POJ 3549 GSM phone(圆+扫描线+最短路)
Posted dd-bond
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了POJ 3549 GSM phone(圆+扫描线+最短路)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目意思是求起点s到终点s的最短路,但是只能在圆的内部和边上走。一种可以想到的方法就是求出所有的交点,然后两两连边并验证合法性,但是这样的交点数规模有n2。
我们可以观察发现,我们在圆求并构成的图形中,在其内部的点是不可能成为最短路上的点,只可能是沿着边上的点擦着经过,所以我们需要把在圆内部的所有点都给扣掉,同样可以证明这样的点的规模只有n个,接下来只需要暴力连边,但是连边的时候需要验证这样的点对是否沿着直线可达。我是直接将这条线段暴力和所有圆求交点,左侧端点计为1,右侧端点计为-1,然后用类似于扫描线的做法sort一遍,最后判断线段的两端是否被这个区间包含即可。
最后跑一边dijk就求出答案。
这个方法感觉不是很好.... 还有比我快20倍的orz...
如果扣的是灰色点那么规模有n2
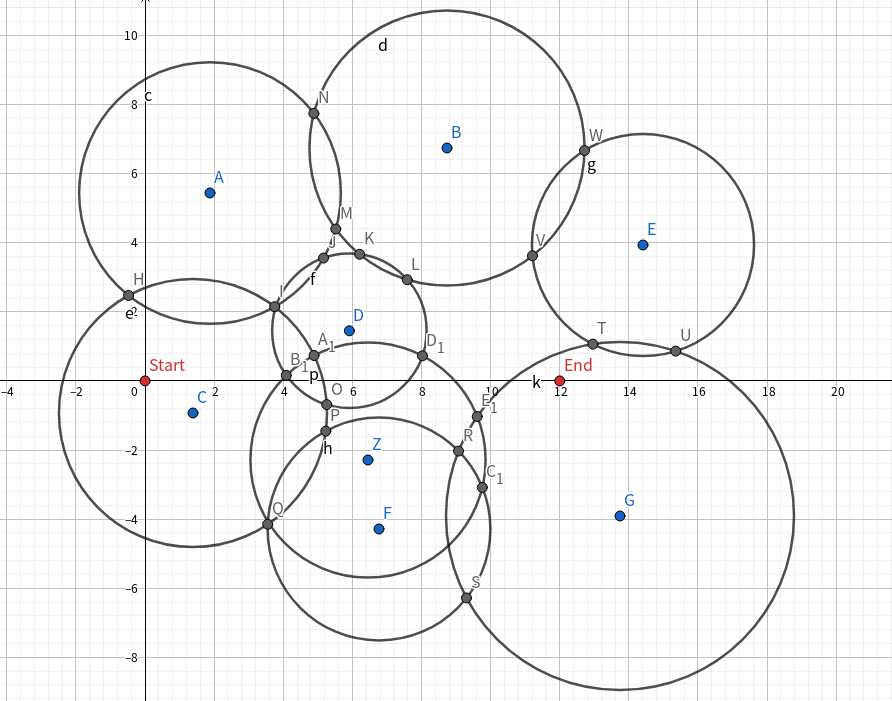
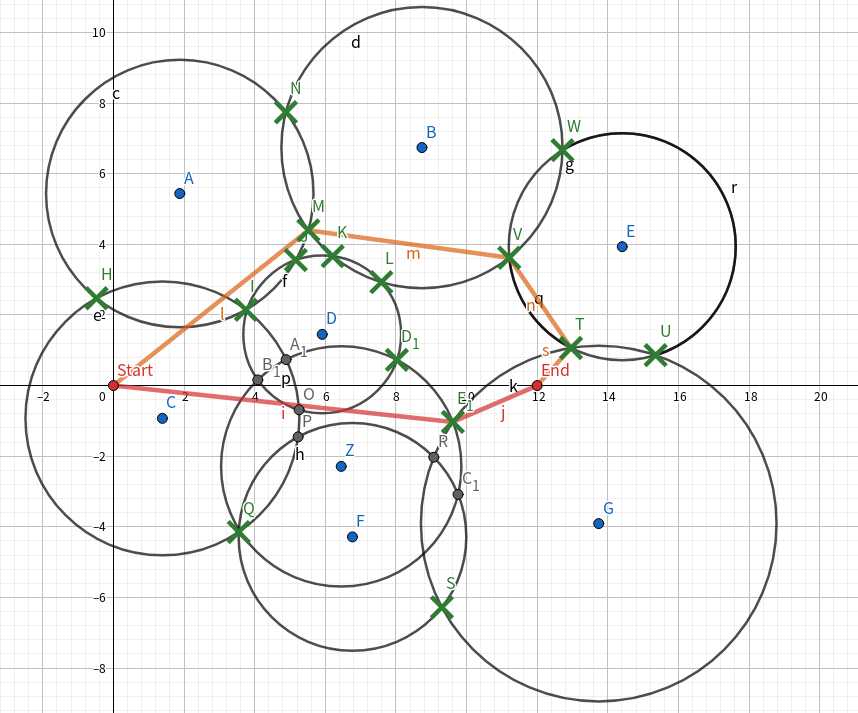
如果是外侧点只有n个,绿色点即为可用点,红色和橙色为两条路,则最短路必然擦过外侧点或者起点终点直接相连
1 // ——By DD_BOND 2 3 //#include<bits/stdc++.h> 4 //#include<unordered_map> 5 //#include<unordered_set> 6 #include<functional> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 #include<iostream> 9 //#include<ext/rope> 10 #include<iomanip> 11 #include<climits> 12 #include<cstring> 13 #include<cstdlib> 14 #include<cstddef> 15 #include<cstdio> 16 #include<memory> 17 #include<vector> 18 #include<cctype> 19 #include<string> 20 #include<cmath> 21 #include<queue> 22 #include<deque> 23 #include<ctime> 24 #include<stack> 25 #include<map> 26 #include<set> 27 #include<cassert> 28 29 #define fi first 30 #define se second 31 #define pb push_back 32 #define MP make_pair 33 34 #pragma GCC optimize(3) 35 #pragma GCC target("sse,sse2,sse3,ssse3,sse4,popcnt,abm,mmx,avx,tune=native") 36 37 using namespace std; 38 39 typedef long double db; 40 typedef long long ll; 41 typedef pair<db,db> Pd; 42 typedef pair<int,int> P; 43 typedef pair<ll,ll> Pll; 44 45 const db eps=1e-8; 46 const int MAXN=1e5+10; 47 const db pi=acos(-1.0); 48 const ll INF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; 49 50 inline int dcmp(db x) 51 if(fabs(x)<eps) return 0; 52 return (x>0? 