Bicriterial routing 双调路径 HYSBZ - 1375(分层最短路)
Posted wtsruvf
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Bicriterial routing 双调路径 HYSBZ - 1375(分层最短路)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Description
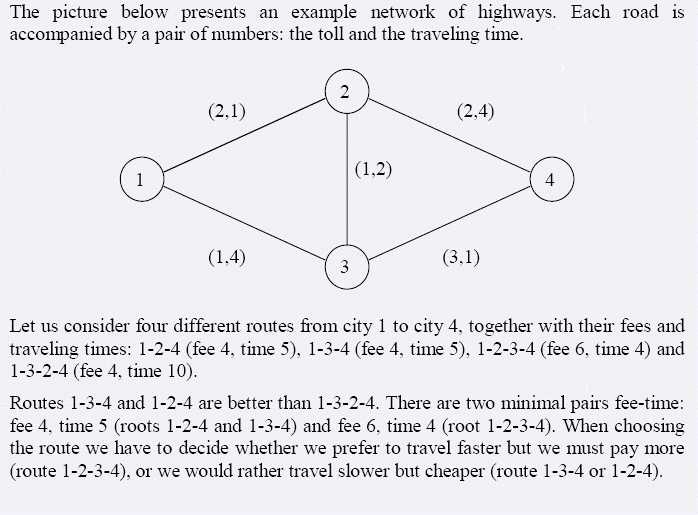
来越多,因此选择最佳路径是很现实的问题。城市的道路是双向的,每条道路有固定的旅行时间以及需要支付的费用。路径由连续的道路组成。总时间是各条道路旅行时间的和,总费用是各条道路所支付费用的总和。同样的出发地和目的地,如果路径A比路径B所需时间少且费用低,那么我们说路径A比路径B好。对于某条路径,如果没有其他路径比它好,那么该路径被称为最优双调路径。这样的路径可能不止一条,或者说根本不存在。 给出城市交通网的描述信息,起始点和终点城市,求最优双条路径的条数。城市不超过100个,边数不超过300,每条边上的费用和时间都不超过100。
Input
第一行给出有多少个点,多少条边,开始点及结束点. 下面的数据用于描述这个地图
Output
有多少条最优双调路径
Sample Input
4 5 1 4
2 1 2 1
3 4 3 1
2 3 1 2
3 1 1 4
2 4 2 4
2 1 2 1
3 4 3 1
2 3 1 2
3 1 1 4
2 4 2 4
Sample Output
2
HINT
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <queue> #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define maxc (n-1)*100 using namespace std; struct edge { int y,ne,c,t; }e[1000]; struct now { int p,c; }; int tot=0,n,m; struct data { int t,f; }d[105][10005]; int s,t,h[105],inq[105][10005]; void Addedge(int x,int y,int co,int ti) { tot++; e[tot].y=y; e[tot].ne=h[x]; h[x]=tot; e[tot].c=co; e[tot].t=ti; } void spfa() { for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) for (int j=0;j<=maxc;j++) d[i][j].f=0,inq[i][j]=0,d[i][j].t=inf; queue<now> q; now x; x.p=s,x.c=0; d[s][0].f=1,d[s][0].t=0; inq[s][0]=1; q.push(x); while (!q.empty()) { x=q.front(); q.pop(); inq[x.p][x.c]=0; for (int i=h[x.p];i;i=e[i].ne) { int y=e[i].y; int co=e[i].c+x.c; if (co>maxc) continue; if (d[y][co].t>d[x.p][x.c].t+e[i].t) { d[y][co].t=d[x.p][x.c].t+e[i].t; d[y][co].f=1; if (!inq[y][co]) { now aa; aa.p=y,aa.c=co; q.push(aa),inq[y][co]=1; } } } } } int main() { scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s,&t); for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) { int x,y,ti,co; scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&co,&ti); Addedge(x,y,co,ti); Addedge(y,x,co,ti); } spfa(); int ans=0,minn=maxc+10; for (int i=0;i<=maxc;i++) { if (!d[t][i].f) continue; if (d[t][i].t>=minn) continue; minn=d[t][i].t; ans++; } cout<<ans<<endl; return 0; }
来越多,因此选择最佳路径是很现实的问题。城市的道路是双向的,每条道路有固定的旅行时间以及需要支付的费用。路径由连续的道路组成。总时间是各条道路旅行时间的和,总费用是各条道路所支付费用的总和。同样的出发地和目的地,如果路径A比路径B所需时间少且费用低,那么我们说路径A比路径B好。对于某条路径,如果没有其他路径比它好,那么该路径被称为最优双调路径。这样的路径可能不止一条,或者说根本不存在。 给出城市交通网的描述信息,起始点和终点城市,求最优双条路径的条数。城市不超过100个,边数不超过300,每条边上的费用和时间都不超过100。Input第一行给出有多少个点,多少条边,开始点及结束点. 下面的数据用于描述这个地图Output有多少条最优双调路径Sample Input4 5 1 4
2 1 2 1
3 4 3 1
2 3 1 2
3 1 1 4
2 4 2 4
Sample Output2Hint
以上是关于Bicriterial routing 双调路径 HYSBZ - 1375(分层最短路)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章