2架构设计
Posted gshao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2架构设计相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
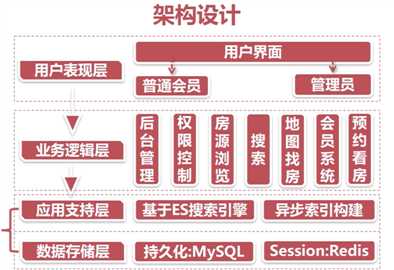
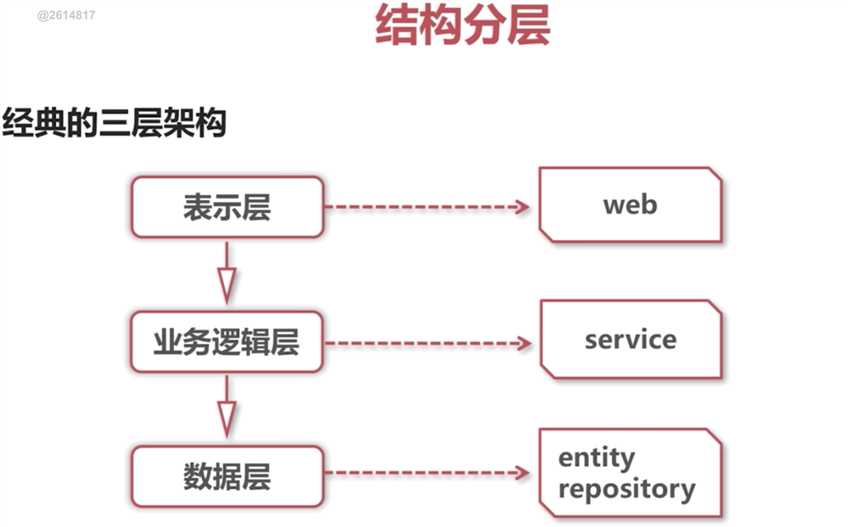
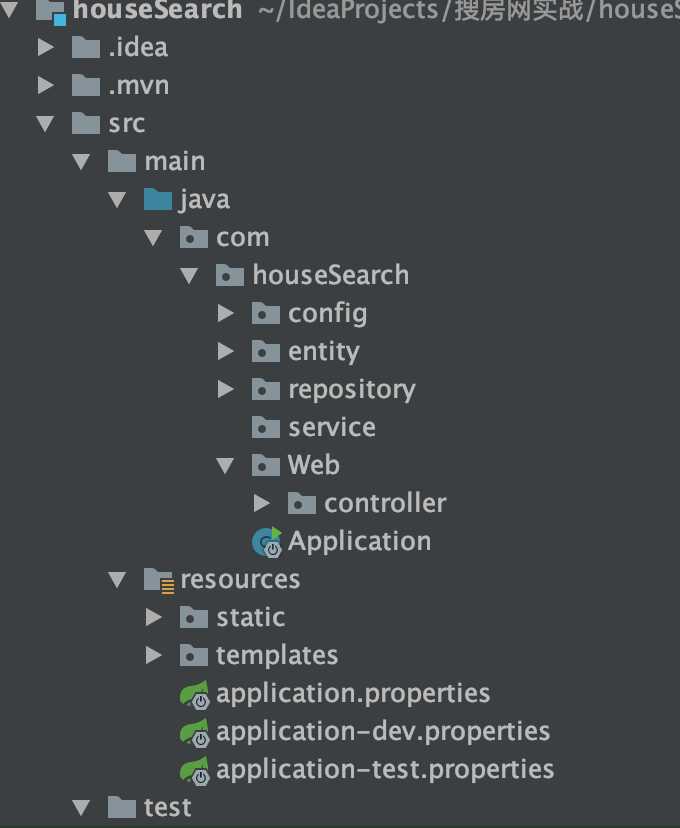
1、架构设计与分层
2、API结构设计_RESTFul API
什么是REST?
REST,即Representational State Transfer的缩写,中文是"表现层状态转化"。
它是一种互联网应用程序的API设计理念:可以用URL定位资源,用HTTP动词(GET,POST,DELETE,DETC)描述操作来解释什么是REST。
其实全称是 Resource Representational State Transfer:通俗来讲就是:资源在网络中以某种表现形式进行状态转移。(再通俗来说,就是通过HTTP请求服务器上的某资源,使该资源copy了一份到服务请求方那去了(get动作)。个人这么理解)
我们分解开来进行解释:
Resource:资源,即数据它可以是一段文本、一张图片、一首歌曲等;
Representational:某种表现形式,比如用JSON,XML,JPEG等;HTTP请求的头信息中用Accept和Content-Type字段指定,这两个字段才是对"表现形式"的描述。
State Transfer:状态变化。通过HTTP动词实现。
注:互联网通信协议HTTP协议,是一个无状态协议。**这意味着,所有的状态都保存在服务器端。**因此,如果客户端想要操作服务器,必须通过某种手段,让服务器端发生"状态转化"(State Transfer)。HTTP协议里面,四个表示操作方式的动词:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE。它们分别对应四种基本操作:GET用来获取资源,POST用来新建资源(也可以用于更新资源),PUT用来更新资源,DELETE用来删除资源。
什么是REST ful API ?
