数据结构——二叉树遍历之“递归与非递归遍历”
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构——二叉树遍历之“递归与非递归遍历”相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
简述
二叉树的遍历分为先序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历。如下图所示:
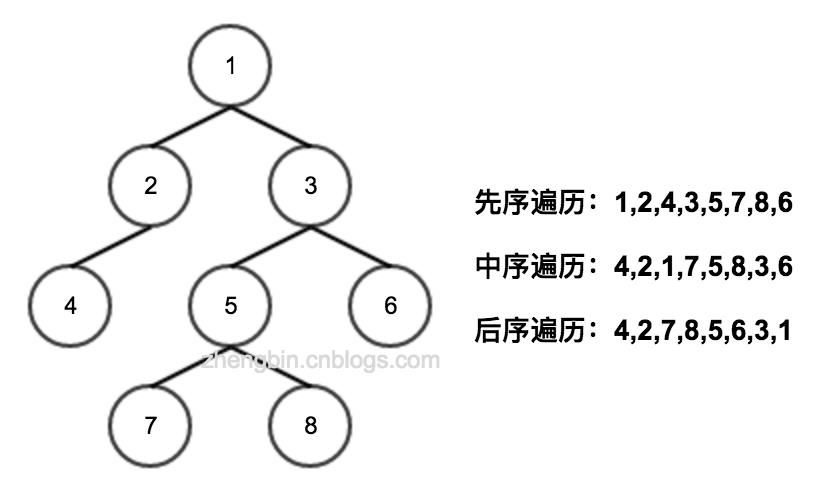
递归遍历
private void bianli1(List<Integer> list, TreeNode root) { // 先序遍历 if (root == null) { return; } list.add(root.val); bianli1(list, root.left); bianli1(list, root.right); } private void bianli2(List<Integer> list, TreeNode root) { // 中序遍历 if (root == null) { return; } bianli2(list, root.left); list.add(root.val); bianli2(list, root.right); } private void bianli3(List<Integer> list, TreeNode root) { // 后序遍历 if (root == null) { return; } bianli3(list, root.left); bianli3(list, root.right); list.add(root.val); }
递归遍历实现比较简单,递归利用函数栈来保存信息。
非递归遍历
非递归需要额外自己申请数据结构来代替函数栈。
先序遍历:
1.申请一个栈 stack。然后将头结点 head 压入 stack 中。
2.从 stack 中弹出栈顶结点,记为 cur,然后打印 cur 结点的值,再将 cur 的右孩子(非空的话)和左孩子(非空的话)分别压入栈中。
3.不断重复步骤 2,直到栈 stack 为空,全部过程结束。
中序遍历:
1.申请一个栈 stack。初始时,令变量 cur=head。
2.先把 cur 结点压入栈中,然后依次把左边界压入栈中,即不停的令 cur=cur.left,重复该步骤。
3.不断重复步骤 2,直到 cur 为空为止,此时从 stack 中弹出栈顶元素,记为 node。打印 node 的值,并将 cur=node.right,然后继续重复步骤2。
4.当 stack 为空且 cur 为空时,整个过程停止。
后序遍历:
1.申请一个栈,记为s1,然后将头结点 head 压入 s1 中。
2.从 s1 中弹出的结点记为 cur,然后依次将 cur 的左孩子和右孩子压入 s1 中。
3.整个过程中 s1 所弹出的结点都压入 s2 中。
4.不断重复步骤2-3,直到 s1 为空为止。
5.从 s2 中弹出结点并打印,打印的顺序就是后序遍历的顺序。
源码实现:
/** * 先序遍历 */ private static void xianxu(List<Integer> list, TreeNode root) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); stack.add(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { root = stack.pop(); list.add(root.val); if (root.right != null) { stack.push(root.right); } if (root.left != null){ stack.push(root.left); } } } /** * 中序遍历 */ private static void zhongxu(List<Integer> list, TreeNode root) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); while (!stack.isEmpty() || root!=null) { if (root != null) { stack.push(root); root = root.left; }else { root = stack.pop(); list.add(root.val); root = root.right; } } } /** * 后序遍历 */ private static void houxu(List<Integer> list, TreeNode root) { Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<TreeNode>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<TreeNode>(); stack1.add(root); while (!stack1.isEmpty()) { root = stack1.pop(); stack2.push(root); if (root.left != null) { stack1.push(root.left); } if (root.right != null) { stack1.push(root.right); } } while (!stack2.isEmpty()) { list.add(stack2.pop().val); } }
参考资料
[1] 程序员代码面试, 第三章 - 二叉树问题
以上是关于数据结构——二叉树遍历之“递归与非递归遍历”的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章