1: -1); 53 54 55 inline db Sqrt(db x) 56 return x>0? sqrt(x): 0; 57 58 59 inline db sqr(db x) return x*x; 60 61 struct Point 62 db x,y; 63 Point() x=0,y=0; 64 Point(db _x,db _y):x(_x),y(_y) 65 void input() 66 double _x,_y; 67 scanf("%lf%lf",&_x,&_y); 68 x=_x,y=_y; 69 70 void output() printf("%.2f %.2f\\n",(double)x,(double)y); 71 friend istream &operator >>(istream &os,Point &b) 72 os>>b.x>>b.y; 73 return os; 74 75 friend ostream &operator <<(ostream &os,Point &b) 76 os<<b.x<<‘ ‘<<b.y; 77 return os; 78 79 bool operator ==(const Point &b)const 80 return (dcmp(x-b.x)==0&&dcmp(y-b.y)==0); 81 82 bool operator !=(const Point &b)const 83 return !((dcmp(x-b.x)==0&&dcmp(y-b.y)==0)); 84 85 bool operator <(const Point &b)const 86 return (dcmp(x-b.x)==0? dcmp(y-b.y)<0 : x<b.x); 87 88 db operator ^(const Point &b)const //叉积 89 return x*b.y-y*b.x; 90 91 db operator *(const Point &b)const //点积 92 return x*b.x+y*b.y; 93 94 Point operator +(const Point &b)const 95 return Point(x+b.x,y+b.y); 96 97 Point operator -(const Point &b)const 98 return Point(x-b.x,y-b.y); 99 100 Point operator *(db a) 101 return Point(x*a,y*a); 102 103 Point operator /(db a) 104 return Point(x/a,y/a); 105 106 db len2() //长度平方 107 return sqr(x)+sqr(y); 108 109 db len() //长度 110 return Sqrt(len2()); 111 112 Point change_len(db r) //转化为长度为r的向量 113 db l=len(); 114 if(dcmp(l)==0) return *this; //零向量 115 return Point(x*r/l,y*r/l); 116 117 Point rotate_left() //逆时针旋转90度 118 return Point(-y,x); 119 120 Point rotate_right() //顺时针旋转90度 121 return Point(y,-x); 122 123 ; 124 125 inline db cross(Point a,Point b) //叉积 126 return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x; 127 128 129 inline db dot(Point a,Point b) //点积 130 return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y; 131 132 133 inline db dis(Point a,Point b) //两点的距离 134 Point p=b-a; return p.len(); 135 136 137 struct Line 138 Point s,e; 139 Line() 140 Line(Point _s,Point _e):s(_s),e(_e) //两点确定直线 141 void input() 142 s.input(); 143 e.input(); 144 145 db length() //线段长度 146 return dis(s,e); 147 148 ; 149 150 inline db point_to_line(Point p,Line a) //点到直线距离 151 return fabs(cross(p-a.s,a.e-a.s)/a.length()); 152 