x264代码剖析:encode()函数之x264_encoder_open()函数
Posted 成长Bar
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了x264代码剖析:encode()函数之x264_encoder_open()函数相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
x264代码剖析(五):encode()函数之x264_encoder_open()函数
我们知道x264源码从主观上分为两大块,一是解析函数parse(),另一个是编码函数encode()。解析函数parse()较简单,并且不涉及H.264编码算法,故不是重点,所以我们要学习的重点自然而然地就是编码函数encode()了。
encode()函数是x264的主干函数,主要包括x264_encoder_open()函数、x264_encoder_headers()函数、x264_encoder_encode()函数与x264_encoder_close()函数四大部分,如下图所示,其中x264_encoder_encode()函数是其核心部分,具体的H.264视频编码算法均在此模块。

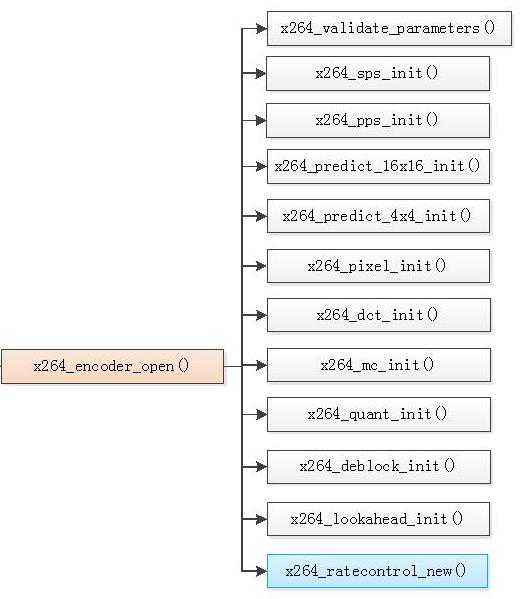
本文主要分析x264_encoder_open()函数,x264_encoder_open()用于打开编码器,其中初始化了libx264编码所需要的各种变量,如下图所示。它调用了下面的函数:
x264_validate_parameters():检查输入参数(例如输入图像的宽高是否为正数)。
x264_sps_init():初始化SPS
x264_pps_init():初始化PPS
x264_predict_16x16_init():初始化Intra16x16帧内预测汇编函数。
x264_predict_4x4_init():初始化Intra4x4帧内预测汇编函数。
x264_pixel_init():初始化像素值计算相关的汇编函数(包括SAD、SATD、SSD等)。
x264_dct_init():初始化DCT变换和DCT反变换相关的汇编函数。
x264_mc_init():初始化运动补偿相关的汇编函数。
x264_quant_init():初始化量化和反量化相关的汇编函数。
x264_deblock_init():初始化去块效应滤波器相关的汇编函数。
x264_lookahead_init():初始化Lookahead相关的变量。
x264_ratecontrol_new():初始化码率控制相关的变量。
对应的代码如下:
/******************************************************************/
/******************************************************************/
/*
======Analysed by RuiDong Fang
======Csdn Blog:http://blog.csdn.net/frd2009041510
======Date:2016.03.08
*/
/******************************************************************/
/******************************************************************/
/************====== x264_encoder_open()函数 ======************/
/*
功能:打开编码器
*/
/****************************************************************************
* x264_encoder_open:
****************************************************************************/
x264_t *x264_encoder_open( x264_param_t *param )
{
x264_t *h;
char buf[1000], *p;
int i_slicetype_length;
CHECKED_MALLOCZERO( h, sizeof(x264_t) );
/* Create a copy of param */
memcpy( &h->param, param, sizeof(x264_param_t) ); //将参数拷贝进来
if( param->param_free )
param->param_free( param );
#if HAVE_INTEL_DISPATCHER
x264_intel_dispatcher_override();
#endif
if( x264_threading_init() )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "unable to initialize threading\\n" );
goto fail;
}
if( x264_validate_parameters( h, 1 ) < 0 ) 检查输入参数(例如输入图像的宽高是否为正数)
goto fail;
if( h->param.psz_cqm_file )
if( x264_cqm_parse_file( h, h->param.psz_cqm_file ) < 0 )
goto fail;
if( h->param.rc.psz_stat_out )
h->param.rc.psz_stat_out = strdup( h->param.rc.psz_stat_out );
if( h->param.rc.psz_stat_in )
h->param.rc.psz_stat_in = strdup( h->param.rc.psz_stat_in );
x264_reduce_fraction( &h->param.i_fps_num, &h->param.i_fps_den );
x264_reduce_fraction( &h->param.i_timebase_num, &h->param.i_timebase_den );
/* Init x264_t */
h->i_frame = -1;
h->i_frame_num = 0;
if( h->param.i_avcintra_class )
h->i_idr_pic_id = 5;
else
h->i_idr_pic_id = 0;
