论如何设计一款端对端加密通讯软件
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了论如何设计一款端对端加密通讯软件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
本文仅讨论设计思路,软件demo已经写好,是基于QT版本编写的,后期会挂在我的gitee上供大家参考,本文中部分片段代码均为demo中的代码片段。
设计架构
在目前IPv4的大前提下,为了在复杂网络环境中稳定通讯,都采用了C/S的模式,需要消息中转服务器(网络基础知识不在本文讨论范围,自行填空)。
消息服务器主要作用:
1、处理客户端与服务器之间的C/S消息。此类消息不需要其他客户端参与,由客户端发起请求,服务器执行完毕后将结果返回给该客户端。主要有:登录、注册、修改用户信息、获取离线消息等。
2、协助客户端与客户端之间的C2C消息。如果两个客户端均在线(登录状态)则直接转发消息,如果有一方离线,则缓存消息到数据库,等待该客户端上线后拉取离线消息时发还。
3、处理用户身份认证。对用户的登录、注销请求进行认证,并发放一次性访问令牌。
通讯加密的主要方式:
1、客户端与客户端之间的C2C消息中,聊天内容字段肯定是要加密的,且加解密仅限于两个客户端之间,服务器在转发和缓存消息的过程中,无法解密消息内容。参考signal聊天软件的模式,可以采用DH密钥协商算法(本文使用的是openssl库的ECDH),协商后的AES加密密钥保存在两个客户端自己本地,服务器不参与该内容的加解密。(网络包格式图片中灰色部分)
2、客户端与服务器之间的C/S消息理论上无需加密,因为没有聊天内容字段的信息,但为了保护用户登录认证、用户信息等内容,通讯内容也最好加密。本文使用的方法是:客户端使用预服务器设好的AES对称密钥加密后发送给服务器,服务器对内容进行解密后再进一步处理。(网络包格式图片中橙色部分)

网络包的结构:
总结以上两个方面,本文设计的网络封包格式如下:

部分细节:
仅展示消息结构体(网络包格式图片中绿色部分)的设计详情,其他细节请参考项目源码。
请求数据包(客户端->服务器)

返回数据包(服务器->客户端)

Flutter上线项目实战——即时通讯端对端加密(E2E)
1.背景知识
- 数字签名算法EdDSA: ed25519
- 密钥交换算法ECDH: x25519
- 加密算法AES
- 参考阅读: http://www.freebuf.com/articles/database/113855.html
2.设计思路
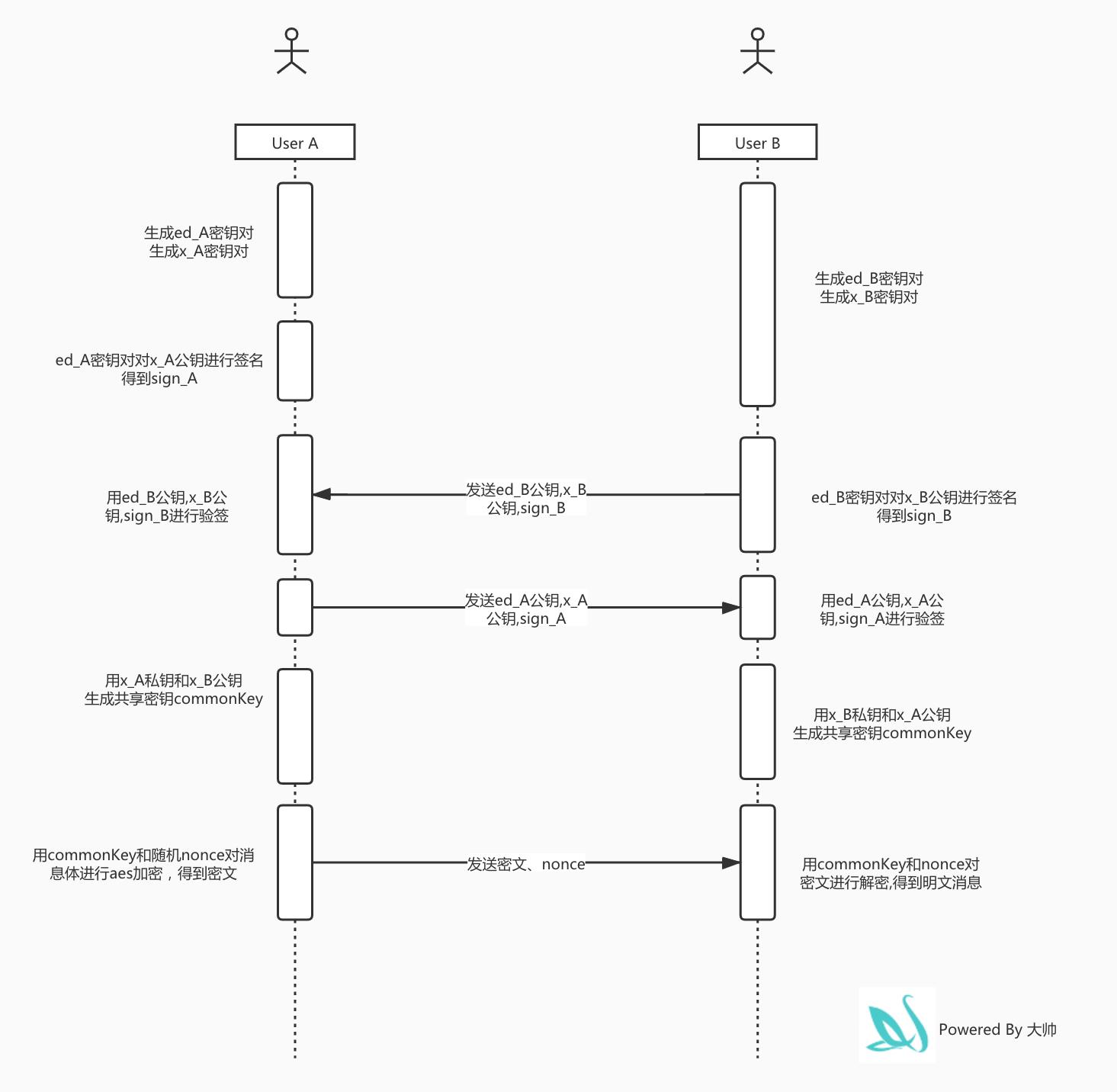
>> image link
3.流程代码
- 引入加解密库
cryptography: ^1.4.0
- 主流程
static Future<void> mainLogic() async {
// User A 生成密钥
var keyPairEd25519App1 = await ed25519.newKeyPair();
var keyPairX25519App1 = await x25519.newKeyPair();
// User B 生成密钥
var keyPairEd25519App2 = await ed25519.newKeyPair();
var keyPairX25519App2 = await x25519.newKeyPair();
// User A通过 ed25519 密钥对对 x25519 的公钥进行签名
var signature1 = await EncryptUtil.sign(keyPairX25519App1.publicKey.bytes, keyPairEd25519App1);
// User B通过 ed25519 密钥对对 x25519 的公钥进行签名
var signature2 = await EncryptUtil.sign(keyPairX25519App2.publicKey.bytes, keyPairEd25519App2);
// User A验证签名
