数据结构——线性表
Posted noneplus
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构——线性表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
什么是线性表?
线性表是具有相同类型的n个元素(n>=0)的有限序列。
1.顺序表
- 线性表采用顺序存储方式
- 其逻辑顺序和物理顺序相同
问题:需要连续存储空间,插入等操作需要移动大量元素,时间复杂度高。
2.单链表
线性表采用链式存储方式称为单链表。
链式存储是采用节点来进行存储的。
每个节点包括data域和next域。(不一定连续存储)

- 单链表反转
- 单链表的增删改查
- 约瑟夫环
单链表反转

单链表的增删改查
import java.util.Stack;
//定义单个节点
class Node
public String data; //定义数据节点
public Node next; //定义指向下一个节点的指针
public Node()
public Node(String data)
this.data = data;
public String getData()
return data;
public void setData(String data)
this.data = data;
public Node getNext()
return next;
public void setNext(Node next)
this.next = next;
@Override
public String toString()
return "Note" +
"data='" + data + '\\'' +
'';
public class Operation
//初始化头结点
private static Node head = new Node();
private static Node reverseHead = new Node();
//插入节点(头插)
public void insertToHead(Node node)
Node temp = head;
//头插法需要设置head.next和node.next的值。其中nodeNext指向headNext,而headNext指向node。
//由于是赋值的关系,二者顺序不可颠倒
node.next=temp.next;
temp.next=node;
//插入节点(尾插)
public void insertToLast(Node node)
Node temp = head;
while (true)
if(temp.next==null)
break;
temp=temp.next;
temp.next=node;
//插入节点(指定位置k之后)
public void insertToK(Node node,int k)
Node temp = head;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
temp=temp.next;
node.next=temp.next;
temp.next=node;
//删除第m个节点
public void deleteM(int m)
Node temp = head;
for(int i=0;i<m-1;i++)
temp=temp.next;
temp.next=temp.next.next;
//修改第n个节点(n)
public void updateN(int n)
Node temp = head;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
temp=temp.next;
temp.data="up";
//递归反转
public Node reverseLinkedList(Node node)
if (node == null || node.next == null)
return node;
else
Node headNode = reverseLinkedList(node.next);
node.next.next = node;
node.next = null;
return headNode;
//遍历反转
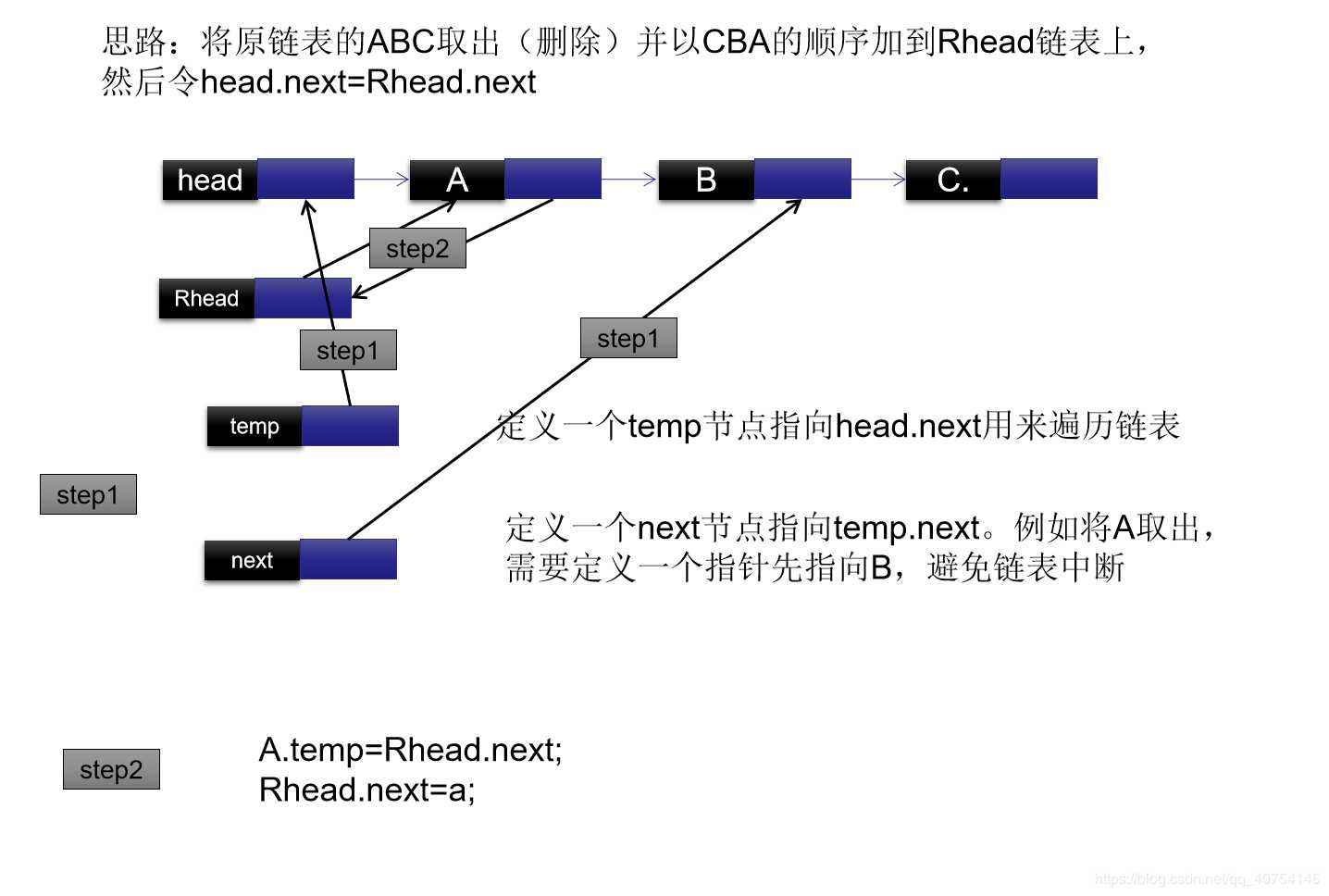
public Node reserveByFor(Node head)
Node cur = head.next;
Node next = null;
Node Rhead = new Node();
while(true)
if(cur==null)
break;
else
next=cur.next;
cur.next=Rhead.next;
Rhead.next=cur;
cur=next;
head.next=Rhead.next;
return head;
//print(last to first)
public void printLtoF(Node head)
Stack<Node>stack = new Stack<>();
Node cur = head.next;
while (cur!=null)
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.next;
while (stack.size()>0)
System.out.println(stack.pop());
public static void main(String[] args)
Operation operation = new Operation();
