如何学习word2vec
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何学习word2vec相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在word2vec之前所有的词汇表示都是用 one hot表示
类似man这个单词如下表示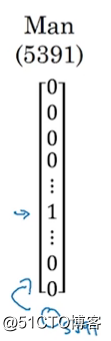
他把每个词语孤立起来,该网络如果想在下面一个句子中填入一个单词,就不会根据apple联想到orange
所以就希望能够使用向量化的方式来表示单词: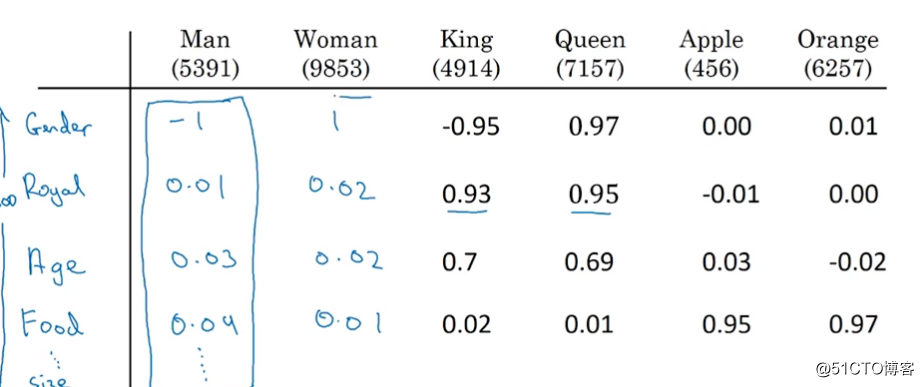
这样Apple和Orange就会有相似的地方,在这个特征空间内会距离比较近。
而且还有这样的特性: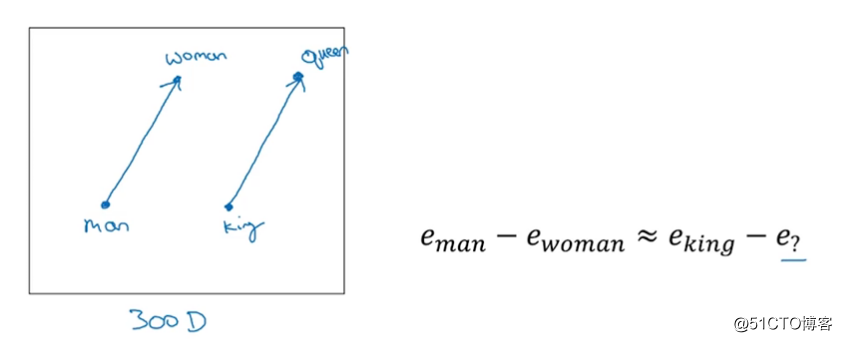
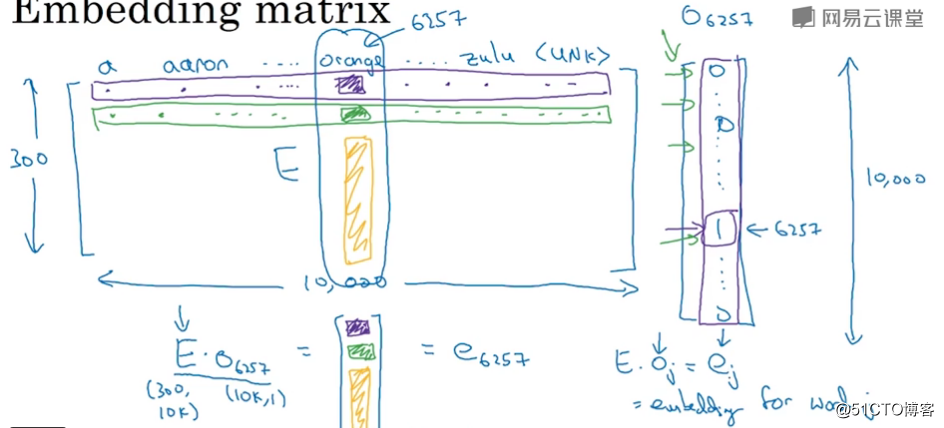
如何学习到这个词嵌入矩阵: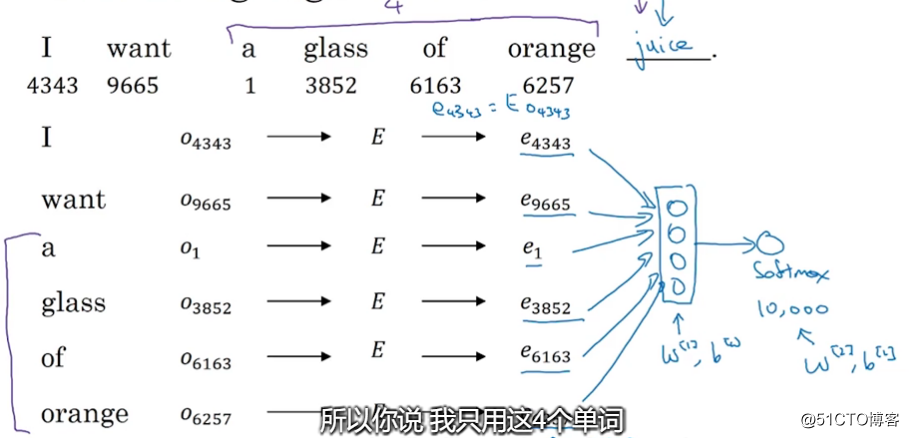
我们建立一个神经网络像上图那样用前面几个词 预测后面一个词
通过误差反向传播就学会了 E矩阵
代码如下:
# coding: utf-8
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import collections
import math
import os
import random
import zipfile
import numpy as np
from six.moves import urllib
from six.moves import xrange # pylint: disable=redefined-builtin
import tensorflow as tf
import pickle
# Step 1: Download the data.
url = ‘http://mattmahoney.net/dc/‘
# 下载数据集
def maybe_download(filename, expected_bytes):
"""Download a file if not present, and make sure it‘s the right size."""
if not os.path.exists(filename):
filename, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(url + filename, filename)
# 获取文件相关属性
statinfo = os.stat(filename)
# 比对文件的大小是否正确
if statinfo.st_size == expected_bytes:
print(‘Found and verified‘, filename)
else:
print(statinfo.st_size)
raise Exception(
‘Failed to verify ‘ + filename + ‘. Can you get to it with a browser?‘)
return filename
filename = maybe_download(‘text8.zip‘, 31344016)