var publicKeyEd25519App2 = base64.encode(keyPairEd25519App2.publicKey.bytes);
var publicKeyX25519App2 = base64.encode(keyPairX25519App2.publicKey.bytes);
var isMatch1 = await EncryptUtil.verify(publicKeyEd25519App2, publicKeyX25519App2, signature2);
assert(isMatch1);
// User B验证签名
var publicKeyEd25519App1 = base64.encode(keyPairEd25519App1.publicKey.bytes);
var publicKeyX25519App1 = base64.encode(keyPairX25519App1.publicKey.bytes);
var isMatch2 = await EncryptUtil.verify(publicKeyEd25519App1, publicKeyX25519App1, signature1);
assert(isMatch2);
// User A 生成共享密钥
var commomKey1 = await EncryptUtil.sharedSecret(keyPairX25519App1.privateKey, publicKeyX25519App2);
L.d('app1 计算共享密钥: ${base64.encode(sc1)}');
// User B 生成共享密钥
var commomKey2 = await EncryptUtil.sharedSecret(keyPairX25519App2.privateKey, publicKeyX25519App1);
L.d('app2 计算共享密钥: ${base64.encode(sc2)}');
assert(base64.encode(commomKey1) == base64.encode(commomKey2));
// User A 加密消息
SecretKey secretKey = SecretKey(base64.decode(commonKey1));
Nonce nonce = Nonce.randomBytes(12);
List<int> message = utf8.encode('要加密的消息');
Uint8List encrypted = await EncryptUtil.encrypt(message, secretKey, nonce);
// 发送加密消息
String nonceString = nonce.bytes.toString();
String body = base64Encode(encrypted);
sendMsg(body, nonceString);
// User B 解密
SecretKey secretKey = SecretKey(base64.decode(commonKey2));
Nonce nonce = await getNonceByString(nonceString);
Uint8List decrypted = await EncryptUtil.decrypt(base64Decode(body), secretKey, nonce);
// 打印明文
String result = utf8.decode(decrypted);
}
- 元子操作
class EncryptUtil {
// 根据本地密钥和远程公钥,计算出共享密钥
static Future<List<int>> sharedSecret(PrivateKey localPrivateKey, String remotePublicKey) async {
PublicKey pk = PublicKey(base64.decode(remotePublicKey));
// We can now calculate a shared 256-bit secret
