动态高优先权优先调度算法
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了动态高优先权优先调度算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、 实验要求1. 用户输入进程名、优先权、服务时间2. 显示初始作业队列3. 每次调度前后显示作业队列要代码和截图!!!!!!!!!!!!!!急急急
动态高优先权优先调度算法:
动态优先权是指,在创建进程时所赋予的优先权,是可以随进程的推进或随其等待时间的增加而改变的,以便获得更好的调度性能。例如,我们可以规定,在就绪队列中的进程,随其等待时间的增长,其优先权以速率a提高。若所有的进程都具有相同的优先权初值,则显然是最先进入就绪队列的进程,将因其动态优先权变得最高而优先获得处理机,此即FCFS算法。若所有的就绪进程具有各不相同的优先权初值,那么,对于优先权初值低的进程,在等待了足够的时间后,其优先权便可能升为最高,从而可以获得处理机。当采用抢占式优先权调度算法时,如果再规定当前进程的优先权以速率b下降,则可防止一个长作业长期地垄断处理机。
算法代码模拟实现:
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>
#define N 6
// 待插入就绪队列的进程数据
int id[N] = 0, 1,
2, 3, 4,
5 ;
int priority[N] = 9, 38, 17,
2, 7, 18 ;
int cpuTime[N] = 0,
0, 0, 0,
0, 0 ;
int allTime[N] = 3,
2, 3, 6,
1, 3 ;
//********************************
//
// 模拟进程/PCB数据结构
//
//********************************
//
枚举进程的状态:就绪、执行、阻塞、完成
enum STATE Ready, Run, Block, Finish
;
// 建立PCB结构体
struct PCB
int id; // 标志数
int priority; // 优先数
int cpuTime; //
已占CPU时间
int allTime; //
还需占CPU时间
int blockTime; // 已被阻塞的时间
STATE state; //
进程状态
PCB *pre; //
PCB的前指针
PCB *nxt; //
PCB的后指针
;
//********************************
//
// 模拟进程队列
//
//********************************
// 进程入列
void queQush(PCB *process, PCB
*queHead)
process->pre = NULL;
process->nxt =
queHead->nxt;
if(queHead->nxt != NULL)
// 非第一个入列
queHead->nxt->pre =
process;
queHead->nxt = process;
// 进程出列
void quePop(PCB *process, PCB
*queHead)
if(process->pre != NULL)
// 不是头节点
process->pre->nxt =
process->nxt;
else
queHead->nxt =
process->nxt;
if(process->nxt != NULL)
// 不是尾节点
process->nxt->pre =
process->pre;
//
清空进程指针
process->pre = process->nxt =
NULL;
// 查看队列里进程的信息
void queWalk(PCB *queHead)
PCB *pro = queHead->nxt;
if(pro == NULL)
printf("(无进程)\\n");
return;
while(pro != NULL)
printf("id:%d,
pri:%d, alltime:%d\\n",
pro->id,
pro->priority,
pro->allTime);
pro =
pro->nxt;
//********************************
//
// 模拟就绪队列
//
//********************************
int readyQueNum; // 就绪队列的进程数量
PCB readyQueHead; //
就绪队列的头部
PCB *readyMaxProcess; // 就绪队列中优先级最高的进程
// 进程插入到就绪队列
void readyQueQush(PCB
*process)
readyQueNum ++;
process->state = Ready;
queQush(process, &readyQueHead);
// 优先级最高的进程出列
PCB* readyQuePop()
readyQueNum --;
quePop(readyMaxProcess,
&readyQueHead);
return readyMaxProcess;
// 每个时间片,更新就绪队列里进程的信息
void readyQueUpdate()
int maxPriority = -1;
PCB *pro = readyQueHead.nxt;
if(pro == NULL)
// 就绪队列没有进程
readyMaxProcess =
NULL;
return;
while(pro != NULL)
pro->priority
++;
if(pro->priority > maxPriority)
maxPriority =
pro->priority;
readyMaxProcess = pro;
pro =
pro->nxt;
// 返回就绪队列最高优先级的值
int readyMaxPriority()
return readyMaxProcess->priority;
// 查看就绪队列里进程的信息
void readyQueWalk()
printf("就绪队列里的进程信息为:\\n");
queWalk(&readyQueHead);
//********************************
//
// 模拟阻塞队列
//
//********************************
#define EndBlockTime 3
// 进程最长被阻塞时间
int blockQueNum; // 阻塞队列的进程数量
PCB blockQueHead; //
阻塞队列的头部
PCB *blockMaxProcess; // 阻塞队列中优先级最高的进程
// 进程插入到阻塞队列
void blockQueQush(PCB
*process)
blockQueNum ++;
process->blockTime = 0;
process->state = Block;
queQush(process, &blockQueHead);