# Read the data into a list of strings.
def read_data(filename):
"""Extract the first file enclosed in a zip file as a list of words"""
with zipfile.ZipFile(filename) as f:
data = tf.compat.as_str(f.read(f.namelist()[0])).split()
return data
# 单词表
words = read_data(filename)
# Data size
print(‘Data size‘, len(words))
# Step 2: Build the dictionary and replace rare words with UNK token.
# 只留50000个单词,其他的词都归为UNK
vocabulary_size = 50000
def build_dataset(words, vocabulary_size):
count = [[‘UNK‘, -1]]
# extend追加一个列表
# Counter用来统计每个词出现的次数
# most_common返回一个TopN列表,只留50000个单词包括UNK
# c = Counter(‘abracadabra‘)
# c.most_common()
# [(‘a‘, 5), (‘r‘, 2), (‘b‘, 2), (‘c‘, 1), (‘d‘, 1)]
# c.most_common(3)
# [(‘a‘, 5), (‘r‘, 2), (‘b‘, 2)]
# 前50000个出现次数最多的词
count.extend(collections.Counter(words).most_common(vocabulary_size - 1))
# 生成 dictionary,词对应编号, word:id(0-49999)
# 词频越高编号越小
dictionary = dict()
for word, _ in count:
dictionary[word] = len(dictionary)
# data把数据集的词都编号
data = list()
unk_count = 0
for word in words:
if word in dictionary:
index = dictionary[word]
else:
index = 0 # dictionary[‘UNK‘]
unk_count += 1
data.append(index)
# 记录UNK词的数量
count[0][1] = unk_count
# 编号对应词的字典
reverse_dictionary = dict(zip(dictionary.values(), dictionary.keys()))
return data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary
# data 数据集,编号形式
# count 前50000个出现次数最多的词
# dictionary 词对应编号
# reverse_dictionary 编号对应词
data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary = build_dataset(words, vocabulary_size)
del words # Hint to reduce memory.
