迷宫问题
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了迷宫问题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、问题描述:就是在一个迷宫中,找出能够一条路线,从起点到终点的一条路线,走出迷宫,走过的路线均被标记出来。
分析:这个的用到栈来保存路径,并且对每种情况都得考虑清楚。
2、代码实现:
因为要用到栈,所以用C++写比较方便;
#include<iostream> #include<stack> #include<time.h> #include<ctype.h> using namespace std; //迷宫 :Maze #define ROW_COUNT 8 #define COL_COUNT 8 #define WALL 1 #define NOT_WALL 0 #define WALL_COUNT 24 typedef struct POS{ int x; //行 int y; //列 }POS; typedef enum{RIGHT, DOWN, LEFT, UP}DIR; //枚举类型,0,1,2,3,我自定义位置:右、下、左、上 typedef struct MAN{ //定义一个人的类型 POS pos; //位置 DIR di; //方向 }MAN; void initMaze(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], int count);//初始化迷宫 void showMaze(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], int row, int col);//显示迷宫 bool pass(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], POS curpos);//判断当前点是否能通过 void footMaze(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], POS pos);//走过的线路做好标记 POS nextPos(POS pos, DIR di); //获得下一个位置 void markPrint(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], POS pos);//回退的路线做的标记 bool MazePath(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], POS start, POS end);//处理迷宫路径的函数 bool MazePath(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], POS start, POS end){ MAN man; stack<MAN> st; POS curpos = start; do{ if(pass(Maze, curpos)){ //能否通过 man.pos = curpos; man.di = RIGHT; footMaze(Maze, man.pos); if(curpos.x == end.x && curpos.y == end.y)//判断是否走到终点了 return true; st.push(man); curpos = nextPos(man.pos, man.di); }else{ if(!st.empty()){ man = st.top(); while(man.di==UP && !st.empty()){ //判断4个方向还有的走吗? markPrint(Maze, man.pos); //就是四个方向都不能走了,回退时标记为4; st.pop(); man = st.top(); } if(man.di < UP){ st.pop(); man.di =(DIR)(man.di+1); //下一个方向 st.push(man); curpos = nextPos(man.pos, man.di); } } } }while(!st.empty()); return true; } void markPrint(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], POS pos){ Maze[pos.x][pos.y] = 4; } POS nextPos(POS pos, DIR di){ switch(di){ case RIGHT: pos.y += 1; break; case DOWN: pos.x += 1; break; case LEFT: pos.y -= 1; break; case UP: pos.x -= 1; break; } return pos; } void footMaze(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], POS pos){ Maze[pos.x][pos.y] = 2; } bool pass(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], POS curpos){ if(Maze[curpos.x][curpos.y] == NOT_WALL) return true; return false; } void showMaze(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], int row, int col){ int i; int j; for(i = 0; i < row; i++){ for(j = 0; j < col; j++){ cout<<Maze[i][j]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } } void initMaze(int (*Maze)[COL_COUNT], int count){ int i; int index; srand(time(NULL)); for(i = 0; i < WALL_COUNT; i++){ index = rand()%count; if(Maze[0][index] != WALL){ Maze[0][index] = WALL; } } } int main(void){ int Maze[ROW_COUNT][COL_COUNT] = {0}; POS start = {1, 0}; POS end = {7, 7}; initMaze(Maze, ROW_COUNT*COL_COUNT); if(Maze[1][0] == WALL || Maze[7][7] == WALL){ cout<<"起始、终止位置有一个为墙,游戏结束"<<endl; return 0; } showMaze(Maze, ROW_COUNT, COL_COUNT); MazePath(Maze, start, end); cout<<"------------------------------------"<<endl; showMaze(Maze, ROW_COUNT, COL_COUNT); return 0; }
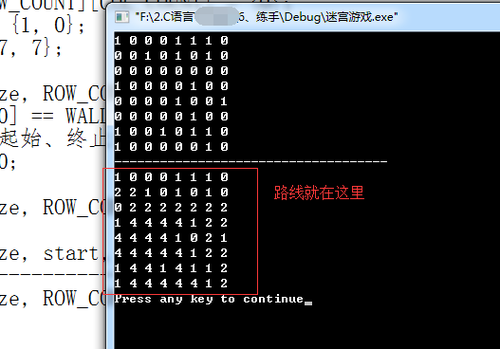
运行结果
2:代表走的路线,从<1, 0>----><7, 7>
4:代表回退的路线。
本文出自 “11586096” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://11596096.blog.51cto.com/11586096/1858999
以上是关于迷宫问题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章