css,关于盒子模型
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了css,关于盒子模型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一个div,width是100,padding是10,那麼这个div在横向上占据的空间应该是120还是100?
按W3C的盒子模型的话,最后是 120=100+10+10IE6 下,会显示 100
当没DTD文档声明时,IE系列浏览器显示这个的宽度也为 100(兼容/怪异 模式)。
当然,显示100的,只是IE一个解释错误罢了…… 参考技术A 120
关于CSS3弹性盒子的flex布局以及媒体查询
CSS3弹性盒子(Flex Box)
弹性盒子是css3中一种新的布局手段,它主要用来代替浮动来完成页面的布局,当页面需要适应不同的屏幕大小以及设备类型时确保元素拥有恰当的行为的布局方式,换句话来讲就是可以让元素跟随页面大小的改变而改变,引入弹性盒布局模型的目的是提供一种更加有效的方式来对一个容器中的子元素进行排列、对齐和分配空白空间。
弹性容器
要使用弹性盒子,必须将一个元素设置为弹性容器,我们通过 display:flex 来设置弹性容器,display:inline-flex 设置为行内的弹性容器
弹性元素:
- 弹性容器的子元素称为弹性元素(弹性项)
- 一个元素可以同时设置弹性容器和弹性元素
下面具体看下代码
未设置弹性容器,样式如下
<style>
*
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
ul
width: 800px;
border: 10px solid red;
display: flex;
li
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
border-bottom-color: #bfa;
font-size: 50px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
li:nth-child(1)
background-color: #bfa;
li:nth-child(2)
background-color: pink;
li:nth-child(3)
background-color: orange;