print(‘Most common words (+UNK)‘, count[:5])
print(‘Sample data‘, data[:10], [reverse_dictionary[i] for i in data[:10]])
data_index = 0
# Step 3: Function to generate a training batch for the skip-gram model.
def generate_batch(batch_size, num_skips, skip_window):
global data_index
assert batch_size % num_skips == 0
assert num_skips <= 2 * skip_window
batch = np.ndarray(shape=(batch_size), dtype=np.int32)
labels = np.ndarray(shape=(batch_size, 1), dtype=np.int32)
span = 2 * skip_window + 1 # [ skip_window target skip_window ]
buffer = collections.deque(maxlen=span)
# [ skip_window target skip_window ]
# [ skip_window target skip_window ]
# [ skip_window target skip_window ]
# [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ...]
# t i
# 循环3次
for _ in range(span):
buffer.append(data[data_index])
data_index = (data_index + 1) % len(data)
# 获取batch和labels
for i in range(batch_size // num_skips):
target = skip_window # target label at the center of the buffer
targets_to_avoid = [skip_window]
# 循环2次,一个目标单词对应两个上下文单词
for j in range(num_skips):
while target in targets_to_avoid:
# 可能先拿到前面的单词也可能先拿到后面的单词
target = random.randint(0, span - 1)
targets_to_avoid.append(target)
batch[i * num_skips + j] = buffer[skip_window]
labels[i * num_skips + j, 0] = buffer[target]
buffer.append(data[data_index])
data_index = (data_index + 1) % len(data)
# Backtrack a little bit to avoid skipping words in the end of a batch
# 回溯3个词。因为执行完一个batch的操作之后,data_index会往右多偏移span个位置
data_index = (data_index + len(data) - span) % len(data)
return batch, labels
# 打印sample data
batch, labels = generate_batch(batch_size=8, num_skips=2, skip_window=1)
for i in range(8):
print(batch[i], reverse_dictionary[batch[i]],
‘->‘, labels[i, 0], reverse_dictionary[labels[i, 0]])
# Step 4: Build and train a skip-gram model.
batch_size = 128
# 词向量维度
embedding_size = 128 # Dimension of the embedding vector.
skip_window = 1 # How many words to consider left and right.
num_skips = 2 # How many times to reuse an input to generate a label.
# We pick a random validation set to sample nearest neighbors. Here we limit the
# validation samples to the words that have a low numeric ID, which by
# construction are also the most frequent.
valid_size = 16 # Random set of words to evaluate similarity on.
valid_window = 100 # Only pick dev samples in the head of the distribution.
# 从0-100抽取16个整数,无放回抽样
valid_examples = np.random.choice(valid_window, valid_size, replace=False)
# 负采样样本数
num_sampled = 64 # Number of negative examples to sample.