if( (uint64_t)h->param.i_timebase_den * 2 > UINT32_MAX )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "Effective timebase denominator %u exceeds H.264 maximum\\n", h->param.i_timebase_den );
goto fail;
}
x264_set_aspect_ratio( h, &h->param, 1 );
//x264_sps_init()根据输入参数生成H.264码流的SPS (Sequence Parameter Set,序列参数集)信息
x264_sps_init( h->sps, h->param.i_sps_id, &h->param ); 初始化SPS
//x264_pps_init()根据输入参数生成H.264码流的PPS(Picture Parameter Set,图像参数集)信息
x264_pps_init( h->pps, h->param.i_sps_id, &h->param, h->sps ); 初始化PPS
x264_validate_levels( h, 1 ); //检查级Level-通过宏块个数等等
h->chroma_qp_table = i_chroma_qp_table + 12 + h->pps->i_chroma_qp_index_offset;
if( x264_cqm_init( h ) < 0 )
goto fail;
//赋值
h->mb.i_mb_width = h->sps->i_mb_width;
h->mb.i_mb_height = h->sps->i_mb_height;
h->mb.i_mb_count = h->mb.i_mb_width * h->mb.i_mb_height;
h->mb.chroma_h_shift = CHROMA_FORMAT == CHROMA_420 || CHROMA_FORMAT == CHROMA_422;
h->mb.chroma_v_shift = CHROMA_FORMAT == CHROMA_420;
/* Adaptive MBAFF and subme 0 are not supported as we require halving motion
* vectors during prediction, resulting in hpel mvs.
* The chosen solution is to make MBAFF non-adaptive in this case. */
h->mb.b_adaptive_mbaff = PARAM_INTERLACED && h->param.analyse.i_subpel_refine;
/* Init frames. */
if( h->param.i_bframe_adaptive == X264_B_ADAPT_TRELLIS && !h->param.rc.b_stat_read )
h->frames.i_delay = X264_MAX(h->param.i_bframe,3)*4;
else
h->frames.i_delay = h->param.i_bframe;
if( h->param.rc.b_mb_tree || h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size )
h->frames.i_delay = X264_MAX( h->frames.i_delay, h->param.rc.i_lookahead );
i_slicetype_length = h->frames.i_delay;
h->frames.i_delay += h->i_thread_frames - 1;
h->frames.i_delay += h->param.i_sync_lookahead;
h->frames.i_delay += h->param.b_vfr_input;
h->frames.i_bframe_delay = h->param.i_bframe ? (h->param.i_bframe_pyramid ? 2 : 1) : 0;
h->frames.i_max_ref0 = h->param.i_frame_reference;
h->frames.i_max_ref1 = X264_MIN( h->sps->vui.i_num_reorder_frames, h->param.i_frame_reference );
h->frames.i_max_dpb = h->sps->vui.i_max_dec_frame_buffering;
h->frames.b_have_lowres = !h->param.rc.b_stat_read
&& ( h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_ABR
|| h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF
|| h->param.i_bframe_adaptive
|| h->param.i_scenecut_threshold
|| h->param.rc.b_mb_tree
|| h->param.analyse.i_weighted_pred );
h->frames.b_have_lowres |= h->param.rc.b_stat_read && h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size > 0;
h->frames.b_have_sub8x8_esa = !!(h->param.analyse.inter & X264_ANALYSE_PSUB8x8);
h->frames.i_last_idr =
h->frames.i_last_keyframe = - h->param.i_keyint_max;
h->frames.i_input = 0;
h->frames.i_largest_pts = h->frames.i_second_largest_pts = -1;
h->frames.i_poc_last_open_gop = -1;
//CHECKED_MALLOCZERO(var, size)
//调用malloc()分配内存,然后调用memset()置零
CHECKED_MALLOCZERO( h->frames.unused[0], (h->frames.i_delay + 3) * sizeof(x264_frame_t *) );