// 优先级最高的进程出列
PCB* blockQuePop()
blockQueNum --;
quePop(blockMaxProcess,
&blockQueHead);
return blockMaxProcess;
// 每个时间片,更新阻塞队列里进程的信息
void blockQueUpdate()
int maxPriority = -1;
PCB *pro = blockQueHead.nxt;
while(pro != NULL)
pro->blockTime
++;
if(pro->blockTime >= EndBlockTime)
PCB *process = pro;
pro = pro->nxt;
// 阻塞时间到,调入就绪队列
blockQueNum --;
quePop(process,
&blockQueHead);
readyQueQush(process);
else
if(pro->priority > maxPriority)
// 更新阻塞队列里优先级最高的进程指针
maxPriority =
pro->priority;
blockMaxProcess = pro;
pro = pro->nxt;
// 查看阻塞队列里进程的信息
void blockQueWalk()
printf("阻塞队列里的进程信息为:\\n");
queWalk(&blockQueHead);
//********************************
//
// 模拟动态优先权的进程调度
//
//********************************
// 初始化数据
void initData()
//
初始化就绪队列和阻塞队列
readyQueNum = blockQueNum = 0;
readyMaxProcess = blockMaxProcess = NULL;
readyQueHead.pre = readyQueHead.nxt = NULL;
blockQueHead.pre = blockQueHead.nxt = NULL;
//
初始化进程进入就绪队列
int i, maxPriority = -1;
for(i = 0; i < N; i
++)
// 分配一个PCB的内存空间
PCB *pro = (PCB
*)malloc(sizeof(PCB));
// 给当前的PCB赋值
pro->id
= id[i];
pro->priority
= priority[i];
pro->cpuTime
= cpuTime[i];
pro->allTime
= allTime[i];
pro->blockTime
= 0;
if(pro->allTime > 0)
// 插入到就绪队列中
readyQueQush(pro);
// 更新就绪队列优先级最高的进程指针
if(pro->priority >
maxPriority)
maxPriority = pro->priority;
readyMaxProcess = pro;
// 模拟cpu执行1个时间片的操作
void cpuWord(PCB
*cpuProcess)
cpuProcess->priority -= 3;
if(cpuProcess->priority < 0)
cpuProcess->priority = 0;
cpuProcess->cpuTime ++;
cpuProcess->allTime --;
//
显示正执行进程的信息:
printf("CPU正执行的进程信息为:\\n");
printf("id:M, pri:M,
alltime:M\\n",
cpuProcess->id,
cpuProcess->priority,
cpuProcess->allTime);
int main()
int timeSlice = 0; //
模拟时间片
int cpuBusy = 0;
// 模拟cpu状态
PCB *cpuProcess = NULL; // 当前在cpu执行的进程
//
初始化数据
initData();
//
模拟进程调度
while(1)
if(readyQueNum == 0
&& blockQueNum == 0
&& cpuBusy == 0)
// 就绪队列、阻塞队列和cpu无进程,退出
break;
//printf("\\n%d %d",
readyQueNum, blockQueNum);
if(cpuBusy == 0)
// cpu空闲,选择一个进程进入cpu
if(readyQueNum > 0)
//
选择绪队列优先级最高的进程
cpuProcess
= readyQuePop();
else
//
就绪队列没有进程,改为选择阻塞队列优先级最高的进程
cpuProcess
= blockQuePop();
cpuProcess->cpuTime =
0;
cpuProcess->state =
Run;
cpuBusy = 1;
timeSlice ++;
printf("\\n第%d个时间片后:\\n",
timeSlice);
//
模拟cpu执行1个时间片的操作
cpuWord(cpuProcess);
if(cpuProcess->allTime == 0)
cpuProcess->state =
Finish;
// 释放已完成进程的PCB
free(cpuProcess);
cpuBusy = 0;
//
更新就绪队列和阻塞队列里的进程信息
blockQueUpdate();
readyQueUpdate();
//
查看就绪队列和阻塞队列的进程信息
readyQueWalk();
blockQueWalk();
if(cpuBusy == 1
&& readyQueNum >0
&&
cpuProcess->priority
< readyMaxPriority())
// 需抢占cpu,当前执行的进程调入阻塞队列
blockQueQush(cpuProcess);
cpuProcess = readyQuePop();
printf("\\n模拟进程调度算法结束\\n");
return 0;
参考技术A 在百度文库里有样例的
http://wenku.baidu.com/view/1aee3f5e3b3567ec102d8aa2.html
参考资料:http://wenku.baidu.com/view/1aee3f5e3b3567ec102d8aa2.html
操作系统综合实验——动态高优先权优先进程调度算法
导读
PS:最近有很多小伙伴问我怎么准备算法竞赛和面试的问题,还有一些刚入门的新同学不知道怎么学习编程,肥学给大家准备了一些专栏有兴趣的可以去看看哦!
📣小白练手专栏,适合刚入手的新人欢迎订阅编程小白进阶
📣python有趣练手项目里面包括了像《机器人尬聊》《恶搞程序》这样的有趣文章,可以让你快乐学python练手项目专栏
📣另外想学JavaWeb进厂的同学可以看看这个专栏:传送们
📣这是个面试和考研的算法练习我们一起加油上岸之路
好了今天我们给大家准备了操纵系统的期末综合实验大家可以参考参考哦!
