被置为1了。其中4这个索引被覆盖了,因为“baidu”和“tencent”都将其置为1,覆盖的索引与误判率有关,详情见下面的介绍
④去查询一个不存在的元素,并且确定其肯定不存在:例如现在我们去查询“dongshao”这个元素,假设调用上面的三个哈希函数返回的索引是1、5、8,通过上图我们知道5这个索引处为0,因此“dongshao”这个元素一定不存在,因为如果存在的话,那么5这个位置应该被置为1才对(见上面的“一个重要概念”)
⑤去查询“baidu”这个元素,不能判断其百分百存在:我们将“baidu”传入上面的三个哈希函数中,哈希返回的对应索引值为1、4、7,发现1、4、7这几个索引处都为1,因此我们判断“baidu”这个元素可能存在。为什么不是百分百确定呢?见下面的误判率介绍
误判率
布隆过滤器允许存在一定的误判断,误判率也称为“假阳”
误判率一般是出现在查询的时候
例如上面我们去查询“baidu”的时候,由于“baidu”之前被我们插入过,为什么还不能百分百确定它一定存在呢?
- 因为“tencent”这个元素在插入的时候,将4这个索引置为1了
- 假设我们查询“baidu”的时候实际返回的是1、7索引为1,4索引为0。而4索引又被tencent覆盖为1,所以最终“baidu”最终看到的是1、4、7索引都为1,我们不能百分百确定“baidu”这个元素存在
因此,当随着增加的值越来越多时,bit向量被置为1的数量也就会越来越多,因此误判率会越来越大。例如,当查询“taobao”时,万一所有的哈希函数返回的对应bit都为1,那么布隆过滤器可能也认为“taobao”这个元素存在
布隆过滤器一般不拥有删除的功能
我们一般不能从布隆过滤器中删除元素。考虑下面几种情况:
- 因为要删除该元素,我们必须百分百确保该元素存在于布隆过滤器中,而布隆过滤器由于存在误判率,无法确定该元素百分百存在于布隆过滤器内
- 另外计数器回绕也会造成问题
- 如果我们因为某一个元素而将其对应的bit位删除变为0,那么如果这些bit位也是其他元素正在使用的,那么其他元素在查询时就会返回0,从而认为元素不存在而造成误判
四、误判概率的相关证明和计算
证明①(哈希函数越多、插入元素越少,误判率越低)
假设布隆过滤器中的hash函数满足simple uniform hashing(简单一致散列)假设:每个元素都等概率地hash到m个slot中的任何一个,与其它元素被hash到哪个slot无关
若m为bit数(向量表的长度), 则对某一特定bit位在一个元素由某特定hash函数插入时没有被置位为1的概率为:

则k个hash函数中没有一个对其置位的概率为,随着k的增加,概率会变小:

如果插入了n个元素,但都没有将其置位的概率为:

现在考虑查询阶段,若对应某个待查询元素的k bits全部置位为1,则可判定其在集合中。 因此将某元素误判的概率p为:
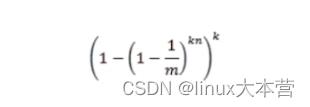
现在考虑查询阶段,若对应某个待query元素的k bits全部置位为1,则可判定其在集合中。 因此将某元素误判的概率p为:

由于

当x→0时,并且

当m很大时趋近于0,所以:

从上式中可以看出,当m增大或n减小时,都会使得误判率减小
证明②(何时误判率最低?)
现在计算对于给定的m和n,k为何值时可以使得误判率最低。设误判率为k的函数为:

下面求最值,即是误差趋近于0

因此,即当
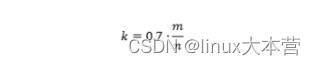
时误判率最低,此时误判率为:
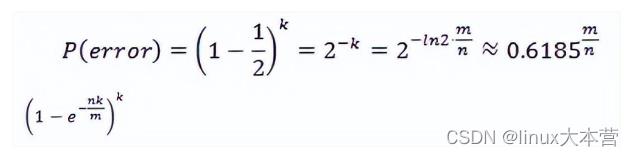
可以看出若要使得误判率≤1/2,则:

这说明了若想保持某固定误判率不变,布隆过滤器的bit数m与被增加的元素数n应该是线性同步增加的
五、Hash函数的选择
常见的应用比较广的hash函数有MD5, SHA1, SHA256,一般用于信息安全方面,比如签名认证和加密等。比如我们传输文件时习惯用对原文件内容计算它的MD5值,生成128 bit的整数,通 常我们说的32位MD5值,是转换为HEX格式后的32个字符
MurmurHash:
- MurmurHash是2008年发明的,相比较MD5, MurMurhash不太安全(当然MD5也被破译了, sha也可以被破译),但是性能是MD5的几十倍
- MurmurHash有很多个版本, MurmurHash3修复了MurmurHash2的一些缺陷同时速度还要快一些,因此很多开源项目有用,比如nginx、 redis、 memcashed、 Hadoop等,比如用于计算一致性hash等
- MurmurHash被比较好的测试过了,测试方法见https://github.com/aappleby/smhasher
- MurMurhash的实现也可以参考smhasher,或者参考https://sites.google.com/site/murmurhash
- 我们演示的布隆过滤器中的hash函数选择MurmurHash2算法
补充:双重散列
双重散列是线性开型寻址散列(开放寻址法)中的冲突解决技术。双重散列使用在发生冲突时将第二个散列函数应用于键的想法
此算法使用下面的公式来进行双哈希处理。hash1() 和 hash2() 是哈希函数,而 TABLE_SIZE 是哈希表的大小。 当发生碰撞时,我们通过重复增加步长i 来寻找键

六、布隆过滤器的实现
布隆过滤器在实现时一般设计考虑下面几样东西:
- n:布隆过滤器最大处理的元素的个数
- P:希望的误差率
- m:布隆过滤器的bit位数目
- k:哈希函数的个数
应用时首先要先由用户决定要增加的最多元素个数n和希望的误差率P。这也是一个设计完整的布隆过滤器需要用户输入的仅有的两个参数(加入hash种子则为3个),之后的所有参数将由系统计算,并由此建立布隆过滤器
①首先根据传入的n和p计算需要的内存大小m bits:

②再由m,n得到hash function的个数:
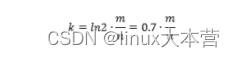
至此系统所需的参数已经备齐,后面就可以添加n个元素到布隆过滤器中,进行查询
布隆过滤器空间利用率问题
根据公式,当k最优时:

因此可验证当P=1%时,存储每个元素需要9.6 bits:
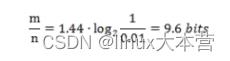
而每当想将误判率降低为原来的1/10,则存储每个元素需要增加4.8 bits:

布隆过滤器误判率对比表
如果方便知道需要使用多少位才能降低错误概率,可以从下表所示的存储项目和位数 比率估计布隆过滤器的误判率

为每个URL分配两个字节就可以达到千分之几的冲突。比较保守的实现是,为每个URL 分配4个字节,项目和位数比是1∶32,误判率是0.00000021167340。对于5000万数量级的URL,布隆过滤器只占用200MB的空间
七、在线验证公式
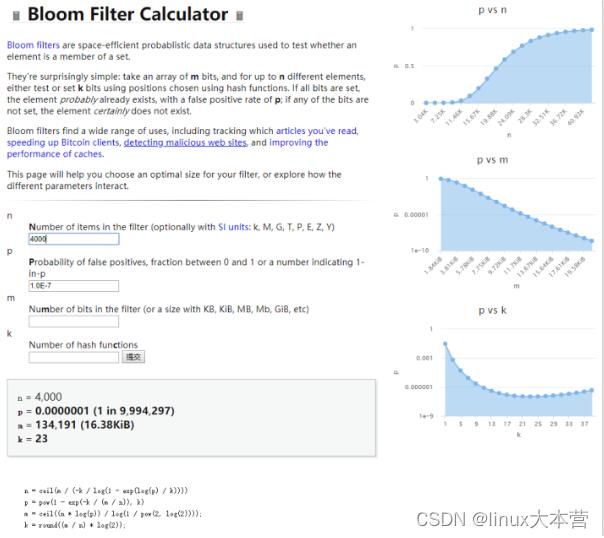
测试网址:
https://hur.st/bloomfilter/
下面是一个测试网址,可以根据你输入的数值返回对应的数据:
- n:布隆过滤器最大处理的元素的个数
- P:希望的误差率
- m:布隆过滤器的bit位数目
- k:哈希函数的个数
八、编码实现
bloomfilter.h
这个代码是布隆过滤器的实现代码
#ifndef __MICRO_BLOOMFILTER_H__
#define __MICRO_BLOOMFILTER_H__
/**
*
* 仿照Cassandra中的BloomFilter实现,Hash选用MurmurHash2,通过双重散列公式生成散列函数,参考:http://hur.st/bloomfilter
* Hash(key, i) = (H1(key) + i * H2(key)) % m
*
**/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#define __BLOOMFILTER_VERSION__ "1.1"
#define __MGAIC_CODE__ (0x01464C42)
/**
* BloomFilter使用例子:
* static BaseBloomFilter stBloomFilter = 0;
*
* 初始化BloomFilter(最大100000元素,不超过0.00001的错误率):
* InitBloomFilter(&stBloomFilter, 0, 100000, 0.00001);
* 重置BloomFilter:
* ResetBloomFilter(&stBloomFilter);
* 释放BloomFilter:
* FreeBloomFilter(&stBloomFilter);
*
* 向BloomFilter中新增一个数值(0-正常,1-加入数值过多):
* uint32_t dwValue;
* iRet = BloomFilter_Add(&stBloomFilter, &dwValue, sizeof(uint32_t));
* 检查数值是否在BloomFilter内(0-存在,1-不存在):
* iRet = BloomFilter_Check(&stBloomFilter, &dwValue, sizeof(uint32_t));
*
* (1.1新增) 将生成好的BloomFilter写入文件:
* iRet = SaveBloomFilterToFile(&stBloomFilter, "dump.bin")
* (1.1新增) 从文件读取生成好的BloomFilter:
* iRet = LoadBloomFilterFromFile(&stBloomFilter, "dump.bin")
**/
// 注意,要让Add/Check函数内联,必须使用 -O2 或以上的优化等级
#define FORCE_INLINE __attribute__((always_inline))
#define BYTE_BITS (8)
#define MIX_UINT64(v) ((uint32_t)((v>>32)^(v)))
#define SETBIT(filter, n) (filter->pstFilter[n/BYTE_BITS] |= (1 << (n%BYTE_BITS)))
#define GETBIT(filter, n) (filter->pstFilter[n/BYTE_BITS] & (1 << (n%BYTE_BITS)))
#pragma pack(1)
// BloomFilter结构定义
typedef struct
uint8_t cInitFlag; // 初始化标志,为0时的第一次Add()会对stFilter[]做初始化
uint8_t cResv[3];
uint32_t dwMaxItems; // n - BloomFilter中最大元素个数 (输入量)
double dProbFalse; // p - 假阳概率(误判率) (输入量,比如万分之一:0.00001)
uint32_t dwFilterBits; // m = ; - BloomFilter的比特数
uint32_t dwHashFuncs; // k = round(log(2.0) * m / n); - 哈希函数个数
uint32_t dwSeed; // MurmurHash的种子偏移量
uint32_t dwCount; // Add()的计数,超过MAX_BLOOMFILTER_N则返回失败
uint32_t dwFilterSize; // dwFilterBits / BYTE_BITS
unsigned char *pstFilter; // BloomFilter存储指针,使用malloc分配
uint32_t *pdwHashPos; // 存储上次hash得到的K个bit位置数组(由bloom_hash填充)
BaseBloomFilter;
// BloomFilter文件头部定义
typedef struct
uint32_t dwMagicCode; // 文件头部标识,填充 __MGAIC_CODE__
uint32_t dwSeed;
uint32_t dwCount;
uint32_t dwMaxItems; // n - BloomFilter中最大元素个数 (输入量)
double dProbFalse; // p - 假阳概率 (输入量,比如万分之一:0.00001)
uint32_t dwFilterBits; // m = ceil((n * log(p)) / log(1.0 / (pow(2.0, log(2.0))))); - BloomFilter的比特数
uint32_t dwHashFuncs; // k = round(log(2.0) * m / n); - 哈希函数个数
uint32_t dwResv[6];
uint32_t dwFileCrc; // (未使用)整个文件的校验和
uint32_t dwFilterSize; // 后面Filter的Buffer长度
BloomFileHead;
#pragma pack()
// 计算BloomFilter的参数m,k
static inline void _CalcBloomFilterParam(uint32_t n, double p, uint32_t *pm, uint32_t *pk)