</style>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>
</body>

给元素 li 的父元素 ul 设置display:flex后我们发现li元素自动横向排列
ul
width: 500px;
border: 10px solid red;
display: flex;

弹性元素的属性
flex-grow:指定弹性元素的伸展指数 默认值0,当父元素有多余空间时,子元素如何伸展,父元素剩余空间会按照比例进行分配flex-shrink:指定弹性元素的收缩指数 默认值1,当父元素中的空间不足以容纳所有元素时 ,如果对子元素进行收缩值越大收缩越大
给每一个li设置flex-grow不同的值发现li自动填满了父元素ul,并且每一个li所占的大小与flex-grow的值成正比
li:nth-child(1)
background-color: #bfa;
flex-grow: 1;
li:nth-child(2)
background-color: pink;
flex-grow: 2;
li:nth-child(3)
background-color: orange;
flex-grow: 8;

我们将父元素宽度设置成500px,此时ul子元素li的宽度虽然大于父元素宽度但还是可以填满父元素,我们给每个子元素设置flex-shrink看看效果
li:nth-child(1)
background-color: #bfa;
/* flex-grow: 1; */
flex-shrink: 1;
li:nth-child(2)
background-color: pink;
/* flex-grow: 2; */
flex-shrink: 2;
li:nth-child(3)
background-color: orange;
/* flex-grow: 8; */
flex-shrink: 8;
我们发现flex-shrink设置的值越大,收缩效果越好,flex-shrink设置为1不收缩
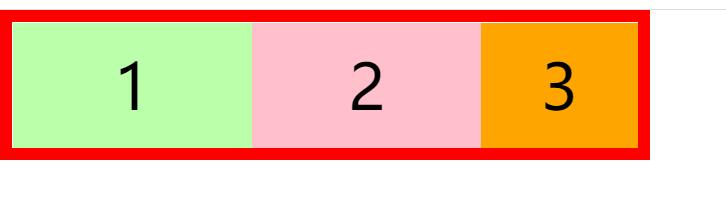
弹性容器的属性
flex-flow 即盒子的方向,是flex-direction和flex-wrap两个属性的组合
flex-direction指定容器中弹性元素的排列方式
可选值:row默认值,弹性元素在容器中水平排列(左向右排列)
row-reverse 反向排列
column 垂直排列 上到下排列
