吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型
Posted tszr
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
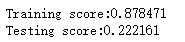
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def load_data_regression(): ‘‘‘ 加载用于回归问题的数据集 ‘‘‘ #使用 scikit-learn 自带的一个糖尿病病人的数据集 diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes() # 拆分成训练集和测试集,测试集大小为原始数据集大小的 1/4 return train_test_split(diabetes.data,diabetes.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0) #集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型 def test_GradientBoostingRegressor(*data): X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor() regr.fit(X_train,y_train) print("Training score:%f"%regr.score(X_train,y_train)) print("Testing score:%f"%regr.score(X_test,y_test)) # 获取分类数据 X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_regression() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor test_GradientBoostingRegressor(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
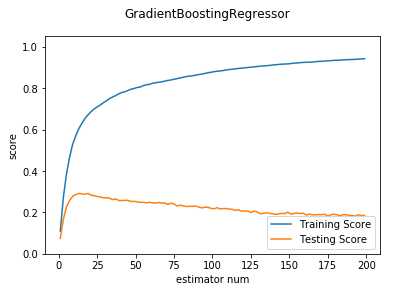
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 n_estimators 参数的影响 ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data nums=np.arange(1,200,step=2) fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) testing_scores=[] training_scores=[] for num in nums: regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train)) testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test)) ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score") ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score") ax.set_xlabel("estimator num") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="lower right") ax.set_ylim(0,1.05) plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor") plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
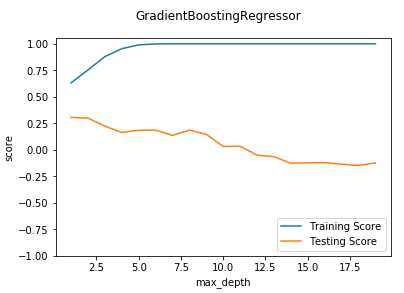
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 max_depth 参数的影响 ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data maxdepths=np.arange(1,20) fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) testing_scores=[] training_scores=[] for maxdepth in maxdepths: regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(max_depth=maxdepth,max_leaf_nodes=None) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train)) testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test)) ax.plot(maxdepths,training_scores,label="Training Score") ax.plot(maxdepths,testing_scores,label="Testing Score") ax.set_xlabel("max_depth") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="lower right") ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05) plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor") plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
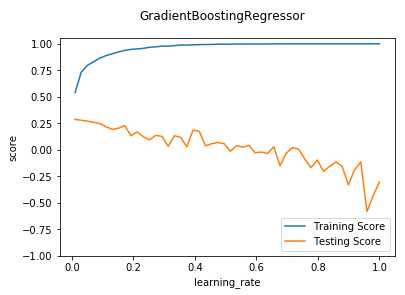
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learning(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 learning_rate 参数的影响 ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data learnings=np.linspace(0.01,1.0) fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) testing_scores=[] training_scores=[] for learning in learnings: regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(learning_rate=learning) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train)) testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test)) ax.plot(learnings,training_scores,label="Training Score") ax.plot(learnings,testing_scores,label="Testing Score") ax.set_xlabel("learning_rate") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="lower right") ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05) plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor") plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learning test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learning(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
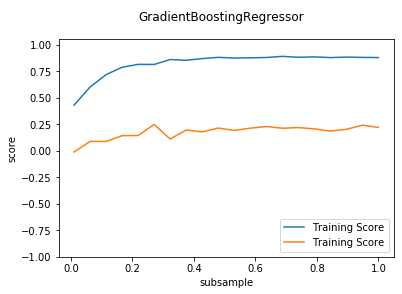
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 subsample 参数的影响 ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) subsamples=np.linspace(0.01,1.0,num=20) testing_scores=[] training_scores=[] for subsample in subsamples: regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(subsample=subsample) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train)) testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test)) ax.plot(subsamples,training_scores,label="Training Score") ax.plot(subsamples,testing_scores,label="Training Score") ax.set_xlabel("subsample") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="lower right") ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05) plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor") plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
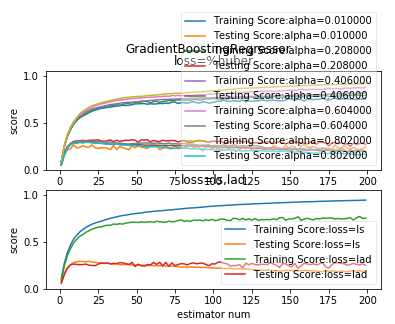
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随不同的损失函数和 alpha 参数的影响 ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data fig=plt.figure() nums=np.arange(1,200,step=2) ########## 绘制 huber ###### ax=fig.add_subplot(2,1,1) alphas=np.linspace(0.01,1.0,endpoint=False,num=5) for alpha in alphas: testing_scores=[] training_scores=[] for num in nums: regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num,loss=‘huber‘,alpha=alpha) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train)) testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test)) ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score:alpha=%f"%alpha) ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score:alpha=%f"%alpha) ax.set_xlabel("estimator num") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="lower right",framealpha=0.4) ax.set_ylim(0,1.05) ax.set_title("loss=%huber") plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor") #### 绘制 ls 和 lad ax=fig.add_subplot(2,1,2) for loss in [‘ls‘,‘lad‘]: testing_scores=[] training_scores=[] for num in nums: regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num,loss=loss) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train)) testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test)) ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score:loss=%s"%loss) ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score:loss=%s"%loss) ax.set_xlabel("estimator num") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="lower right",framealpha=0.4) ax.set_ylim(0,1.05) ax.set_title("loss=ls,lad") plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor") plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
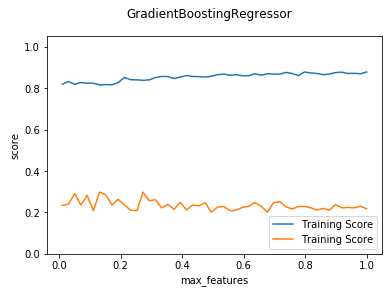
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 max_features 参数的影响 ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) max_features=np.linspace(0.01,1.0) testing_scores=[] training_scores=[] for features in max_features: regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(max_features=features) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train)) testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test)) ax.plot(max_features,training_scores,label="Training Score") ax.plot(max_features,testing_scores,label="Training Score") ax.set_xlabel("max_features") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="lower right") ax.set_ylim(0,1.05) plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor") plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
以上是关于吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法回归模型
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法分类模型
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestClassifier分类模型