/**
* n - Number of items in the filter
* p - Probability of false positives, float between 0 and 1 or a number indicating 1-in-p
* m - Number of bits in the filter
* k - Number of hash functions
*
* f = ln(2) × ln(1/2) × m / n = (0.6185) ^ (m/n)
* m = -1 * ln(p) × n / 0.6185 , 这里有错误
* k = ln(2) × m / n = 0.6931 * m / n
* darren修正:
* m = -1*n*ln(p)/((ln(2))^2) = -1*n*ln(p)/(ln(2)*ln(2)) = -1*n*ln(p)/(0.69314718055995*0.69314718055995))
* = -1*n*ln(p)/0.4804530139182079271955440025
* k = ln(2)*m/n
**/
uint32_t m, k, m2;
// printf("ln(2):%lf, ln(p):%lf\\n", log(2), log(p)); // 用来验证函数正确性
// 计算指定假阳(误差)概率下需要的比特数
m =(uint32_t) ceil(-1.0 * n * log(p) / 0.480453); //darren 修正
//m2 =(uint32_t) ceil(-1 * n * log(p) / 0.480453); //错误写法
m = (m - m % 64) + 64; // 8字节对齐
// 计算哈希函数个数
double double_k = (0.69314 * m / n); // ln(2)*m/n // 这里只是为了debug出来看看具体的浮点数值
k = round(double_k); // 返回x的四舍五入整数值。
printf("orig_k:%lf, k:%u\\n", double_k, k);
*pm = m;
*pk = k;
return;
// 根据目标精度和数据个数,初始化BloomFilter结构
/**
* @brief 初始化布隆过滤器
* @param pstBloomfilter 布隆过滤器实例
* @param dwSeed hash种子
* @param dwMaxItems 存储容量
* @param dProbFalse 允许的误判率
* @return 返回值
* -1 传入的布隆过滤器为空
* -2 hash种子错误或误差>=1
*/
inline int InitBloomFilter(BaseBloomFilter *pstBloomfilter,
uint32_t dwSeed,
uint32_t dwMaxItems, double dProbFalse)
if (pstBloomfilter == NULL)
return -1;
if ((dProbFalse <= 0) || (dProbFalse >= 1))
return -2;
// 先检查是否重复Init,释放内存
if (pstBloomfilter->pstFilter != NULL)
free(pstBloomfilter->pstFilter);
if (pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos != NULL)
free(pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos);
memset(pstBloomfilter, 0, sizeof(BaseBloomFilter));
// 初始化内存结构,并计算BloomFilter需要的空间
pstBloomfilter->dwMaxItems = dwMaxItems; // 最大存储
pstBloomfilter->dProbFalse = dProbFalse; // 误差
pstBloomfilter->dwSeed = dwSeed; // hash种子
// 计算 m, k
_CalcBloomFilterParam(pstBloomfilter->dwMaxItems, pstBloomfilter->dProbFalse,
&pstBloomfilter->dwFilterBits, &pstBloomfilter->dwHashFuncs);
// 分配BloomFilter的存储空间
pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize = pstBloomfilter->dwFilterBits / BYTE_BITS;
pstBloomfilter->pstFilter = (unsigned char *) malloc(pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize);
if (NULL == pstBloomfilter->pstFilter)
return -100;
// 哈希结果数组,每个哈希函数一个
pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos = (uint32_t*) malloc(pstBloomfilter->dwHashFuncs * sizeof(uint32_t));
if (NULL == pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos)
return -200;
printf(">>> Init BloomFilter(n=%u, p=%e, m=%u, k=%d), malloc() size=%.6fMB, items:bits=1:%0.1lf\\n",
pstBloomfilter->dwMaxItems, pstBloomfilter->dProbFalse, pstBloomfilter->dwFilterBits,
pstBloomfilter->dwHashFuncs, (double)pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize/1024/1024,
pstBloomfilter->dwFilterBits*1.0/pstBloomfilter->dwMaxItems);
// 初始化BloomFilter的内存
memset(pstBloomfilter->pstFilter, 0, pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize);
