Flume简介及使用
Posted areyouready
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Flume简介及使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、Flume概述
1)官网地址 http://flume.apache.org/ 2)日志采集工具
Flume是一种分布式,可靠且可用的服务,用于有效地收集,聚合和移动大量日志数据。它具有基于流数据流的简单灵活的架构。它具有可靠的可靠性机制和许多故障转移和恢复机制,具有强大的容错能力。
它使用简单的可扩展数据模型,允许在线分析应用程序。 3)为什么需要flume 数据从哪里来? -》爬虫 -》日志数据 flume -》传统型数据库 sqoop 4)flume架构 source:数据源 产生数据流,同时source将产生的数据流传输到channel channel:传输通道 用于桥接Source和sinks sinks:下沉 从channel收集数据 event:传输单元 Flume数据传传输的基本单元,以事件的形式将数据送往目的地。
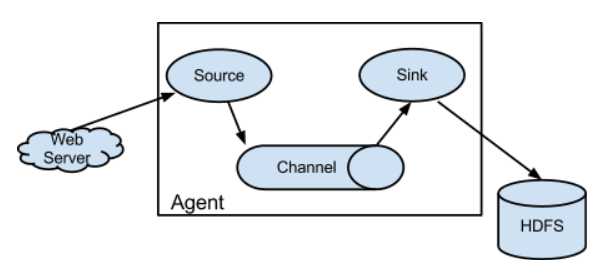
二、Flume安装部署
1)下载安装包 http://archive.apache.org/dist/flume/1.6.0/ 2)上传到linux alt+p 3)解压 tar -zxvf apache-flume-1.6.0-bin.tar.gz 4)重命名 mv apache-flume-1.6.0-bin/ flume cd flume/conf mv flume-env.sh.template flume-env.sh 5)修改配置文件 vi flume-env.sh export JAVA_HOME=/root/hd/jdk1.8.0_144
三、Flume监听端口
1、安装telnet
yum search telnet
yum intsall telnet.x86_64
2、写配置文件 flumejob_telnet.conf
#smple.conf: A single-node Flume configuration # Name the components on this agent 定义变量方便调用 加s可以有多个此角色 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source 描述source角色 进行内容定制 # 此配置属于tcp source 必须是netcat类型 a1.sources.r1.type = netcat a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 # Describe the sink 输出日志文件 a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory(file) 使用内存 总大小1000 每次传输100 a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel 一个source可以绑定多个channel # 一个sinks可以只能绑定一个channel 使用的是图二的模型 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