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
# Input data.
train_inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size])
train_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size, 1])
valid_dataset = tf.constant(valid_examples, dtype=tf.int32)
# Ops and variables pinned to the CPU because of missing GPU implementation
# with tf.device(‘/cpu:0‘):
# 词向量
# Look up embeddings for inputs.
embeddings = tf.Variable(
tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0))
# embedding_lookup(params,ids)其实就是按照ids顺序返回params中的第ids行
# 比如说,ids=[1,7,4],就是返回params中第1,7,4行。返回结果为由params的1,7,4行组成的tensor
# 提取要训练的词
embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, train_inputs)
# Construct the variables for the noise-contrastive estimation(NCE) loss
nce_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, embedding_size],
stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(embedding_size)))
nce_biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([vocabulary_size]))
# Compute the average NCE loss for the batch.
# tf.nce_loss automatically draws a new sample of the negative labels each
# time we evaluate the loss.
loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.nce_loss(weights=nce_weights,
biases=nce_biases,
labels=train_labels,
inputs=embed,
num_sampled=num_sampled,
num_classes=vocabulary_size))
# Construct the SGD optimizer using a learning rate of 1.0.
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1).minimize(loss)
# Compute the cosine similarity between minibatch examples and all embeddings.
norm = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(embeddings), 1, keep_dims=True))
normalized_embeddings = embeddings / norm
# 抽取一些常用词来测试余弦相似度
valid_embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(
normalized_embeddings, valid_dataset)
# valid_size == 16
# [16,1] * [1*50000] = [16,50000]
similarity = tf.matmul(
valid_embeddings, normalized_embeddings, transpose_b=True)
# Add variable initializer.
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Step 5: Begin training.
num_steps = 100001
final_embeddings = []
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as session:
# We must initialize all variables before we use them.
init.run()
print("Initialized")
average_loss = 0
for step in xrange(num_steps):
# 获取一个批次的target,以及对应的labels,都是编号形式的
batch_inputs, batch_labels = generate_batch(
batch_size, num_skips, skip_window)
feed_dict = {train_inputs: batch_inputs, train_labels: batch_labels}
# We perform one update step by evaluating the optimizer op (including it
# in the list of returned values for session.run()
_, loss_val = session.run([optimizer, loss], feed_dict=feed_dict)
average_loss += loss_val
# 计算训练2000次的平均loss
if step % 2000 == 0:
if step > 0:
average_loss /= 2000
# The average loss is an estimate of the loss over the last 2000 batches.
print("Average loss at step ", step, ": ", average_loss)
average_loss = 0
# Note that this is expensive (~20% slowdown if computed every 500 steps)
if step % 20000 == 0:
sim = similarity.eval()
# 计算验证集的余弦相似度最高的词
for i in xrange(valid_size):
# 根据id拿到对应单词
valid_word = reverse_dictionary[valid_examples[i]]
top_k = 8 # number of nearest neighbors
# 从大到小排序,排除自己本身,取前top_k个值
nearest = (-sim[i, :]).argsort()[1:top_k + 1]
log_str = "Nearest to %s:" % valid_word
for k in xrange(top_k):
close_word = reverse_dictionary[nearest[k]]
log_str = "%s %s," % (log_str, close_word)
print(log_str)
# 训练结束得到的词向量
final_embeddings = normalized_embeddings.eval()
# Step 6: Visualize the embeddings.
def plot_with_labels(low_dim_embs, labels, filename=‘tsne.png‘):
assert low_dim_embs.shape[0] >= len(labels), "More labels than embeddings"
# 设置图片大小
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 15)) # in inches
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
x, y = low_dim_embs[i, :]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.annotate(label,
xy=(x, y),
xytext=(5, 2),
textcoords=‘offset points‘,
ha=‘right‘,
va=‘bottom‘)
plt.savefig(filename)
try:
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
tsne = TSNE(perplexity=30, n_components=2, init=‘pca‘, n_iter=5000, method=‘exact‘)# mac:method=‘exact‘
# 画500个点
plot_only = 500
low_dim_embs = tsne.fit_transform(final_embeddings[:plot_only, :])
labels = [reverse_dictionary[i] for i in xrange(plot_only)]
plot_with_labels(low_dim_embs, labels)
except ImportError:
print("Please install sklearn, matplotlib, and scipy to visualize embeddings.")以上是关于如何学习word2vec的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章