吴裕雄 python 机器学习——支持向量机SVM非线性分类SVC模型
Posted tszr
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了吴裕雄 python 机器学习——支持向量机SVM非线性分类SVC模型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model,svm from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def load_data_classfication(): ‘‘‘ 加载用于分类问题的数据集 ‘‘‘ # 使用 scikit-learn 自带的 iris 数据集 iris=datasets.load_iris() X_train=iris.data y_train=iris.target # 分层采样拆分成训练集和测试集,测试集大小为原始数据集大小的 1/4 return train_test_split(X_train, y_train,test_size=0.25,random_state=0,stratify=y_train) #支持向量机SVM非线性分类SVC模型 def test_SVC_linear(*data): X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data cls=svm.SVC(kernel=‘linear‘) cls.fit(X_train,y_train) print(‘Coefficients:%s, intercept %s‘%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_)) print(‘Score: %.2f‘ % cls.score(X_test, y_test)) # 生成用于分类的数据集 X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_classfication() # 调用 test_SVC_linear test_SVC_linear(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
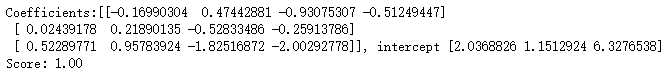
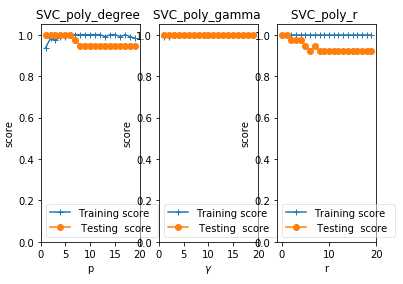
def test_SVC_poly(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试多项式核的 SVC 的预测性能随 degree、gamma、coef0 的影响. ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data fig=plt.figure() ### 测试 degree #### degrees=range(1,20) train_scores=[] test_scores=[] for degree in degrees: cls=svm.SVC(kernel=‘poly‘,degree=degree) cls.fit(X_train,y_train) train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train)) test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test)) ax=fig.add_subplot(1,3,1) # 一行三列 ax.plot(degrees,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker=‘+‘ ) ax.plot(degrees,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker=‘o‘ ) ax.set_title( "SVC_poly_degree ") ax.set_xlabel("p") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.set_ylim(0,1.05) ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5) ### 测试 gamma ,此时 degree 固定为 3#### gammas=range(1,20) train_scores=[] test_scores=[] for gamma in gammas: cls=svm.SVC(kernel=‘poly‘,gamma=gamma,degree=3) cls.fit(X_train,y_train) train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train)) test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test)) ax=fig.add_subplot(1,3,2) ax.plot(gammas,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker=‘+‘ ) ax.plot(gammas,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker=‘o‘ ) ax.set_title( "SVC_poly_gamma ") ax.set_xlabel(r"$\\gamma$") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.set_ylim(0,1.05) ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5) ### 测试 r ,此时 gamma固定为10 , degree 固定为 3###### rs=range(0,20) train_scores=[] test_scores=[] for r in rs: cls=svm.SVC(kernel=‘poly‘,gamma=10,degree=3,coef0=r) cls.fit(X_train,y_train) train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train)) test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test)) ax=fig.add_subplot(1,3,3) ax.plot(rs,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker=‘+‘ ) ax.plot(rs,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker=‘o‘ ) ax.set_title( "SVC_poly_r ") ax.set_xlabel(r"r") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.set_ylim(0,1.05) ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5) plt.show() # 调用 test_SVC_poly test_SVC_poly(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
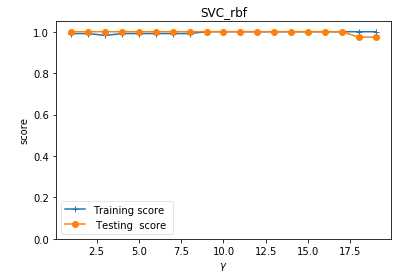
def test_SVC_rbf(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 高斯核的 SVC 的预测性能随 gamma 参数的影响 ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data gammas=range(1,20) train_scores=[] test_scores=[] for gamma in gammas: cls=svm.SVC(kernel=‘rbf‘,gamma=gamma) cls.fit(X_train,y_train) train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train)) test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test)) fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) ax.plot(gammas,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker=‘+‘ ) ax.plot(gammas,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker=‘o‘ ) ax.set_title( "SVC_rbf") ax.set_xlabel(r"$\\gamma$") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.set_ylim(0,1.05) ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5) plt.show() # 调用 test_SVC_rbf test_SVC_rbf(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
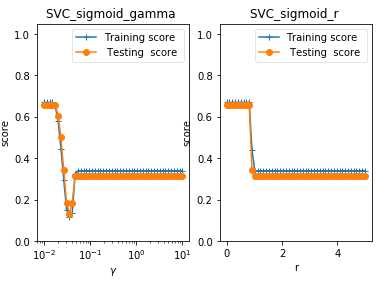
def test_SVC_sigmoid(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 sigmoid 核的 SVC 的预测性能随 gamma、coef0 的影响. ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data fig=plt.figure() ### 测试 gamma ,固定 coef0 为 0 #### gammas=np.logspace(-2,1) train_scores=[] test_scores=[] for gamma in gammas: cls=svm.SVC(kernel=‘sigmoid‘,gamma=gamma,coef0=0) cls.fit(X_train,y_train) train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train)) test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test)) ax=fig.add_subplot(1,2,1) ax.plot(gammas,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker=‘+‘ ) ax.plot(gammas,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker=‘o‘ ) ax.set_title( "SVC_sigmoid_gamma ") ax.set_xscale("log") ax.set_xlabel(r"$\\gamma$") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.set_ylim(0,1.05) ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5) ### 测试 r,固定 gamma 为 0.01 ###### rs=np.linspace(0,5) train_scores=[] test_scores=[] for r in rs: cls=svm.SVC(kernel=‘sigmoid‘,coef0=r,gamma=0.01) cls.fit(X_train,y_train) train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train)) test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test)) ax=fig.add_subplot(1,2,2) ax.plot(rs,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker=‘+‘ ) ax.plot(rs,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker=‘o‘ ) ax.set_title( "SVC_sigmoid_r ") ax.set_xlabel(r"r") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.set_ylim(0,1.05) ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5) plt.show() # 调用 test_SVC_sigmoid test_SVC_sigmoid(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
以上是关于吴裕雄 python 机器学习——支持向量机SVM非线性分类SVC模型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——支持向量机非线性回归SVR模型
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——人工神经网络感知机学习算法的应用
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——人工神经网络与原始感知机模型
吴裕雄--天生自然python机器学习:使用朴素贝叶斯过滤垃圾邮件