放置在flume/conf/下
3、启动
bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file conf/flumejob_telnet.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
4、发送数据
telnet localhost 44444
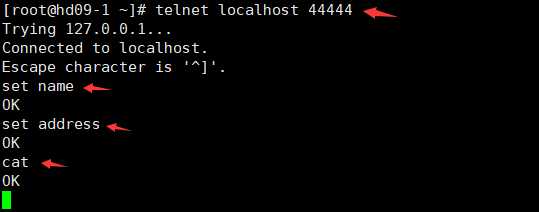
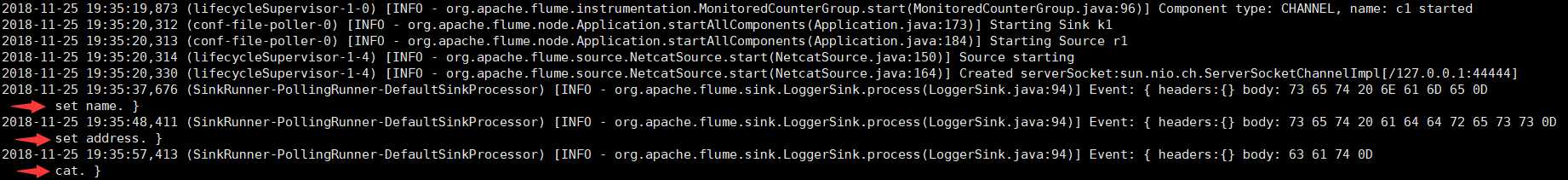
5、查看
四、实时的采集文件到HDFS
1、写配置文件 flumejob_hdfs.conf
# Name the components on this agent a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source # exec 执行一个命令的方式去查看文件 tail -F 实时查看 a1.sources.r1.type = exec # 要执行的脚本command tail -F 默认10行 man tail 查看帮助 a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /tmp/root/hive.log # 执行这个command使用的是哪个脚本 -c 指定使用什么命令 # whereis bash # bash: /usr/bin/bash /usr/share/man/man1/bash.1.gz a1.sources.r1.shell = /usr/bin/bash -c # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hd09-1:9000/flume/%Y%m%d/%H #上传文件的前缀 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = logs- #是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true #多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 秒 (默认30s) a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1 #重新定义时间单位(每小时滚动一个文件夹) a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute #是否使用本地时间戳 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 500 #设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream #多久生成一个新的文件 