Java数据结构与算法——哈希表
Posted 张起灵-小哥
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java数据结构与算法——哈希表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.关于哈希表
散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
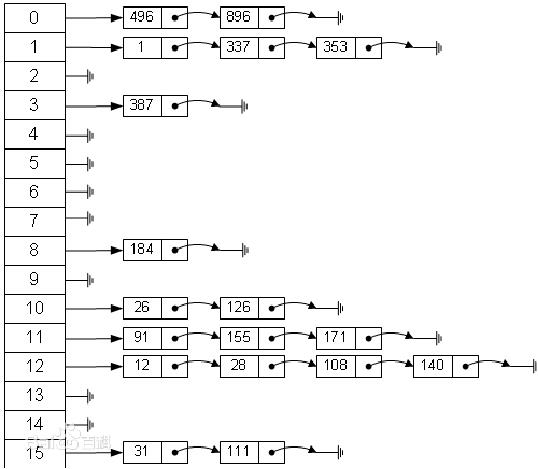
2.代码案例
有一个公司,当有新的员工来报道时,要求将该员工的信息加入 (id,性别,年龄,名字,住址..),当输入该员工的id时,要求查找到该员工的 所有信息。
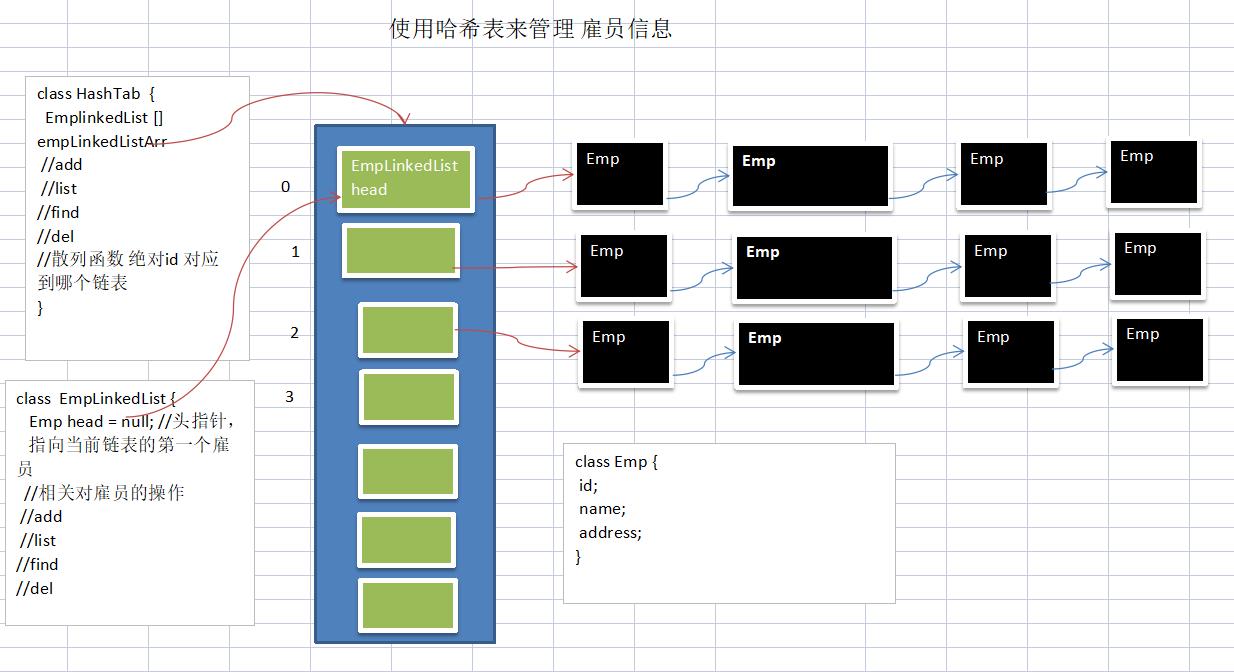
package com.szh.hashtab;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 哈希表
*/
//雇员类
class Employee
public int id;
public String name;
public Employee next;
public Employee(int id, String name)
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
//创建EmpLinkedList, 表示链表
class EmployeeLinkedList
//头指针,指向第一个Emp。因此我们这个链表的head 是直接指向第一个Emp
private Employee head; //默认为null
//添加雇员到链表
//假定,当添加雇员时,id 是自增长,即id的分配总是从小到大,因此我们将该雇员直接加入到本链表的最后即可
public void add(Employee employee)
//如果添加的是第一个雇员
if (head == null)
head = employee;
return;
//如果不是第一个雇员,则使用一个辅助的指针,帮助定位到最后
Employee curEmp = head;
while (true)
if (curEmp.next == null) //此时说明已经到了链表的最后
break;
curEmp = curEmp.next;
//最后将要添加的雇员放在链表的最后
curEmp.next = employee;
//根据传入的no,确定要遍历哪条链表的雇员信息
public void list(int no)
if (head == null) //说明链表为空
System.out.println("第 " + (no + 1) + " 链表为空....");
return;
System.out.print("第 " + (no + 1) + " 链表的信息为: ");
Employee curEmp = head; //辅助指针
while (true)
System.out.printf(" => id = %d, name = %s\\t", curEmp.id, curEmp.name);
if (curEmp.next == null) //说明curEmp已经是最后节点
break;
curEmp = curEmp.next; //后移,遍历
System.out.println();
//根据id查找雇员
//如果查找到,就返回Emp, 如果没有找到,就返回null
public Employee findEmployeeById(int id)
//判断链表是否为空
if (head == null)
System.out.println("链表为空....");
return null;
//辅助指针
Employee curEmp = head;
while (true)
if (curEmp.id == id) //找到了,此时curEmp就是要查找的雇员信息
break;
if (curEmp.next == null) //说明遍历当前链表没有找到该雇员
curEmp = null; //没找到则将curEmp置为null
break;
curEmp = curEmp.next; //向后移动
return curEmp;
//创建HashTab,使用哈希表来管理多条链表
class HashTab
private EmployeeLinkedList[] employeeLinkedLists;