pstBloomfilter->cInitFlag = 1;
return 0;
// 释放BloomFilter
inline int FreeBloomFilter(BaseBloomFilter *pstBloomfilter)
if (pstBloomfilter == NULL)
return -1;
pstBloomfilter->cInitFlag = 0;
pstBloomfilter->dwCount = 0;
free(pstBloomfilter->pstFilter);
pstBloomfilter->pstFilter = NULL;
free(pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos);
pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos = NULL;
return 0;
// 重置BloomFilter
// 注意: Reset()函数不会立即初始化stFilter,而是当一次Add()时去memset
inline int ResetBloomFilter(BaseBloomFilter *pstBloomfilter)
if (pstBloomfilter == NULL)
return -1;
pstBloomfilter->cInitFlag = 0;
pstBloomfilter->dwCount = 0;
return 0;
// 和ResetBloomFilter不同,调用后立即memset内存
inline int RealResetBloomFilter(BaseBloomFilter *pstBloomfilter)
if (pstBloomfilter == NULL)
return -1;
memset(pstBloomfilter->pstFilter, 0, pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize);
pstBloomfilter->cInitFlag = 1;
pstBloomfilter->dwCount = 0;
return 0;
///
/// 函数FORCE_INLINE,加速执行
///
// MurmurHash2, 64-bit versions, by Austin Appleby
// https://sites.google.com/site/murmurhash/
FORCE_INLINE uint64_t MurmurHash2_x64 ( const void * key, int len, uint32_t seed )
const uint64_t m = 0xc6a4a7935bd1e995;
const int r = 47;
uint64_t h = seed ^ (len * m);
const uint64_t * data = (const uint64_t *)key;
const uint64_t * end = data + (len/8);
while(data != end)
uint64_t k = *data++;
k *= m;
k ^= k >> r;
k *= m;
h ^= k;
h *= m;
const uint8_t * data2 = (const uint8_t*)data;
switch(len & 7)
case 7: h ^= ((uint64_t)data2[6]) << 48;
case 6: h ^= ((uint64_t)data2[5]) << 40;
case 5: h ^= ((uint64_t)data2[4]) << 32;
case 4: h ^= ((uint64_t)data2[3]) << 24;
case 3: h ^= ((uint64_t)data2[2]) << 16;
case 2: h ^= ((uint64_t)data2[1]) << 8;
case 1: h ^= ((uint64_t)data2[0]);
h *= m;
;
h ^= h >> r;
h *= m;
h ^= h >> r;
return h;
// 双重散列封装,k个函数函数, 比如要20个
FORCE_INLINE void bloom_hash(BaseBloomFilter *pstBloomfilter, const void * key, int len)
//if (pstBloomfilter == NULL) return;
int i;
uint32_t dwFilterBits = pstBloomfilter->dwFilterBits;
uint64_t hash1 = MurmurHash2_x64(key, len, pstBloomfilter->dwSeed);
uint64_t hash2 = MurmurHash2_x64(key, len, MIX_UINT64(hash1));
for (i = 0; i < (int)pstBloomfilter->dwHashFuncs; i++)
// k0 = (hash1 + 0*hash2) % dwFilterBits; // dwFilterBits bit向量的长度
// k1 = (hash1 + 1*hash2) % dwFilterBits;
pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos[i] = (hash1 + i*hash2) % dwFilterBits;
return;
// 向BloomFilter中新增一个元素
// 成功返回0,当添加数据超过限制值时返回1提示用户
FORCE_INLINE int BloomFilter_Add(BaseBloomFilter *pstBloomfilter, const void * key, int len)
if ((pstBloomfilter == NULL) || (key == NULL) || (len <= 0))
return -1;
int i;
if (pstBloomfilter->cInitFlag != 1)
// Reset后没有初始化,使用前需要memset
memset(pstBloomfilter->pstFilter, 0, pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize);
pstBloomfilter->cInitFlag = 1;
// hash key到bloomfilter中, 为了计算不同hash命中的位置,保存pdwHashPos数组