一、实验目的
通过对进程调度算法的模拟,进一步理解进程的基本概念,加深对进程运行状态和进程调度过程、调度算法的理解。
二、设备与环境
- 硬件设备:PC机一台
- 软件环境:安装Windows操作系统,并安装相关的程序开发环境,如C \\C++\\Java 等编程语言环境。
三、实验内容
实验采用了java语言编程模拟N个进程采用动态高优先权优先进程调度算法。该算法就是按照优先权的大小运行进程,如果一个时间片内未运行完,则将优先权数减3后再插入到链表中按priority的顺序进行排序找到最大的priority作为下一个运行进程且在就绪队列里面的进程priority会加1。
主模块:
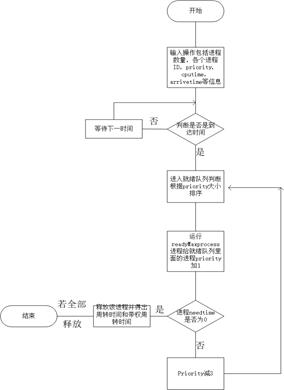
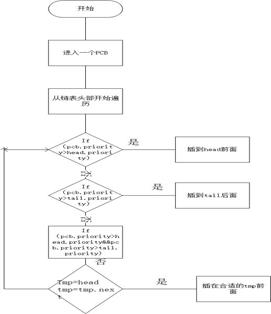
动态priority排序模块:
用来保证头部永远最大
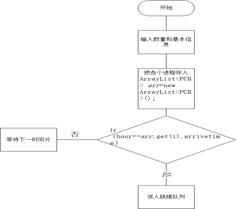
到达时间进入就绪状态模块:
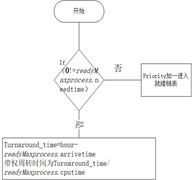
计算周转时间和带权周转时间:
四、实验结果及分析
输入的信息
初始权值都为100,needtime为还需要的时间
进程 到达时刻 服务时间
A 0 3
B 2 6
C 4 4
D 6 5
E 8 2
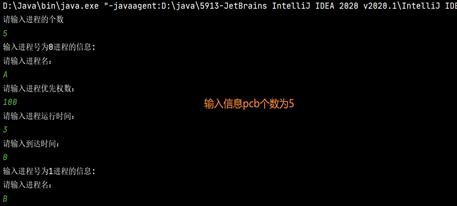

以A为例:
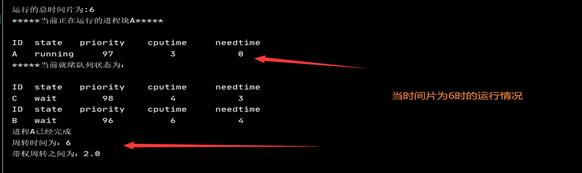
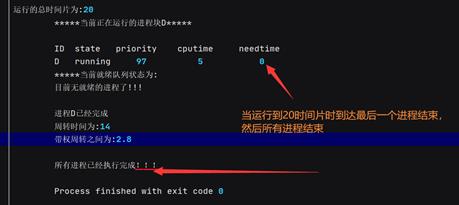
最后结束时:
部分代码展示
//创建结构
class PCB
String ID;
int priority=-1;
int cputime;//服务的时间
int needtime;//进程还需的时间
String state="wait";
int arrivetime;
PCB next;
public PCB(String ID,int priority,int cputime,int arrivetime)
this.ID=ID;
this.priority=priority;
this.cputime=cputime;
this.arrivetime=arrivetime;
判断是否到达,进程进入时间
for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++)
if(h==arr.get(i).arrivetime)
Dynamic_priority.sort(arr.get(i));
arr.remove(i);
//将进程转为就绪态并排序
public static void sort(PCB pcb)
PCB tmp=null;
if(ready==null)//当头结点为空
ready=pcb;
tail=pcb;
else if(pcb.priority>ready.priority)//如果这个结点priority大于头priority
pcb.next=ready;
ready=pcb;
else
boolean m=false;
tmp=ready;//q
while (m==false)
if(tail.priority>=pcb.priority)//插入尾端
tail.next=pcb;
tail=pcb;
pcb.next=null;
m=true;
else
if(tmp.priority>=pcb.priority&&pcb.priority>tail.priority)//逐渐遍历插到tmp前
pcb.next=tmp.next;
tmp.next=pcb;
m=true;
else tmp=tmp.next;
资料领取
回复操作系统综合实验即可获取
这里有python,Java学习资料还有有有趣好玩的编程项目,更有难寻的各种资源。反正看看也不亏。
以上是关于动态高优先权优先调度算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
操作系统| 作业调度算法平均周转时间平均带权周转时间先来先服务FCFS短作业优先SJF高优先权算法FPF高响应比优先算法HRRN
作业调度算法平均周转时间平均带权周转时间先来先服务FCFS短作业优先SJF高优先权(级)算法FPF高响应比优先算法HRRN