column-reverse 垂直排列 下到上排列flex-wrap设置弹性元素是否在弹性容器中自动换行
可选值:nowrap 默认值 元素不会自动换行
wrap 元素会沿着辅轴方向自动换行
wrap-reverse 元素沿着辅轴方向反向换行
justify-content属性
justify-content可以设置如何分配主轴上的空白部分
可选值:
flex-start 元素沿着主轴起边排列
flex-end 元素沿着主轴终边排列
center 元素居中排列
space-around 空白分布到元素两侧
space-evenly 空白分布在单侧
space-between 空白均匀分布在元素间
主要是最后三种容易混淆,下面演示以下效果差别
ul
width: 800px;
border: 10px solid red;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;

ul
width: 800px;
border: 10px solid red;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;

ul
width: 800px;
border: 10px solid red;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;

align-items属性
align-items 可以设置元素在辅轴上如何对齐
可选值:
- stretch 默认值 将元素的长度设置为相同的值
- flex-start 元素沿着辅轴边对齐
- flex-end 元素沿着辅轴终边对齐
- center 居中对齐
- baseline 基线对齐
<style>
*
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
ul
width: 600px;
height: 800px;
border: 10px solid red;
/* 将ul设置弹性容器 */
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
align-items: baseline;
li
width: 200px;
background-color: #bfa;
font-size: 50px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