/* Allocate room for max refs plus a few extra just in case. */
CHECKED_MALLOCZERO( h->frames.unused[1], (h->i_thread_frames + X264_REF_MAX + 4) * sizeof(x264_frame_t *) );
CHECKED_MALLOCZERO( h->frames.current, (h->param.i_sync_lookahead + h->param.i_bframe
+ h->i_thread_frames + 3) * sizeof(x264_frame_t *) );
if( h->param.analyse.i_weighted_pred > 0 )
CHECKED_MALLOCZERO( h->frames.blank_unused, h->i_thread_frames * 4 * sizeof(x264_frame_t *) );
h->i_ref[0] = h->i_ref[1] = 0;
h->i_cpb_delay = h->i_coded_fields = h->i_disp_fields = 0;
h->i_prev_duration = ((uint64_t)h->param.i_fps_den * h->sps->vui.i_time_scale) / ((uint64_t)h->param.i_fps_num * h->sps->vui.i_num_units_in_tick);
h->i_disp_fields_last_frame = -1;
x264_rdo_init(); ///RDO初始化
/* init CPU functions */
//初始化包含汇编优化的函数
//帧内预测
x264_predict_16x16_init( h->param.cpu, h->predict_16x16 ); ///初始化Intra16x16帧内预测汇编函数(该函数的定义位于x264\\common\\predict.c)
x264_predict_8x8c_init( h->param.cpu, h->predict_8x8c );
x264_predict_8x16c_init( h->param.cpu, h->predict_8x16c );
x264_predict_8x8_init( h->param.cpu, h->predict_8x8, &h->predict_8x8_filter );
x264_predict_4x4_init( h->param.cpu, h->predict_4x4 ); ///初始化Intra4x4帧内预测汇编函数
x264_pixel_init( h->param.cpu, &h->pixf ); ///初始化像素值计算相关的汇编函数(包括SAD、SATD、SSD等)(该函数的定义位于common\\pixel.c)
x264_dct_init( h->param.cpu, &h->dctf ); ///初始化DCT变换和DCT反变换相关的汇编函数(该函数的定义位于common\\dct.c)
x264_zigzag_init( h->param.cpu, &h->zigzagf_progressive, &h->zigzagf_interlaced );//“之”字扫描
memcpy( &h->zigzagf, PARAM_INTERLACED ? &h->zigzagf_interlaced : &h->zigzagf_progressive, sizeof(h->zigzagf) );
x264_mc_init( h->param.cpu, &h->mc, h->param.b_cpu_independent ); ///初始化运动补偿相关的汇编函数(该函数的定义位于common\\mc.c)
x264_quant_init( h, h->param.cpu, &h->quantf ); ///初始化量化和反量化相关的汇编函数(该函数的定义位于common\\quant.c)
x264_deblock_init( h->param.cpu, &h->loopf, PARAM_INTERLACED ); ///初始化去块效应滤波器相关的汇编函数(该函数的定义位于common\\deblock.c)
x264_bitstream_init( h->param.cpu, &h->bsf );
//初始化CABAC或者是CAVLC
if( h->param.b_cabac )
x264_cabac_init( h );
else
x264_stack_align( x264_cavlc_init, h );
//决定了像素比较的时候用SAD还是SATD
mbcmp_init( h );
chroma_dsp_init( h );
//CPU属性
p = buf + sprintf( buf, "using cpu capabilities:" );
for( int i = 0; x264_cpu_names[i].flags; i++ )
{
if( !strcmp(x264_cpu_names[i].name, "SSE")
&& h->param.cpu & (X264_CPU_SSE2) )
continue;
if( !strcmp(x264_cpu_names[i].name, "SSE2")
&& h->param.cpu & (X264_CPU_SSE2_IS_FAST|X264_CPU_SSE2_IS_SLOW) )
continue;
if( !strcmp(x264_cpu_names[i].name, "SSE3")
&& (h->param.cpu & X264_CPU_SSSE3 || !(h->param.cpu & X264_CPU_CACHELINE_64)) )
continue;
if( !strcmp(x264_cpu_names[i].name, "SSE4.1")
&& (h->param.cpu & X264_CPU_SSE42) )
continue;
if( !strcmp(x264_cpu_names[i].name, "BMI1")
&& (h->param.cpu & X264_CPU_BMI2) )
continue;
if( (h->param.cpu & x264_cpu_names[i].flags) == x264_cpu_names[i].flags
&& (!i || x264_cpu_names[i].flags != x264_cpu_names[i-1].flags) )