bloom_hash(pstBloomfilter, key, len);
for (i = 0; i < (int)pstBloomfilter->dwHashFuncs; i++)
// dwHashFuncs[0] = hash0(key)
// dwHashFuncs[1] = hash1(key)
// dwHashFuncs[k-1] = hashk-1(key)
SETBIT(pstBloomfilter, pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos[i]);
// 增加count数
pstBloomfilter->dwCount++;
if (pstBloomfilter->dwCount <= pstBloomfilter->dwMaxItems)
return 0;
else
return 1; // 超过N最大值,可能出现准确率下降等情况
// 检查一个元素是否在bloomfilter中
// 返回:0-存在,1-不存在,负数表示失败
FORCE_INLINE int BloomFilter_Check(BaseBloomFilter *pstBloomfilter, const void * key, int len)
if ((pstBloomfilter == NULL) || (key == NULL) || (len <= 0))
return -1;
int i;
bloom_hash(pstBloomfilter, key, len);
for (i = 0; i < (int)pstBloomfilter->dwHashFuncs; i++)
// 如果有任意bit不为1,说明key不在bloomfilter中
// 注意: GETBIT()返回不是0|1,高位可能出现128之类的情况
if (GETBIT(pstBloomfilter, pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos[i]) == 0)
return 1;
return 0;
/* 文件相关封装 */
// 将生成好的BloomFilter写入文件
inline int SaveBloomFilterToFile(BaseBloomFilter *pstBloomfilter, char *szFileName)
if ((pstBloomfilter == NULL) || (szFileName == NULL))
return -1;
int iRet;
FILE *pFile;
static BloomFileHead stFileHeader = 0;
pFile = fopen(szFileName, "wb");
if (pFile == NULL)
perror("fopen");
return -11;
// 先写入文件头
stFileHeader.dwMagicCode = __MGAIC_CODE__;
stFileHeader.dwSeed = pstBloomfilter->dwSeed;
stFileHeader.dwCount = pstBloomfilter->dwCount;
stFileHeader.dwMaxItems = pstBloomfilter->dwMaxItems;
stFileHeader.dProbFalse = pstBloomfilter->dProbFalse;
stFileHeader.dwFilterBits = pstBloomfilter->dwFilterBits;
stFileHeader.dwHashFuncs = pstBloomfilter->dwHashFuncs;
stFileHeader.dwFilterSize = pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize;
iRet = fwrite((const void*)&stFileHeader, sizeof(stFileHeader), 1, pFile);
if (iRet != 1)
perror("fwrite(head)");
return -21;
// 接着写入BloomFilter的内容
iRet = fwrite(pstBloomfilter->pstFilter, 1, pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize, pFile);
if ((uint32_t)iRet != pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize)
perror("fwrite(data)");
return -31;
fclose(pFile);
return 0;
// 从文件读取生成好的BloomFilter
inline int LoadBloomFilterFromFile(BaseBloomFilter *pstBloomfilter, char *szFileName)
if ((pstBloomfilter == NULL) || (szFileName == NULL))
return -1;
int iRet;
FILE *pFile;
static BloomFileHead stFileHeader = 0;
if (pstBloomfilter->pstFilter != NULL)
free(pstBloomfilter->pstFilter);
if (pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos != NULL)
free(pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos);
//
pFile = fopen(szFileName, "rb");
if (pFile == NULL)
perror("fopen");
return -11;
// 读取并检查文件头
iRet = fread((void*)&stFileHeader, sizeof(stFileHeader), 1, pFile);
if (iRet != 1)
perror("fread(head)");
return -21;
if ((stFileHeader.dwMagicCode != __MGAIC_CODE__)
|| (stFileHeader.dwFilterBits != stFileHeader.dwFilterSize*BYTE_BITS))
return -50;
// 初始化传入的 BaseBloomFilter 结构
pstBloomfilter->dwMaxItems = stFileHeader.dwMaxItems;