li:nth-child(1)
background-color: #bfa;
li:nth-child(2)
background-color: pink;
li:nth-child(3)
background-color: orange;
li:nth-child(4)
background-color: yellow;
li:nth-child(5)
background-color: chocolate;
下面分别演示align-items不同属性值的效果
stretch
ul
width: 600px;
height: 800px;
border: 10px solid red;
/* 将ul设置弹性容器 */
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
align-items: stretch;
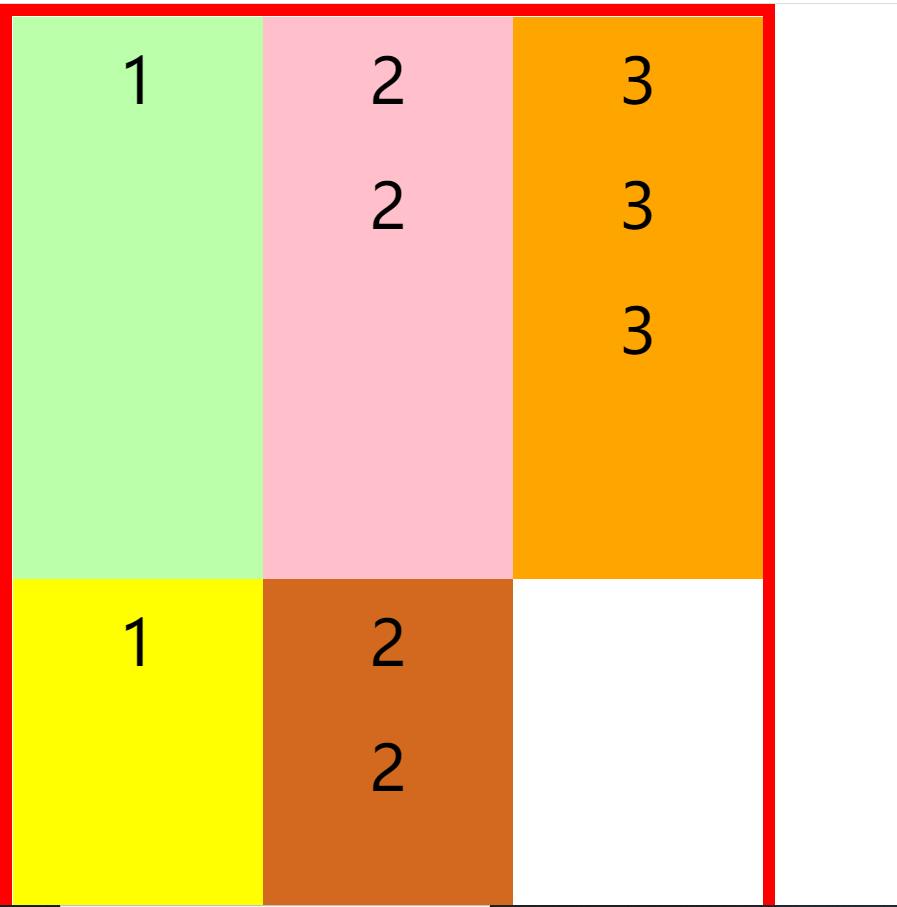
flex-start
ul
width: 600px;
height: 800px;
border: 10px solid red;
/* 将ul设置弹性容器 */
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
align-items: flex-start;
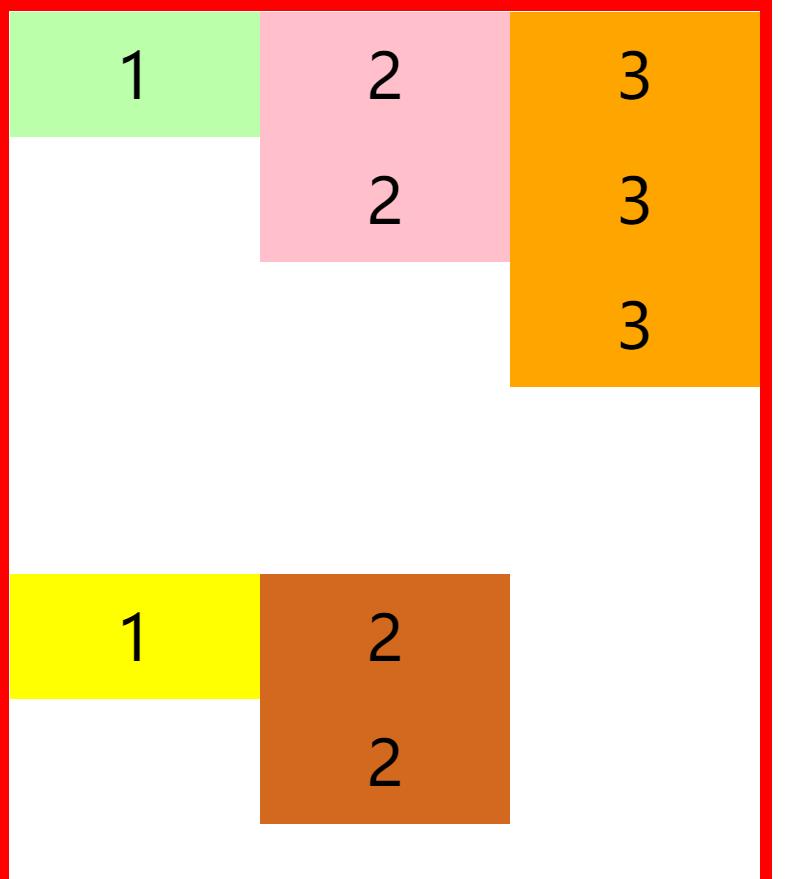
flex-end
ul
width: 600px;
height: 800px;
border: 10px solid red;
/* 将ul设置弹性容器 */
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
align-items: flex-end;
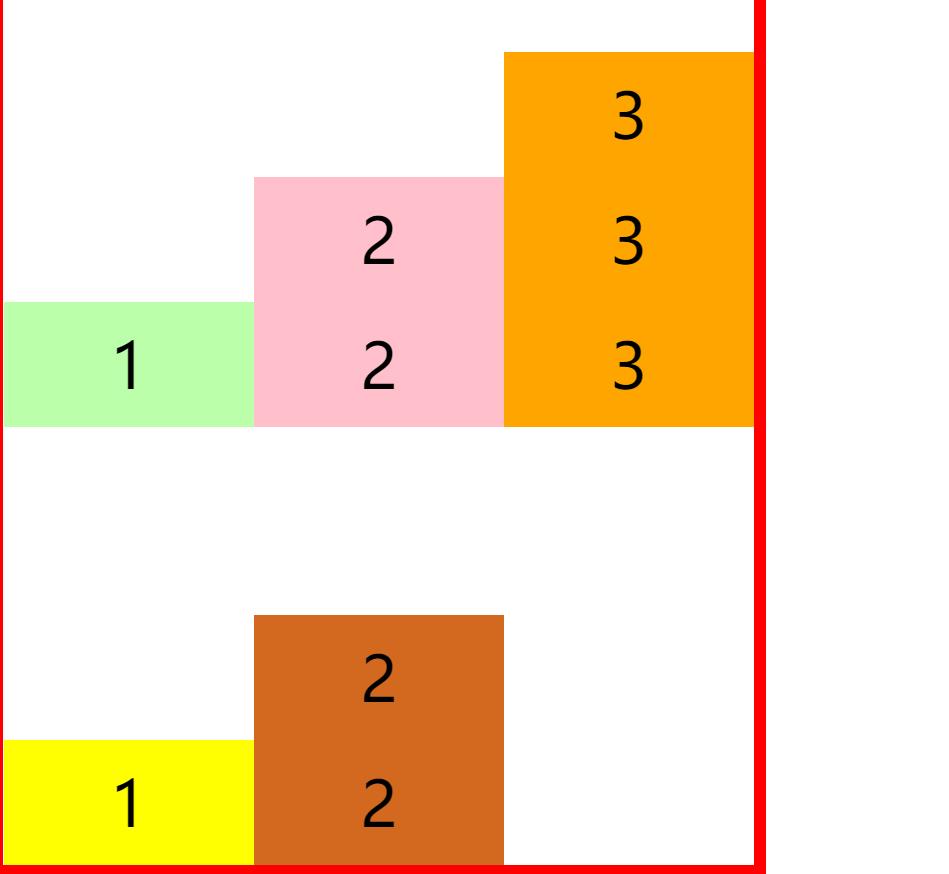
center 居中对齐
ul
width: 600px;
height: 800px;
border: 10px solid red;
/* 将ul设置弹性容器 */
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
align-items: center;
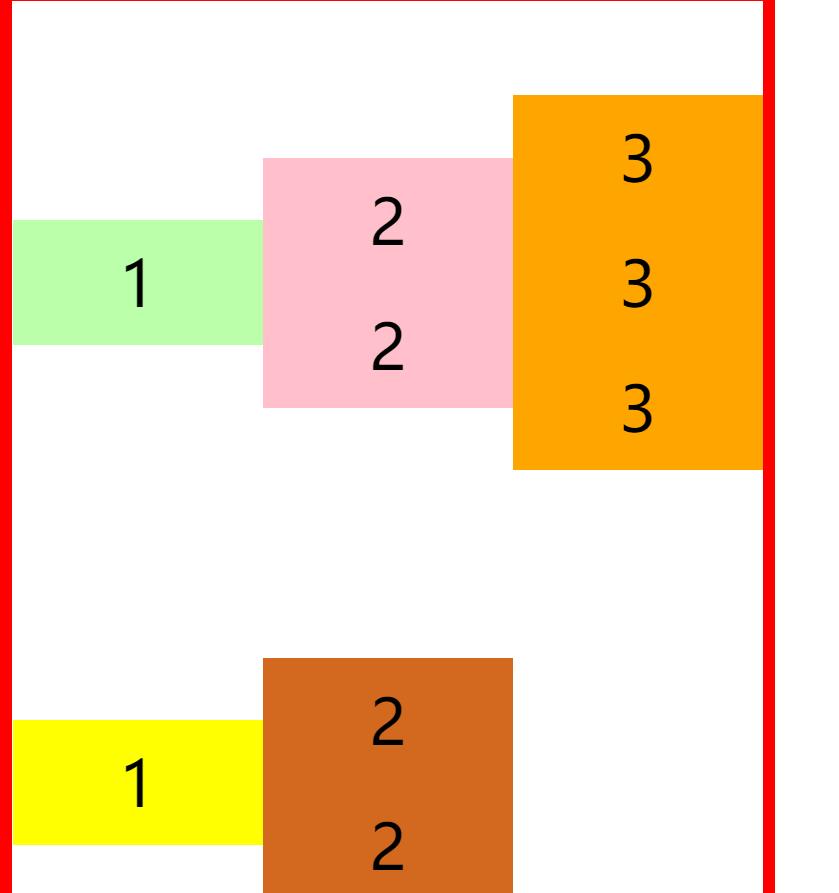
baseline 基线对齐
ul