p += sprintf( p, " %s", x264_cpu_names[i].name );
}
if( !h->param.cpu )
p += sprintf( p, " none!" );
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_INFO, "%s\\n", buf );
if( x264_analyse_init_costs( h ) )
goto fail;
static const uint16_t cost_mv_correct[7] = { 24, 47, 95, 189, 379, 757, 1515 };
/* Checks for known miscompilation issues. */
if( h->cost_mv[X264_LOOKAHEAD_QP][2013] != cost_mv_correct[BIT_DEPTH-8] )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "MV cost test failed: x264 has been miscompiled!\\n" );
goto fail;
}
/* Must be volatile or else GCC will optimize it out. */
volatile int temp = 392;
if( x264_clz( temp ) != 23 )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "CLZ test failed: x264 has been miscompiled!\\n" );
#if ARCH_X86 || ARCH_X86_64
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "Are you attempting to run an SSE4a/LZCNT-targeted build on a CPU that\\n" );
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "doesn't support it?\\n" );
#endif
goto fail;
}
h->out.i_nal = 0;
h->out.i_bitstream = X264_MAX( 1000000, h->param.i_width * h->param.i_height * 4
* ( h->param.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_ABR ? pow( 0.95, h->param.rc.i_qp_min )
: pow( 0.95, h->param.rc.i_qp_constant ) * X264_MAX( 1, h->param.rc.f_ip_factor )));
h->nal_buffer_size = h->out.i_bitstream * 3/2 + 4 + 64; /* +4 for startcode, +64 for nal_escape assembly padding */
CHECKED_MALLOC( h->nal_buffer, h->nal_buffer_size );
CHECKED_MALLOC( h->reconfig_h, sizeof(x264_t) );
if( h->param.i_threads > 1 &&
x264_threadpool_init( &h->threadpool, h->param.i_threads, (void*)x264_encoder_thread_init, h ) )
goto fail;
if( h->param.i_lookahead_threads > 1 &&
x264_threadpool_init( &h->lookaheadpool, h->param.i_lookahead_threads, NULL, NULL ) )
goto fail;
#if HAVE_OPENCL
if( h->param.b_opencl )
{
h->opencl.ocl = x264_opencl_load_library();
if( !h->opencl.ocl )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "failed to load OpenCL\\n" );
h->param.b_opencl = 0;
}
}
#endif
h->thread[0] = h;
for( int i = 1; i < h->param.i_threads + !!h->param.i_sync_lookahead; i++ )
CHECKED_MALLOC( h->thread[i], sizeof(x264_t) );
if( h->param.i_lookahead_threads > 1 )
for( int i = 0; i < h->param.i_lookahead_threads; i++ )
{
CHECKED_MALLOC( h->lookahead_thread[i], sizeof(x264_t) );
*h->lookahead_thread[i] = *h;
}
*h->reconfig_h = *h;
for( int i = 0; i < h->param.i_threads; i++ )
{
int init_nal_count = h->param.i_slice_count + 3;
int allocate_threadlocal_data = !h->param.b_sliced_threads || !i;
if( i > 0 )
*h->thread[i] = *h;
if( x264_pthread_mutex_init( &h->thread[i]->mutex, NULL ) )
goto fail;
if( x264_pthread_cond_init( &h->thread[i]->cv, NULL ) )
goto fail;
if( allocate_threadlocal_data )
{
h->thread[i]->fdec = x264_frame_pop_unused( h, 1 );
if( !h->thread[i]->fdec )
goto fail;
}
else
h->thread[i]->fdec = h->thread[0]->fdec;
CHECKED_MALLOC( h->thread[i]->out.p_bitstream, h->out.i_bitstream );