private int size; //表示共有多少条链表
public HashTab(int size)
this.size = size;
employeeLinkedLists = new EmployeeLinkedList[size];
//这里需要分别初始化每条链表
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
employeeLinkedLists[i] = new EmployeeLinkedList();
//添加雇员
public void add(Employee employee)
//根据员工的id,得到该员工应当添加到哪条链表
int empLinkedListNo = hashFun(employee.id);
//将emp添加到对应的链表中
employeeLinkedLists[empLinkedListNo].add(employee);
//遍历所有的链表,即遍历哈希表
public void list()
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
employeeLinkedLists[i].list(i);
//根据输入的id,查找雇员
public void findEmployeeById(int id)
//使用散列函数确定到哪条链表查找
int empLinkedListNo = hashFun(id);
Employee employee = employeeLinkedLists[empLinkedListNo].findEmployeeById(id);
if (Objects.nonNull(employee)) //找到
System.out.printf("在第 %d 条链表中找到 雇员 id = %d\\n", (empLinkedListNo + 1), id);
else //未找到
System.out.println("在哈希表中,没有找到该雇员~");
//编写散列函数, 使用一个简单取模法
public int hashFun(int id)
return id % size;
public class HashTabDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
//创建哈希表
HashTab hashTab = new HashTab(7);
String key = "";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true)
System.out.println("add: 添加雇员");
System.out.println("list: 显示雇员");
System.out.println("find: 查找雇员");
System.out.println("exit: 退出系统");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key)
case "add":
System.out.println("输入id: ");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入名字: ");
String name = scanner.next();
Employee employee = new Employee(id, name);
hashTab.add(employee);
break;
case "list":
hashTab.list();
break;
case "find":
System.out.println("请输入要查找的id: ");
id = scanner.nextInt();
hashTab.findEmployeeById(id);
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
System.exit(0);
default:
break;
代码中的注释已经写的很清楚了,我就不再多说了,下面是测试相关截图。
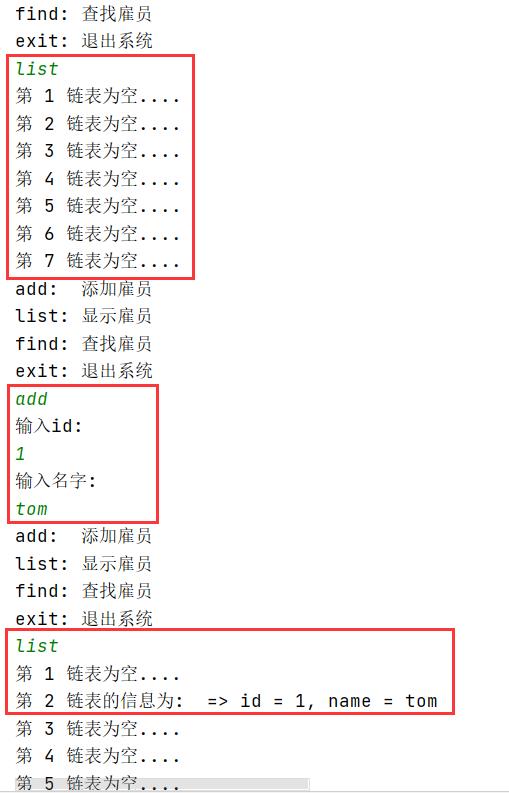



以上是关于Java数据结构与算法——哈希表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章