153 154 inline Point projection(Point p,Line a) //点在直线上的投影 155 return a.s+(((a.e-a.s)*dot(a.e-a.s,p-a.s))/(a.e-a.s).len2()); 156 157 158 struct Circle 159 Point p; 160 db r; 161 Circle() 162 void input() 163 p.input(); 164 double _r; 165 scanf("%lf",&_r); 166 r=_r; 167 168 ; 169 170 inline int relation(Point p,Circle a) //点和圆的位置关系 0:圆外 1:圆上 2:圆内 171 db d=dis(p,a.p); 172 if(dcmp(d-a.r)==0) return 1; 173 return (dcmp(d-a.r)<0? 2: 0); 174 175 176 inline int relation(Line a,Circle b) //直线和圆的位置关系 0:相离 1:相切 2:相交 177 db p=point_to_line(b.p,a); 178 if(dcmp(p-b.r)==0) return 1; 179 return (dcmp(p-b.r)<0? 2: 0); 180 181 182 inline int relation(Circle a,Circle v) //圆和圆的位置关系 1:内含 2:内切 3:相交 4:外切 5:相离 183 db d=dis(a.p,v.p); 184 if(dcmp(d-a.r-v.r)>0) return 5; 185 if(dcmp(d-a.r-v.r)==0) return 4; 186 db l=fabs(a.r-v.r); 187 if(dcmp(d-l)>0) return 3; 188 if(dcmp(d-l)==0) return 2; 189 return 1; 190 191 192 inline int circle_intersection(Circle a,Circle v,Point &p1,Point &p2) //两个圆的交点 193 int rel=relation(a,v); //返回交点个数,保存在引用中 194 if(rel==1||rel==5) return 0; 195 db d=dis(a.p,v.p); 196 db l=(d*d+a.r*a.r-v.r*v.r)/(2*d); 197 db h=Sqrt(a.r*a.r-l*l); 198 Point tmp=a.p+(v.p-a.p).change_len(l); 199 p1=tmp+((v.p-a.p).rotate_left().change_len(h)); 200 p2=tmp+((v.p-a.p).rotate_right().change_len(h)); 201 if(rel==2||rel==4) return 1; 202 return 2; 203 204 205 inline int line_circle_intersection(Line v,Circle u,Point &p1,Point &p2) //直线和圆的交点 206 if(!relation(v,u)) return 0; //返回交点个数,保存在引用中 207 Point a=projection(u.p,v); 208 db d=point_to_line(u.p,v); 209 d=Sqrt(u.r*u.r-d*d); 210 if(dcmp(d)==0) 211 p1=a,p2=a; 212 return 1; 213 214 p1=a+(v.e-v.s).change_len(d); 215 p2=a-(v.e-v.s).change_len(d); 216 return 2; 217 218 219 typedef pair<db,int>pdi; 220 typedef pair<Point,int> pd; 221 222 vector<pdi>edge[MAXN]; 223 224 db d[MAXN]; 225 pd st[MAXN]; 226 bool mark[MAXN]; 227 Circle circle[MAXN]; 228 Point s,t,it1,it2,inter[MAXN],point[MAXN]; 229 230 priority_queue<pdi,vector<pdi>,greater<pdi> >q; 231 232 