/* Start each thread with room for init_nal_count NAL units; it'll realloc later if needed. */
CHECKED_MALLOC( h->thread[i]->out.nal, init_nal_count*sizeof(x264_nal_t) );
h->thread[i]->out.i_nals_allocated = init_nal_count;
if( allocate_threadlocal_data && x264_macroblock_cache_allocate( h->thread[i] ) < 0 )
goto fail;
}
#if HAVE_OPENCL
if( h->param.b_opencl && x264_opencl_lookahead_init( h ) < 0 )
h->param.b_opencl = 0;
#endif
if( x264_lookahead_init( h, i_slicetype_length ) ) ///初始化lookahead
goto fail;
for( int i = 0; i < h->param.i_threads; i++ )
if( x264_macroblock_thread_allocate( h->thread[i], 0 ) < 0 )
goto fail;
if( x264_ratecontrol_new( h ) < 0 ) ///创建码率控制
goto fail;
if( h->param.i_nal_hrd )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_DEBUG, "HRD bitrate: %i bits/sec\\n", h->sps->vui.hrd.i_bit_rate_unscaled );
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_DEBUG, "CPB size: %i bits\\n", h->sps->vui.hrd.i_cpb_size_unscaled );
}
if( h->param.psz_dump_yuv )
{
/* create or truncate the reconstructed video file */
FILE *f = x264_fopen( h->param.psz_dump_yuv, "w" );
if( !f )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "dump_yuv: can't write to %s\\n", h->param.psz_dump_yuv );
goto fail;
}
else if( !x264_is_regular_file( f ) )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "dump_yuv: incompatible with non-regular file %s\\n", h->param.psz_dump_yuv );
fclose( f );
goto fail;
}
fclose( f );
}
const char *profile = h->sps->i_profile_idc == PROFILE_BASELINE ? "Constrained Baseline" :
h->sps->i_profile_idc == PROFILE_MAIN ? "Main" :
h->sps->i_profile_idc == PROFILE_HIGH ? "High" :
h->sps->i_profile_idc == PROFILE_HIGH10 ? (h->sps->b_constraint_set3 == 1 ? "High 10 Intra" : "High 10") :
h->sps->i_profile_idc == PROFILE_HIGH422 ? (h->sps->b_constraint_set3 == 1 ? "High 4:2:2 Intra" : "High 4:2:2") :
h->sps->b_constraint_set3 == 1 ? "High 4:4:4 Intra" : "High 4:4:4 Predictive";
char level[4];
snprintf( level, sizeof(level), "%d.%d", h->sps->i_level_idc/10, h->sps->i_level_idc%10 );
if( h->sps->i_level_idc == 9 || ( h->sps->i_level_idc == 11 && h->sps->b_constraint_set3 &&
(h->sps->i_profile_idc == PROFILE_BASELINE || h->sps->i_profile_idc == PROFILE_MAIN) ) )
strcpy( level, "1b" );
if( h->sps->i_profile_idc < PROFILE_HIGH10 ) //输出型和级
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_INFO, "profile %s, level %s\\n",
profile, level );
}
else
{
static const char * const subsampling[4] = { "4:0:0", "4:2:0", "4:2:2", "4:4:4" };
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_INFO, "profile %s, level %s, %s %d-bit\\n",
profile, level, subsampling[CHROMA_FORMAT], BIT_DEPTH );
}
return h;
fail:
x264_free( h ); //释放
return NULL;
}
以上是关于x264代码剖析:encode()函数之x264_encoder_open()函数的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
x264代码剖析:encode()函数之x264_encoder_open()函数
x264代码剖析:主函数main()解析函数parse()与编码函数encode()