基于REST构建的API就是Restful风格。
3、API结构设计_标准制定
为了满足实际需求,自己封装API格式,代码如下:
package com.houseSearch.base;
/**
* API格式封装
* Created by 小劭.
*/
public class ApiResponse {
private int code;//自定义请求状态码
private String message;//自定义请求相应信息描述
private Object data;//请求目标数据
private boolean more;
public ApiResponse(int code, String message, Object data) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
this.data = data;
}
public ApiResponse() {
this.code = Status.SUCCESS.getCode();
this.message = Status.SUCCESS.getStandardMessage();
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public boolean isMore() {
return more;
}
public void setMore(boolean more) {
this.more = more;
}
public static ApiResponse ofMessage(int code, String message) {
return new ApiResponse(code, message, null);
}
public static ApiResponse ofSuccess(Object data) {
return new ApiResponse(Status.SUCCESS.getCode(), Status.SUCCESS.getStandardMessage(), data);
}
public static ApiResponse ofStatus(Status status) {
return new ApiResponse(status.getCode(), status.getStandardMessage(), null);
}
public enum Status {
SUCCESS(200, "OK"),
BAD_REQUEST(400, "Bad Request"),
NOT_FOUND(404, "Not Found"),
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(500, "Unknown Internal Error"),
NOT_VALID_PARAM(40005, "Not valid Params"),
NOT_SUPPORTED_OPERATION(40006, "Operation not supported"),
NOT_LOGIN(50000, "Not Login");
private int code;
private String standardMessage;
Status(int code, String standardMessage) {
this.code = code;
this.standardMessage = standardMessage;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getStandardMessage() {
return standardMessage;
}
public void setStandardMessage(String standardMessage) {
this.standardMessage = standardMessage;
}
}
}
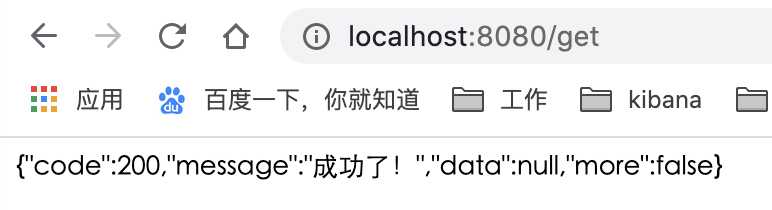
然后在HomeController文件添加如下代码以及运行结果如下:

4、API结构设计_异常拦截器
项目运行过程中,有很多未知的情况,比如:页面或者接口的异常、用户访问的页面不存在、用户的权限不足等等。所以这里设计一个异常拦截器,主要体现着两个方面:
1、页面异常拦截器
2、API异常拦截器
如下,未知的请求,会显示springboot默认的 “Whitelabel Error Page”页面信息。所以要在application.properties配置文件中加上
server.error.whitelabel.enabled=false表示关闭springBoot默认的错误页面显示。
实现步骤:编写AppErrorController web错误 全局配置类,然后添加相应403、404、500等错误页面,这里不展示页面相关代码。
package com.houseSearch.base;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorAttributes;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorController;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* web错误 全局配置
* Created by 小劭.
*/
@Controller
public class AppErrorController implements ErrorController {
private static final String ERROR_PATH = "/error";
private ErrorAttributes errorAttributes;
@Override
public String getErrorPath() {
return ERROR_PATH;
}
@Autowired
public AppErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
this.errorAttributes = errorAttributes;
}
/**
* Web页面错误处理
*/
@RequestMapping(value = ERROR_PATH, produces = "text/html")
public String errorPageHandler(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
int status = response.getStatus();
switch (status) {
case 403:
return "403";
case 404:
return "404";
case 500:
return "500";
}
return "index";
}
/**
* 除Web页面外的错误处理,比如Json/XML等
*/
@RequestMapping(value = ERROR_PATH)
@ResponseBody
public ApiResponse errorApiHandler(HttpServletRequest request) {
RequestAttributes requestAttributes = new ServletRequestAttributes(request);
Map<String, Object> attr = this.errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes(requestAttributes, false);
int status = getStatus(request);
return ApiResponse.ofMessage(status, String.valueOf(attr.getOrDefault("message", "error")));
}
private int getStatus(HttpServletRequest request) {
Integer status = (Integer) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
if (status != null) {
return status;
}
return 500;
}
}
以上是关于2架构设计的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Express实战 - 应用案例- realworld-API - 路由设计 - mongoose - 数据验证 - 密码加密 - 登录接口 - 身份认证 - token - 增删改查API(代码片段