秒 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 30 #设置每个文件的滚动大小 字节(最好128M) a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 #文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0 #最小冗余数(备份数 生成滚动功能则生效roll hadoop本身有此功能 无需配置) 1份 不冗余 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
2、启动
bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file conf/flumejob_hdfs.conf
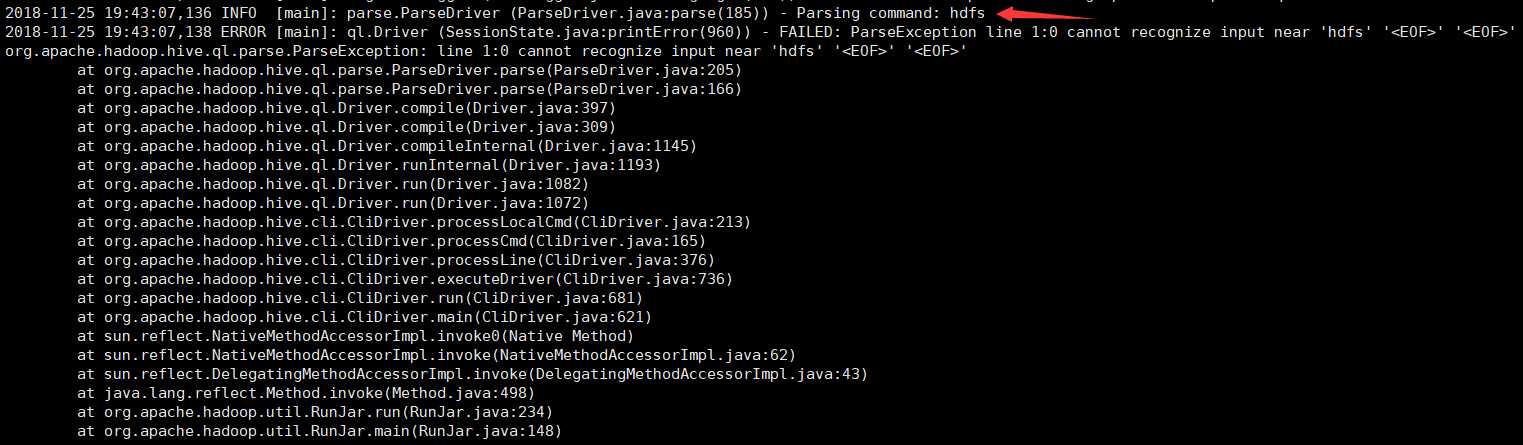
3、此时操作hive客户端
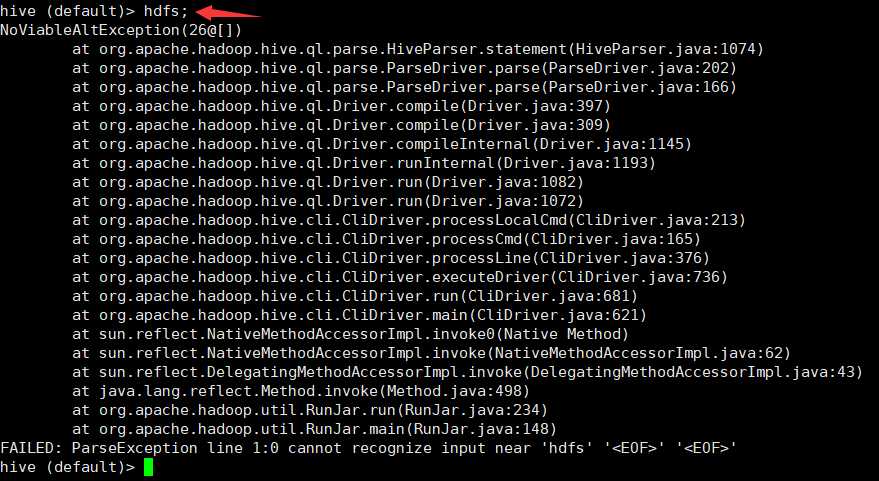
报错日志将存储到hdfs中
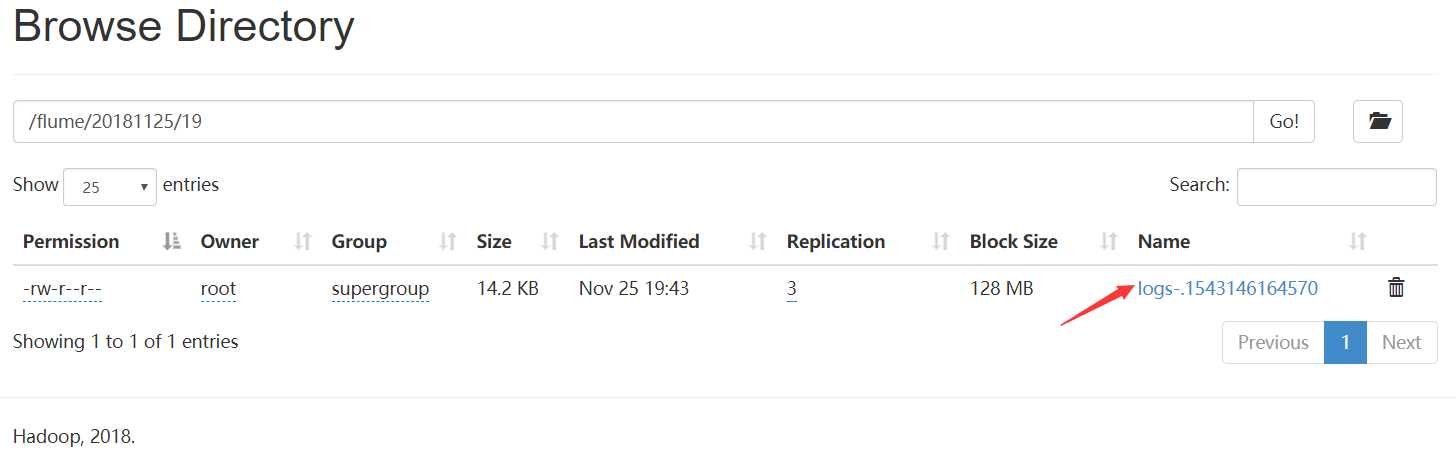
执行
hdfs dfs -cat /flume/20181125/19/logs-.1543146164570
得到文件内容和hive出错的日志一致
五、实时监听文件夹
1、写配置文件 flumejob_dir.conf
# 定义 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir # 监控的文件夹 a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /root/spooldir # 上传成功后显示后缀名 a1.sources.r1.fileSuffix = .COMPLETED # 如论如何 加绝对路径的文件名 默认false a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true #忽略所有以.tmp 结尾的文件(正在被写入),不上传 # ^以任何开头 出现无限次 以.tmp结尾的 a1.sources.r1.ignorePattern = ([^ ]*.tmp) # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hd09-1:9000/flume/spooldir/%Y%m%d/%H #上传文件的前缀 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = spooldir- #是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true #多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1 #重新定义时间单位 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour #是否使用本地时间戳 