operation.insertToHead(new Node("A"));
operation.insertToHead(new Node("B"));
operation.insertToHead(new Node("C"));
operation.insertToLast(new Node("1"));
operation.insertToLast(new Node("2"));
operation.insertToLast(new Node("3"));
// operation.insertToK(new Node("k"),2);
// operation.deleteM(3);
// operation.updateN(1);
Node temp =head;
//遍历链表
while(true)
if(temp.next==null)
break;
else
temp=temp.next;
System.out.println(temp.toString());
System.out.println("//1.求单链表中有效节点个数.");
temp=head;
int count=0;
while(true)
if(temp.next==null)
break;
else
temp=temp.next;
count++;
System.out.println(count);
System.out.println("//2.查找单链表中倒数第K=3个节点");
temp=head;
//获取链表总长
int length=0;
while (true)
if(temp.next==null)
break;
else
temp=temp.next;
length++;
temp=head;
for(int i=0;i<length-2;i++)
temp=temp.next;
System.out.println(temp.data);
System.out.println("3.实现单链表的反转");
// temp=operation.reverseLinkedList(head);
temp = operation.reserveByFor(head);
//遍历链表
while(true)
if(temp.next==null)
break;
else
temp=temp.next;
System.out.println(temp.toString());
System.out.println("4.从尾到头打印单链表");
temp = head;
operation.printLtoF(temp);
单向环形链表输出约瑟夫环

//定义单个节点
class Node
public String data; //定义数据节点
public Node next; //定义指向下一个节点的指针
public Node()
public Node(String data)
this.data = data;
@Override
public String toString()
return "Note" +
"data='" + data + '\\'' +
'';
public class Operation
//初始化头结点
private static Node head = new Node();
//尾插法
public void add(Node node)
Node temp = head;
while (true)
if(temp.next==null)
break;
temp=temp.next;
temp.next=node;
//创建单向环形链表
public Node createCircle(int n)
//创建单链表
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
add(new Node("No:"+(i+1)));
//遍历链表
Node temp = head;
while(temp.next!=null)
temp=temp.next;
System.out.println(temp);
Node last = temp;
temp=head;
last.next=head.next; //连接首尾
System.out.println("last为最后一个数5:");
System.out.println(last);
System.out.println("循环两遍单向环形链表:");
int count=2*n;
while(last!=null)
if(count==0)
break;
System.out.println(last.next);
last=last.next;
count--;
System.out.println("last="+last.data);
return last;
public static void JosephusProblem(int n, int k, int m, Node last)
//定位到第k个节点,输出k+1个节点并删除,并让last定位到第k个节点
Node temp = last;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++) //定位到第k个节点
temp=temp.next;
System.out.println("第一次输出"+temp.next.data);//输出
temp.next=temp.next.next; //删除第K+1个节点
last=temp.next;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)