SecretKey sharedSecret = await x25519.sharedSecret(
localPrivateKey: localPrivateKey,
remotePublicKey: pk,
);
List<int> secretBytes = await sharedSecret.extract();
return secretBytes;
}
/// 用 ED25519 key pair 对 X25519 publicKey 签名
static Future<String> sign(List<int> publicKeyX25519, KeyPair keyPairEd25519) async {
// Sign
Signature signature = await ed25519.sign(publicKeyX25519, keyPairEd25519);
return base64.encode(signature.bytes);
}
/// 验证公钥与签名是否匹配
static Future<bool> verify(publicKeyEd25519, publicKeyX25519, String signature) async {
PublicKey pk = PublicKey(base64.decode(publicKeyEd25519));
Signature s2 = Signature(base64.decode(signature), publicKey: pk);
bool isSignatureCorrect = await ed25519.verify(base64.decode(publicKeyX25519), s2);
return isSignatureCorrect;
}
/// AES-CTR加密消息, 并附加Hmac签名
static Future<Uint8List> encrypt(Uint8List byte, SecretKey secretKey, Nonce nonce) async {
CipherWithAppendedMac cipher = CipherWithAppendedMac(aesCtr, Hmac(sha512));
Uint8List encrypted = await cipher.encrypt(
byte,
secretKey: secretKey,
nonce: nonce,
);
return encrypted;
}
/// AES-CTR解密消息, 并验证Hmac签名
static Future<Uint8List> decrypt(Uint8List encrypted, SecretKey secretKey, Nonce nonce) async {
CipherWithAppendedMac cipher = CipherWithAppendedMac(aesCtr, Hmac(sha512));
Uint8List decrypted = await cipher.decrypt(
encrypted,
secretKey: secretKey,
nonce: nonce,
);
return decrypted;
}
static Future<Nonce> getNonceByString(String nonceStr) async {
String str = nonceStr.substring(1, nonceStr.length - 1);
List nonceList = str.split(',');
List<int> nonceResult = [];
for (int i = 0; i < nonceList.length; i++) {
nonceResult.add(int.parse(nonceList[i]));
}
Nonce nonce = Nonce(nonceResult);
return nonce;
}
}
完结,撒花🎉
以上是关于论如何设计一款端对端加密通讯软件的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章