C——幻方算法
Posted net小伙
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C——幻方算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、幻方按照阶数可分成了三类,即奇数阶幻方、双偶阶幻方、单偶阶幻方。
二、奇数阶幻方(劳伯法)
奇数阶幻方最经典的填法是罗伯法。填写的方法是:
把1(或最小的数)放在第一行正中;按以下规律排列剩下的(n×n-1)个数:
(1)每一个数放在前一个数的右上一格;
(2)如果这个数所要放的格已经超出了顶行那么就把它放在底行,仍然要放在右一列;
(3)如果这个数所要放的格已经超出了最右列那么就把它放在最左列,仍然要放在上一行;
(4)如果这个数所要放的格已经超出了顶行且超出了最右列,那么就把它放在底行且最左列;
(5)如果这个数所要放的格已经有数填入,那么就把它放在前一个数的下一行同一列的格内。
例,用该填法获得的5阶幻方:
|
17 |
24 |
1 |
8 |
15 |
|
23 |
5 |
7 |
14 |
16 |
|
4 |
6 |
13 |
20 |
22 |
|
10 |
12 |
19 |
21 |
3 |
|
11 |
18 |
25 |
2 |
9 |
二、双偶数阶幻方(海尔法)
所谓双偶阶幻方就是当n可以被4整除时的偶阶幻方,即4K阶幻方。在说解法之前我们先说明一个“互补数”定义:就是在n阶幻方中,如果两个数的和等于幻方中最大的数与1的和(即n×n+1),我们称它们为一对互补数。如在三阶幻方中,每一对和为10的数,是一对互补数 ;在四阶幻方中,每一对和为17的数,是一对互补数。
双偶数阶幻方最经典的填法是海尔法。填写的方法是:
以8阶幻方为例:
(1)先把数字按顺序填。然后,按4×4把它分割成4块(如图)
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
|
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
|
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
|
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 |
|
41 |
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 |
47 |
48 |
|
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 |
55 |
56 |
|
57 |
58 |
59 |
60 |
61 |
62 |
63 |
64 |
(2)每个小方阵对角线上的数字(如左上角小方阵部分),换成和它互补的数。
|
64 |
2 |
3 |
61 |
60 |
6 |
7 |
57 |
|
9 |
55 |
54 |
12 |
13 |
51 |
50 |
16 |
|
17 |
47 |
46 |
20 |
21 |
43 |
42 |
24 |
|
40 |
26 |
27 |
37 |
36 |
30 |
31 |
33 |
|
32 |
34 |
35 |
29 |
28 |
38 |
39 |
25 |
|
41 |
23 |
22 |
44 |
45 |
19 |
18 |
48 |
|
49 |
15 |
14 |
52 |
53 |
11 |
10 |
56 |
|
8 |
58 |
59 |
5 |
4 |
62 |
63 |
1 |
三、单偶数阶幻方(斯特拉兹法)
所谓单偶阶幻方就是当n不可以被4整除时的偶阶幻方,即4K+2阶幻方。如(n=6,10,14……)的幻方。
单偶数阶幻方最经典的填法是斯特拉兹法。填写的方法是:
以10阶幻方为例。这时,k=2。
(1)把魔方阵分为A,B,C,D四个象限,这样每一个象限肯定是奇数阶。用罗伯法,依次在A象限,D象限,B象限,C象限按奇数阶幻方的填法填数。
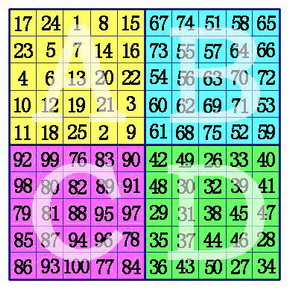
(2)在A象限的中间行、中间格开始,按自左向右的方向,标出k格。A象限的其它行则标出最左边的k格。将这些格,和C象限相对位置上的数互换位置。
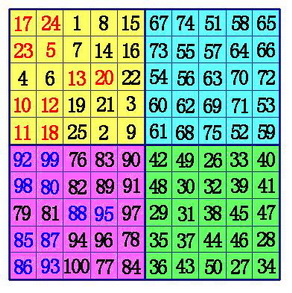
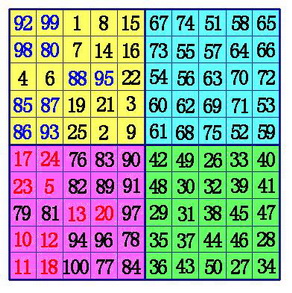
(3)在B象限所有行的中间格,自右向左,标出k-1格。(注:6阶幻方由于k-1=0,所以不用再作B、D象限的数据交换),将这些格,和D象限相对位置上的数互换位置。
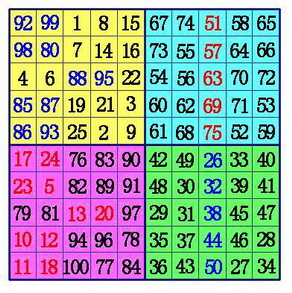
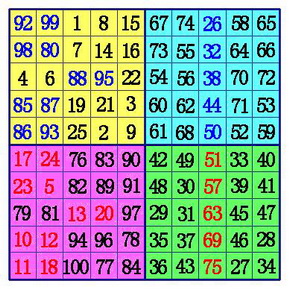
以上内容来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/panlijiao/archive/2012/05/11/2496757.html
实现代码如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 5 #define COL 20 6 #define ROW 20 7 8 void deal_argv(int argc, char **argv, int *degree) { 9 if (argc != 2) { 10 printf("cmd: ./a.out degree\\n"); 11 exit(-1); 12 } else { 13 *degree = atoi(argv[1]); 14 if (*degree <= 2 || *degree > 20) { 15 printf("the degree is between 3 and 20\\n"); 16 exit(-1); 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 21 void show_array(int (*array)[ROW], int degree) { 22 int row, col; 23 for (row = 0; row < degree; row++){ 24 for (col = 0; col < degree; col++) 25 printf("%5d", array[row][col]); 26 printf("\\n"); 27 } 28 } 29 30 void init_array(int (*array)[ROW], int size) { 31 memset(array, 0, size); 32 } 33 34 void odd_num_magic_square(int degree, int (*array)[ROW], int x, int y, int num) { 35 int element = 0; 36 int col = 0; 37 int row = degree / 2; 38 39 for (element = num; element <= degree * degree + num - 1; element++) { 40 array[col + x][row + y] = element; 41 if (array[(col - 1 + degree) % degree + x][(row + 1) % degree + y] != 0) { 42 col = (col + 1 + degree) % degree; 43 } else { 44 row = (row + 1) % degree; 45 col = (col - 1 + degree) % degree; 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 50 void fill_array(int (*array)[ROW], int degree) { 51 int row, col; 52 int num = 1; 53 54 for (col = 0; col < degree; col++) 55 for (row = 0; row < degree; row++) 56 array[col][row] = num++; 57 } 58 59 void double_magic_square(int degree, int (*array)[ROW]) { 60 int complement = 0; 61 int deg = degree / 4; 62 int row, col; 63 64 fill_array(array, degree); 65 complement = degree * degree + 1; 66 67 for (col = 0; col < deg; col++) { 68 for (row = 0; row < deg; row++) { 69 array[col * 4][row * 4] = complement - array[col * 4][row * 4]; 70 array[col * 4 + 1][row * 4 + 1] = complement - array[col * 4 + 1][row * 4 + 1]; 71 array[col * 4 + 2][row * 4 + 2] = complement - array[col * 4 + 2][row * 4 + 2]; 72 array[col * 4 + 3][row * 4 + 3] = complement - array[col * 4 + 3][row * 4 + 3]; 73 74 array[col * 4 + 3][row * 4] = complement - array[col * 4 + 3][row * 4]; 75 array[col * 4 + 2][row * 4 + 1] = complement - array[col * 4 + 2][row * 4 + 1]; 76 array[col * 4 + 1][row * 4 + 2] = complement - array[col * 4 + 1][row * 4 + 2]; 77 array[col * 4][row * 4 + 3] = complement - array[col * 4][row * 4 + 3]; 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 82 void change_value(int *value_a, int *value_b) { 83 int tmp; 84 tmp = *value_a; 85 *value_a = *value_b; 86 *value_b = tmp; 87 } 88 89 void single_magic_square(int degree, int (*array)[ROW]) { 90 int deg = degree / 2; 91 int k = 0; 92 int row, col; 93 int tmp_row = 0; 94 95 odd_num_magic_square(deg, array, 0, 0, 1); 96 odd_num_magic_square(deg, array, deg, deg, deg * deg + 1); 97 odd_num_magic_square(deg, array, 0, deg, deg * deg * 2 + 1); 98 odd_num_magic_square(deg, array, deg, 0, deg * deg * 3 + 1); 99 100 k = (degree - 2) / 4; 101 for (row = 0; row < k; row++) { 102 for (col = 0; col < deg; col++) { 103 if (col == deg / 2) { 104 change_value(&array[col][deg / 2 + row], &array[col + deg][deg / 2 + row]); 105 } else { 106 change_value(&array[col][row], &array[col + deg][row]); 107 } 108 } 109 } 110 111 for (row = 0; row < k - 1; row++) { 112 for (col = 0; col < deg; col++) { 113 tmp_row = row + deg + deg / 2 + 1 - k + 1; 114 change_value(&array[col][tmp_row], &array[col + deg][tmp_row]); 115 } 116 } 117 118 } 119 120 121 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { 122 int array[COL][ROW]; 123 int degree = 0; 124 125 deal_argv(argc, argv, °ree); 126 127 init_array(array, sizeof(array)); 128 if ((degree % 2) != 0) { 129 odd_num_magic_square(degree, array, 0, 0, 1); 130 show_array(array, degree); 131 } else if (degree % 4 == 0) { 132 double_magic_square(degree, array); 133 show_array(array, degree); 134 } else { 135 single_magic_square(degree, array); 136 show_array(array, degree); 137 } 138 139 140 return 0; 141 }
以上是关于C——幻方算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章