width: 600px;
height: 800px;
border: 10px solid red;
/* 将ul设置弹性容器 */
display: flex;
flex-flow: row wrap;
align-items: baseline;
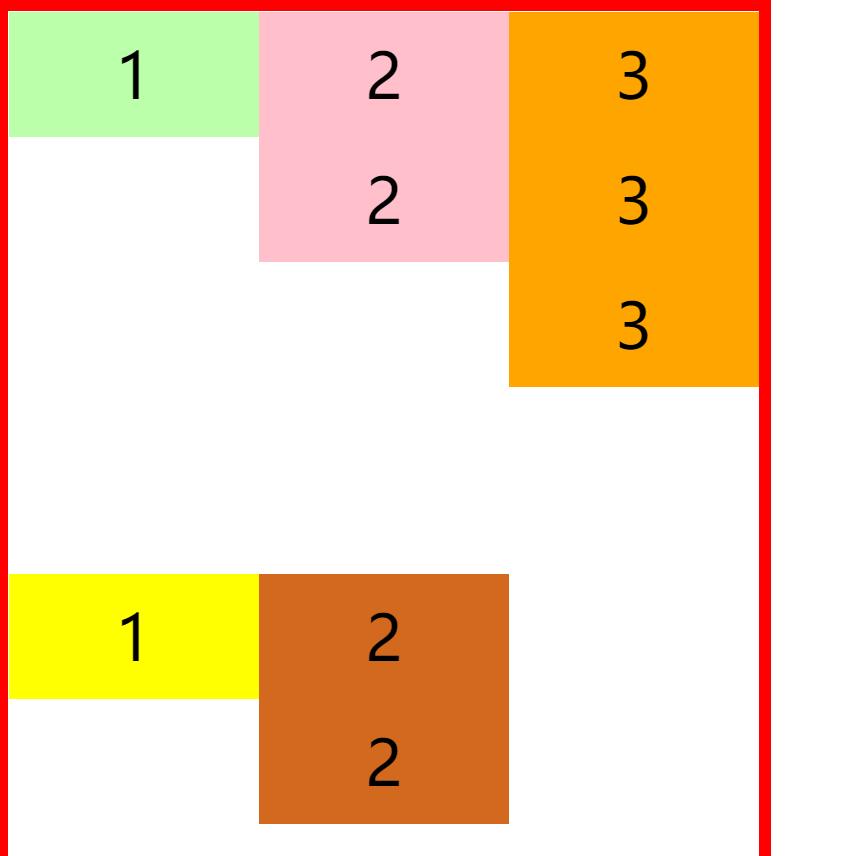
align-content属性:
align-content: 辅轴空白部分的分布
可选值:
- flex-start 元素沿着主轴起边排列
- flex-end 元素沿着主轴终边排列
- center 元素居中排列
- space-around 空白分布到元素两侧
- space-evenly 空白分布在单侧
- space-between 空白均匀分布在元素间
媒体查询
媒体查询(Media Query) ,又称媒介查询,是根据屏幕的比例、窗口的宽度、设备的方向等差异来改变页面的显示方式,媒体查询也是响应式布局的关键
媒体查询的使用
语法:@media 查询规则
媒体类型:
- all 所有设备
- print 打印设备
- screen 屏幕设备
- speech 屏幕阅读器设备
媒体特性:
- width:视口的宽度
- height:视口的高度
- min-width:最小视口宽度 (视口大于指定宽度时生效)
- max-width:最大视口宽度(视口小于指定宽度时生效)
例如当浏览器视口宽度大于575px时,div有指定宽度720px,小于575px时div的宽度同父元素宽度
<style>
.container
height: 50px;
background-color: #bfa;
margin: 0 auto;
@media screen and (max-width:575px)
.container
width: 100%;
@media screen and (min-width:575px)
.container
width: 720px;
</style>
<body>
<div class="container">媒体查询容器</div>
</body>
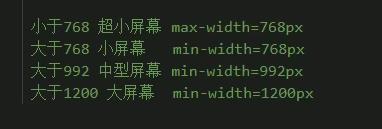
样式切断的分界点称为断点,也就是网页的样式会在这个点时发生变化
一般比较常用的断点
以上是关于css,关于盒子模型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章