聚类的外部指标(Purity, ARI, NMI, ACC) 和内部指标(NCC,Entropy,Compactness,Silhouette Index),附代码 (Python 和 Matlab)
Posted 阿卡西番茄酱
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了聚类的外部指标(Purity, ARI, NMI, ACC) 和内部指标(NCC,Entropy,Compactness,Silhouette Index),附代码 (Python 和 Matlab)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
聚类性能评估的外部指标和内部指标,附代码 (Python 和 Matlab)
文章目录
众所周知,聚类有效性指标,包括外部指标和内部指标,对于评价聚类结果的质量非常有用。
1 外部指标
1.1 Purity
原理解释
先给出Purity的计算公式:

首先解释一下,为什么需要引入纯度计算,因为聚类中总是会出现此类与标签对应的类不一致,虽然他们表示的数字都是1,但是实质内容可能不一致。
用一个例子说明,例子借用了博客评价聚类的指标:纯度、兰德系数以及调整兰德系数 - 简书


详细请见上述我附上的链接地址~
Python代码
def purity(labels_true, labels_pred):
clusters = np.unique(labels_pred)
labels_true = np.reshape(labels_true, (-1, 1))
labels_pred = np.reshape(labels_pred, (-1, 1))
count = []
for c in clusters:
idx = np.where(labels_pred == c)[0]
labels_tmp = labels_true[idx, :].reshape(-1)
count.append(np.bincount(labels_tmp).max())
return np.sum(count) / labels_true.shape[0]
Matlab代码
function [purity] = Purity(labels_true, labels_pred)
clusters = unique(labels_pred);
labels_true = labels_true';
labels_pred = labels_pred';
labels_true = labels_true(:);
labels_pred = labels_pred(:);
count = [];
for c = 1:length(clusters)
idx = find(labels_pred == c);
temp = labels_true(idx);
labels_tmp = reshape(temp,1,length(temp(:)));
T=tabulate(labels_tmp);
count = [count, max(T(:,2))];
end
purity = sum(count)/size(labels_true,1);
end
感谢Redmor提供的matlab代码~
1.2 ARI
原理解释
参考博客 调整兰德系数(Adjusted Rand index,ARI)的计算_的图表~
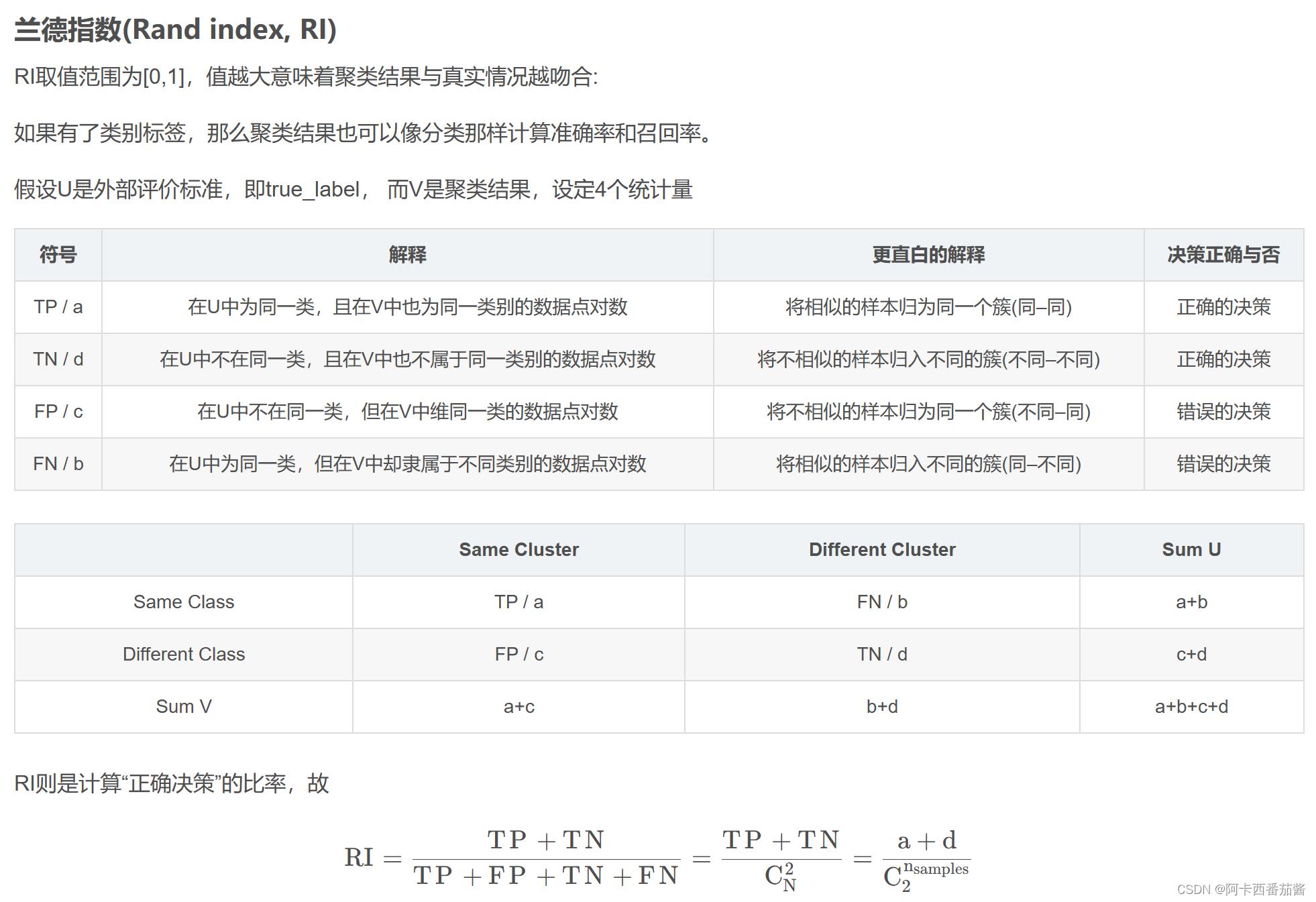
但是由于RI无法保证随机划分的聚类结果的RI值接近于0,所以现在主流科研工作者,使用的外部指标偏向于ARI,更加客观。
ARI的改进如下:
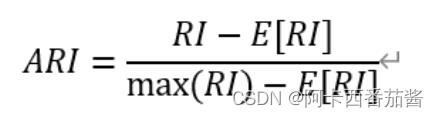
取值为[-1,1],绝对值越大效果越好~注意是绝对值噢。
Python 代码
def ARI(labels_true, labels_pred, beta=1.):
from sklearn.metrics import adjusted_rand_score
ari = adjusted_rand_score(labels_true, labels_pred)
return ari
Matlab 代码
function ri = Eva_ARI(p1, p2, varargin)
%RAND_INDEX Computes the rand index between two partitions.