pstBloomfilter->dProbFalse = stFileHeader.dProbFalse;
pstBloomfilter->dwFilterBits = stFileHeader.dwFilterBits;
pstBloomfilter->dwHashFuncs = stFileHeader.dwHashFuncs;
pstBloomfilter->dwSeed = stFileHeader.dwSeed;
pstBloomfilter->dwCount = stFileHeader.dwCount;
pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize = stFileHeader.dwFilterSize;
pstBloomfilter->pstFilter = (unsigned char *) malloc(pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize);
if (NULL == pstBloomfilter->pstFilter)
return -100;
pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos = (uint32_t*) malloc(pstBloomfilter->dwHashFuncs * sizeof(uint32_t));
if (NULL == pstBloomfilter->pdwHashPos)
return -200;
// 将后面的Data部分读入 pstFilter
iRet = fread((void*)(pstBloomfilter->pstFilter), 1, pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize, pFile);
if ((uint32_t)iRet != pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize)
perror("fread(data)");
return -31;
pstBloomfilter->cInitFlag = 1;
printf(">>> Load BloomFilter(n=%u, p=%f, m=%u, k=%d), malloc() size=%.2fMB\\n",
pstBloomfilter->dwMaxItems, pstBloomfilter->dProbFalse, pstBloomfilter->dwFilterBits,
pstBloomfilter->dwHashFuncs, (double)pstBloomfilter->dwFilterSize/1024/1024);
fclose(pFile);
return 0;
#endifbloomfilter.cpp
这个是布隆过滤器的测试代码
#include "bloomfilter.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_ITEMS 6000000 // 设置最大元素个数
#define ADD_ITEMS 1000 // 添加测试元素
#define P_ERROR 0.0001// 设置误差
//
int main(int argc, char** argv)
printf(" test bloomfilter\\n");
// 1. 定义BaseBloomFilter
static BaseBloomFilter stBloomFilter = 0;
// 2. 初始化stBloomFilter,调用时传入hash种子,存储容量,以及允许的误判率
InitBloomFilter(&stBloomFilter, 0, MAX_ITEMS, P_ERROR);
// 3. 向BloomFilter中新增数值
char url[128] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < ADD_ITEMS; i++)
sprintf(url, "https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285/%d.html", i);
if(0 == BloomFilter_Add(&stBloomFilter, (const void*)url, strlen(url)))
// printf("add %s success", url);
else
printf("add %s failed", url);
memset(url, 0, sizeof(url));
// 4. check url exist or not
char* str = "https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285/0.html";
if (0 == BloomFilter_Check(&stBloomFilter, (const void*)str, strlen(str)) )
printf("https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285/0.html exist\\n");
char* str2 = "https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285/10001.html";
if (0 != BloomFilter_Check(&stBloomFilter, (const void*)str2, strlen(str2)) )
printf("https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285/10001.html not exist\\n");
// 5. free bloomfilter
FreeBloomFilter(&stBloomFilter);
getchar();
return 0;
结果图下图所示:
- n:布隆过滤器最大处理的元素的个数
- P:希望的误差率
- m:布隆过滤器的bit位数目
- k:哈希函数的个数


以上是关于C++数据结构与算法:布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)原理与实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
数据结构与算法:Bloom Filter(布隆过滤器)解决大数据查重问题
C++拾取——Linux下实测布隆过滤器(Bloom filter)和unordered_multiset查询效率