第五周课程总结&试验报告
Posted wangweihanqq2001
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第五周课程总结&试验报告相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
实验三 String类的应用
- 实验目的
- 掌握类String类的使用;
- 学会使用JDK帮助文档;
- 实验内容
一、已知字符串:"this is a test of java".按要求执行以下操作:(要求源代码、结果截图。)
1、统计该字符串中字母s出现的次数。
2、统计该字符串中子串“is”出现的次数。
3、统计该字符串中单词“is”出现的次数。
4、实现该字符串的倒序输出。
1-1、实验代码(统计该字符串中字母s出现的次数)
public class text { public static void main(String args[]) { int count=0; String s = "this is a test of java"; char a[]=s.toCharArray(); for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) { if(a[i]==‘s‘) { count++; } } System.out.println(count); } }
1-1、运行结果截图
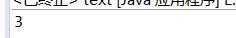
1-2、实验代码(统计该字符串中子串“is”出现的次数)
public class text { public static void main(String args[]) { int count=0; String s = "this is a test of java"; char a[]=s.toCharArray(); for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) { if(a[i]==‘i‘ && a[i+1]==‘s‘) { count++; } } System.out.println(count); } }
1-2、运行结果截图

1-3、实验代码(统计该字符串中单词“is”出现的次数)
public class text { public static void main(String args[]) { int count=0; String s = "this is a test of java"; char a[]=s.toCharArray(); for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) { if(a[i]==‘i‘ && a[i+1]==‘s‘&&a[i-1]==‘ ‘) { count++; } } System.out.println(count); } }
1-3、运行结果截图

1-4、实验代码(实现该字符串的倒序输出)
public class text { public static void main(String args[]) { String s = "this is a test of java"; char a[]=s.toCharArray(); int count=a.length-1; for(int i=count;i>=0;i--) { System.out.print(a[i]); } } }
1-4、运行结果截图

二、请编写一个程序,使用下述算法加密或解密用户输入的英文字串。(要求源代码、结果截图。)
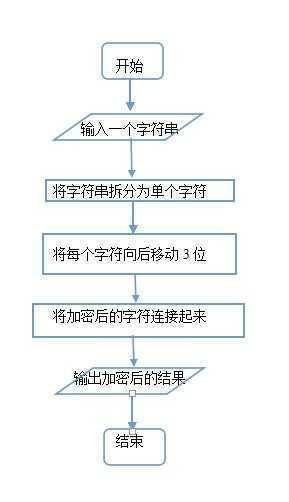
1、实验代码
import java.util.Scanner; public class text { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入一行字符串"); String str = s.nextLine(); char a[]=str.toCharArray(); int j=0; for(int i=0;i < a.length;i++) { if(i < 3) { j=a.length+i-3; } else { j=i-3; } System.out.print(a[j]); } } }
2、运行结果截图

三、已知字符串“ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed”。输出字符串里的大写字母数,小写英文字母数,非英文字母数。
1、实验代码
public class text { public static void main(String args[]) { int a=0,b=0,c=0; String s = "ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed"; char A[]=s.toCharArray(); for(int i=0;i<A.length;i++) { if(A[i] >= ‘a‘ && A[i] <= ‘z‘) { a++; } else if((A[i] >= ‘A‘ && A[i] <= ‘Z‘)) { b++; } else { c++; } System.out.println("小写字母="+a); System.out.println("大写字母="+b); System.out.println("非英文字母数="+c); } } }
2、运行结果截图
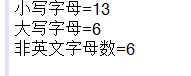
总结:这一次题目难度总体来说不大,但是在第二题上卡了很久,感觉还是实力不足,还要继续努力。
二、学习总结
1、类的继承格式
Class 父类{}
Class 子类 extends 父类{}
2、 继承的限制
只允许多层继承,不能多重继承。
3、方法的重载与覆写的区别
|
序号 |
区别点 |
重载 |
覆写 |
|
1 |
单词 |
Overloading |
Overriding |
|
2 |
定义 |
方法名称相同,参数的类型或个数不同 |
方法名称、参数的类型、返回值类型全部相同 |
|
3 |
对权限没有要求 |
被覆写的方法不能拥有更严格的权限 |
|
|
4 |
范围 |
发生在一个类中 |
发生在继承类中 |
4、在使用继承的时候也应该注意的是:子类是不能直接访问父类中的私有成员的,但是子类可以调用父类中的非私有方法,但是不能直接调用父类中的私有成员
5、抽象类的定义及使用规则
(1)包含一个抽象方法的类必须是抽象类
(2)抽象类和抽象方法都要使用abstract关键字声明
(3)抽象方法只需声明而不需要实现
(4)抽象类必须被子类继承,子类(如果不是抽象类)必须覆写抽象类中的全部抽象方法
6、final关键字
(1)使用final声明的类不能有子类
(2)使用final声明的方法不能被子类覆写
(3)使用final声明的变量为常量,常量不可以修改
以上是关于第五周课程总结&试验报告的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章