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 50 #设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream #多久生成一个新的文件 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 600 #设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是 128M a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 #文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0 #最小副本数 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
2、创建/root/spooldir文件夹
cd /root
mkdir spooldir
3、启动
bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file conf/flumejob_dir.conf
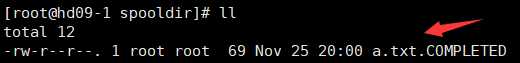
4、将/root下的a.txt复制到spooldir目录下
cp -rf /root/a.txt /root/spooldir/
此时
然后查看hdfs
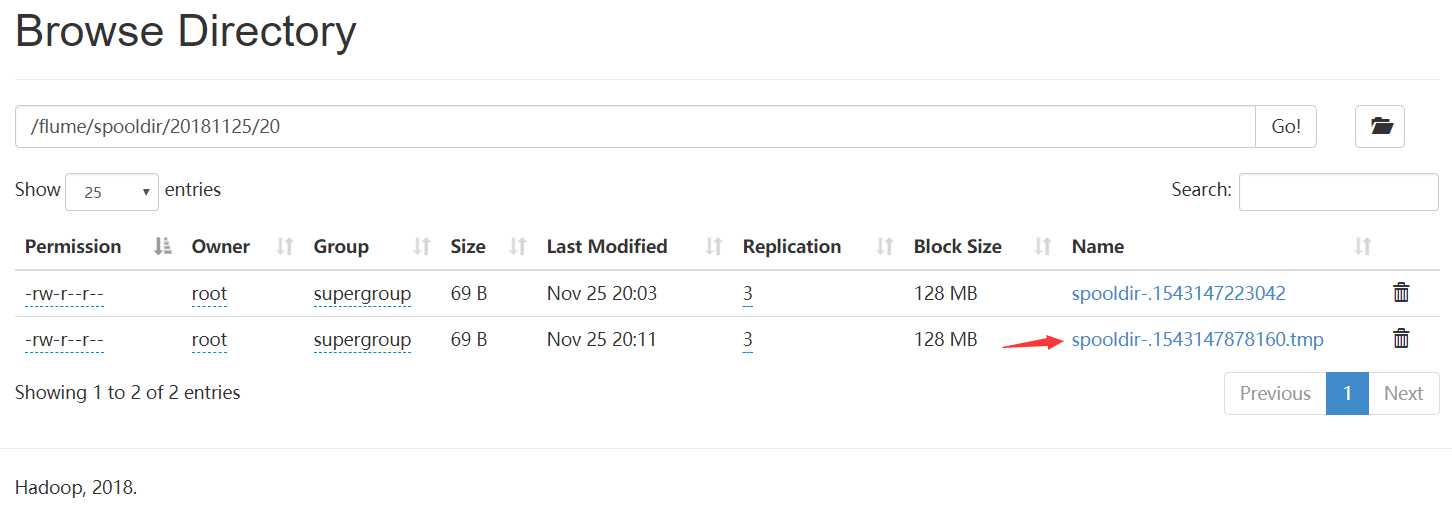
此时/flume/spooldir/20181125/20/spooldir-.1543147878160.tmp 文件中的内容就是a.txt文件中的内容,
如果此时关闭监听命令,那么spooldir-.1543147878160.tmp文件就变成spooldir-.1543147878160文件持久化到hdfs中。
六、多个channel/sink
1、需求
需求:监控hive.log文件,同时产生两个channel,一个channel对应的sink存储到hdfs中,另外一个channel对应的sink存储到本地。
2、示意图
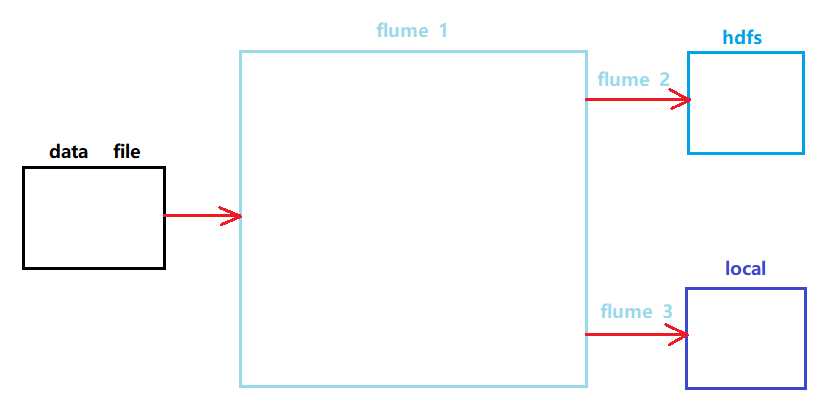
3、写配置文件 flumejob_1.conf
# name the components on this agent a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.channels = c1 c2 # 将数据流复制给多个 channel a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating # Describe/configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = exec a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /tmp/root/hive.log a1.sources.r1.shell = /bin/bash -c # Describe the sink # 分两个端口发送数据 a1.sinks.k1.type = avro a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hd09-1 a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141 a1.sinks.k2.type = avro a1.sinks.k2.hostname = hd09-1 a1.sinks.k2.port = 4142 # Describe the channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 a1.channels.c2.type = memory a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
4、写配置文件 flumejob_2.conf
# Name the components on this agent a2.sources = r1 a2.sinks = k1 a2.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a2.sources.r1.type = avro # 端口抓取数据 a2.sources.r1.bind = hd09-1 a2.sources.r1.port = 4141 # Describe the sink a2.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hd09-1:9000/flume2/%Y%m%d/%H #上传文件的前缀 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = flume2- #是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true #多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1 #重新定义时间单位 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour #是否使用本地时间戳 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100 #设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream #多久生成一个新的文件 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 600 #设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是 128M a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 #文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0 #最小副本数 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1 # Describe the channel a2.channels.c1.type = memory a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
5、写配置文件 flumejob_3.conf
# Name the components on this agent a3.sources = r1 a3.sinks = k1 a3.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a3.sources.r1.type = avro a3.sources.r1.bind = hd09-1 a3.sources.r1.port = 4142 # Describe the sink a3.sinks.k1.type = file_roll a3.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /root/flume2 # Describe the channel a3.channels.c1.type = memory a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a3.sources.r1.channels = c1 a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
6、启动,分别在三个窗口依次执行以下命令
bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file conf/flumejob_1.conf bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file conf/flumejob_2.conf bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file conf/flumejob_3.conf
7、操作hive
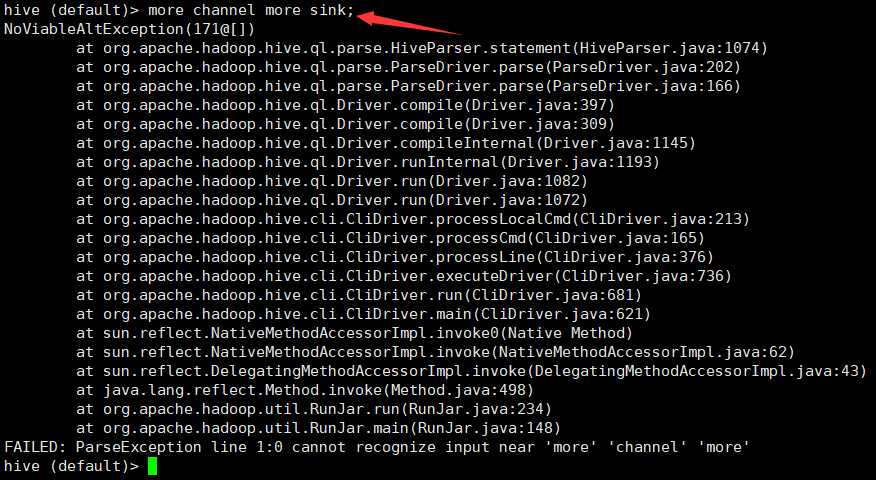
8、此时/root/flume2文件夹中
9、hdfs中
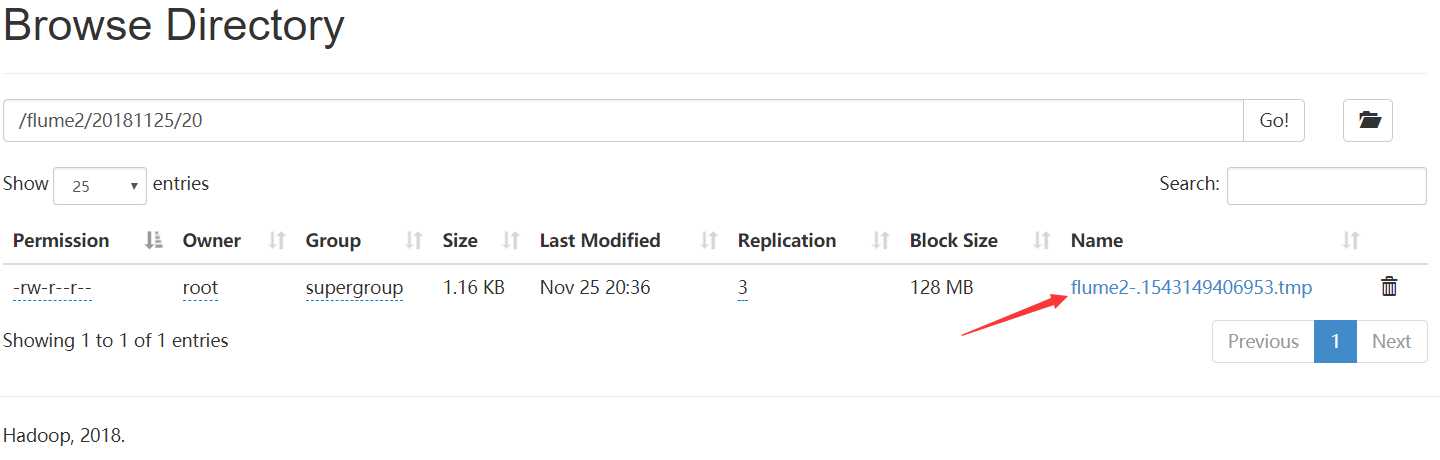
执行
hdfs dfs -cat /flume2/20181125/20/flume2-.1543149406953.tmp
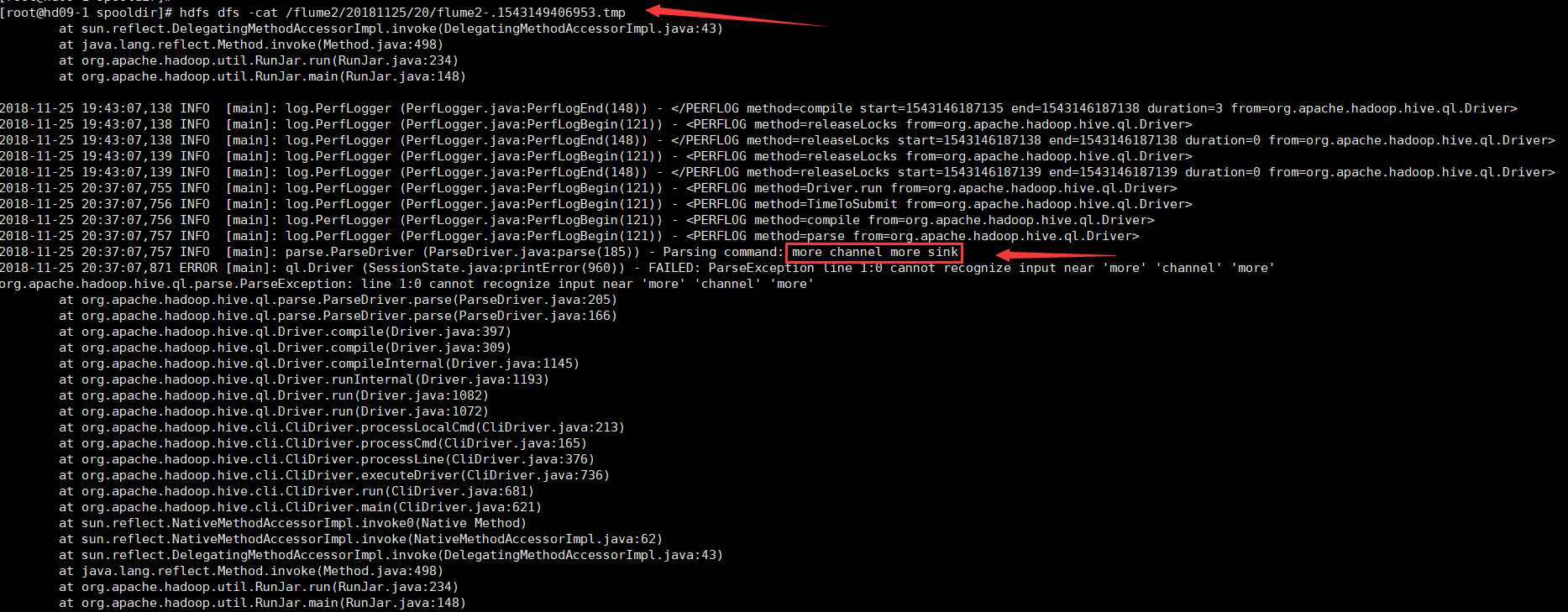
文件flume2-.1543149406953.tmp过一会就变成flume2-.1543149406953
10、至此,实现了监控hive.log文件,同时产生两个channel,一个channel对应的sink存储到hdfs中,另外一个channel对应的sink存储到本地。
以上是关于Flume简介及使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章