temp=last;
System.out.println("第二次输出"+temp.next.data);
temp.next=temp.next.next;
last=temp.next;
public static void main(String[] args)
Operation operation = new Operation();
//定义人数
int n=5;
Node last = operation.createCircle(n);
//定义从第几个节点开始数
int k=1;
//定义数的次数
int m=2;
System.out.println("输出约瑟夫环:");
JosephusProblem(n,k,m,last);
3.双向链表
双向链表与单向链表的区别
单向列表只能从前往后查找,而双向链表可以向前向后查找。
单向链表删除节点需要依靠辅助节点,而双向链表可以实现自我删除。
双向链表与单项列表的实际区别在于多了一个pre域。

双向链表增删改查
import java.util.Stack;
//定义单个节点
class Node
public String data; //定义数据节点
public Node next; //定义指向下一个节点的指针
public Node pre; //定义指向上一个节点的指针
public Node()
public Node(String data)
this.data = data;
@Override
public String toString()
return "Note" +
"data='" + data + '\\'' +
'';
public class Operation
//初始化头结点
private static Node head = new Node();
//插入节点(尾插法)
public void addNode(Node node)
Node temp = head;
while(true)
if(temp.next==null)
break;
temp=temp.next;
temp.next=node;
node.pre=temp;
//插入节点(头插法)
public void addNodeToHead(Node node)
Node temp = head;
node.pre=temp;
node.next=temp.next;
temp.next.pre=node;
temp.next=node;
//插入到第k个节点后
public void addToK(Node node,int k)
Node temp = head;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
temp=temp.next;
//先建立单链表联系
node.next=temp.next;
temp.next=node;
//建立pre指向
node.pre=temp;
node.next.pre=node;
//删除第n个结点
public void deleteNode(int n)
Node temp = head;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
temp=temp.next;
temp.next.pre=temp.pre;
temp.pre.next=temp.next;
public void list()
//遍历链表
Node temp = head;
while(temp.next!=null)
temp=temp.next;
System.out.println(temp.toString());
System.out.println("=============");
//修改第m个结点
public void update(int m)
Node temp = head;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
temp=temp.next;
temp.data="up";
public static void main(String[] args)
Operation operation = new Operation();
operation.addNode(new Node("A"));
operation.addNode(new Node("B"));
operation.addNode(new Node("C"));
operation.addNode(new Node("D"));
operation.addNodeToHead(new Node("head1"));
operation.addNodeToHead(new Node("head2"));
operation.addNodeToHead(new Node("head3"));
//遍历链表
operation.list();
System.out.println("删除第n个节点");
operation.deleteNode(3);
//遍历链表
operation.list();
System.out.println("修改第m个节点");
operation.update(3);
operation.list();
System.out.println("插入到第k个节点后");
operation.addToK(new Node("k" ),3);
operation.list();
以上是关于数据结构——线性表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章