bool cmp(pd a,pd b) 233 if(a==b) return a.se>b.se; 234 return a<b; 235 236 237 int main(void) 238 s.input(); t.input(); 239 int n,m=1,cnt=1; scanf("%d",&n); 240 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) circle[i].input(); 241 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 242 for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++) 243 int p=relation(circle[i],circle[j]); 244 if(p==2||p==3||p==4) 245 circle_intersection(circle[i],circle[j],it1,it2); 246 point[m++]=it1,point[m++]=it2; 247 248 249 sort(point+1,point+m); 250 m=unique(point+1,point+m)-point; 251 for(int i=1;i<m;i++) 252 for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) 253 if(relation(point[i],circle[j])==2) 254 mark[i]=1; 255 break; 256 257 for(int i=1;i<m;i++) 258 if(mark[i]==0) 259 point[cnt++]=point[i]; 260 m=cnt; point[0]=s,point[m]=t; 261 for(int i=0;i<=m;i++) 262 for(int j=i+1;j<=m;j++) 263 int p=0; 264 Line l(point[i],point[j]); 265 Point p1=point[i],p2=point[j]; 266 if(p2<p1) swap(p1,p2); 267 for(int k=1;k<=n;k++) 268 Circle c=circle[k]; 269 if(relation(l,c)) 270 line_circle_intersection(l,c,it1,it2); 271 if(it2<it1) swap(it1,it2); 272 st[p++]=pd(it1,1); 273 st[p++]=pd(it2,-1); 274 275 276 int found=0; 277 sort(st,st+p,cmp); 278 for(int k=0,sum=0,start=0;k<p;k++) 279 sum+=st[k].se; 280 if(sum==0) 281 if(!(p1<st[start].fi)&&!(st[k].fi<p2)) found=1; 282 start=k+1; 283 284 285 if(found) 286 edge[i].pb(pdi(l.length(),j)); 287 edge[j].pb(pdi(l.length(),i)); 288 289 290 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) d[i]=1e20; 291 q.push(pdi(0,0)); 292 while(!q.empty()) 293 pdi p=q.top(); q.pop(); 294 if(dcmp(d[p.se]-p.fi)<0) continue; 295 for(int i=0;i<edge[p.se].size();i++) 296 int v=edge[p.se][i].se; 297 db val=edge[p.se][i].fi; 298 if(dcmp(d[p.se]+val-d[v])<0) 299 d[v]=d[p.se]+val; 300 q.push(pdi(d[v],v)); 301 302 303 304 printf("%.5f\\n",(double)d[m]); 305 return 0; 306
以上是关于POJ 3549 GSM phone(圆+扫描线+最短路)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章