% RAND_INDEX(p1, p2) computes the rand index between partitions p1 and
% p2.
%
% RAND_INDEX(p1, p2, 'adjusted'); computes the adjusted rand index
% between partitions p1 and p2. The adjustment accounts for chance
% correlation.
% Parse the input and throw errors
adj = 0;
if nargin == 0
end
if nargin > 3
error('Too many input arguments');
end
if nargin == 3
if strcmp(varargin1, 'adjusted')
adj = 1;
else
error('%s is an unrecognized argument.', varargin1);
end
end
if length(p1)~=length(p2)
error('Both partitions must contain the same number of points.');
end
% Preliminary computations and cleansing of the partitions
N = length(p1);
[~, ~, p1] = unique(p1);
N1 = max(p1);
[~, ~, p2] = unique(p2);
N2 = max(p2);
% Create the matching matrix
for i=1:1:N1
for j=1:1:N2
G1 = find(p1==i);
G2 = find(p2==j);
n(i,j) = length(intersect(G1,G2));
end
end
% If required, calculate the basic rand index
if adj==0
ss = sum(sum(n.^2));
ss1 = sum(sum(n,1).^2);
ss2 =sum(sum(n,2).^2);
ri = (nchoosek2(N,2) + ss - 0.5*ss1 - 0.5*ss2)/nchoosek2(N,2);
end
% Otherwise, calculate the adjusted rand index
if adj==1
ssm = 0;
sm1 = 0;
sm2 = 0;
for i=1:1:N1
for j=1:1:N2
ssm = ssm + nchoosek2(n(i,j),2);
end
end
temp = sum(n,2);
for i=1:1:N1
sm1 = sm1 + nchoosek2(temp(i),2);
end
temp = sum(n,1);
for i=1:1:N2
sm2 = sm2 + nchoosek2(temp(i),2);
end
NN = ssm - sm1*sm2/nchoosek2(N,2);
DD = (sm1 + sm2)/2 - sm1*sm2/nchoosek2(N,2);
ri = NN/DD;
end
% Special definition of n choose k
function c = nchoosek2(a,b)
if a>1
c = nchoosek(a,b);
else
c = 0;
end
end
end
hungarian函数可以直接去matlab中文社区获取噢或者后台私信我~
1.3 NMI
原理解释
大家可以参考这一篇博客,讲的很详细~
我就简单附上代码啦
Python 代码
def NMI_sklearn(predict, label):
# return metrics.adjusted_mutual_info_score(predict, label)
return metrics.normalized_mutual_info_score(predict, label)
Matlab代码
function z = Eva_NMI(x, y)
assert(numel(x) == numel(y));
n = numel(x);
x = reshape(x,1,n);
y = reshape(y,1,n);
l = min(min(x),min(y));
x = x-l+1;
y = y-l+1;
k = max(max(x),max(y));
idx = 1:n;
Mx = sparse(idx,x,1,n,k,n);
My = sparse(idx,y,1,n,k,n);
Pxy = nonzeros(Mx'*My/n);
Hxy = -dot(Pxy,log2(Pxy));
Px = nonzeros(mean(Mx,1));
Py = nonzeros(mean(My,1));
Hx = -dot(Px,log2(Px));
Hy = -dot(Py,log2(Py));
MI = Hx + Hy - Hxy;
z = sqrt((MI/Hx)*(MI/Hy));
z = max(0,z);
感谢开源社区~
1.4 ACC
精确度计算,有一点值得提醒,Python是直接与标签对比,没有进行Mapping步骤,适用于分类结果评估;matlab进行了Mapping步骤适用于聚类结果评估。
Python 代码
def AC(labels_true, labels_pre):
acc = accuracy_score(labels_true, labels_pre)
# acc = np.sum(labels_true==labels_pre) / np.size(labels_true)
return acc
Matlab 代码
function [accuracy, ConMtx] = Eva_CA(dataCluster,dataLabel)
nData = length( dataLabel );
nC = max(dataLabel);
E = zeros( nC, nC );
for m = 1 : nData
i1 = dataCluster( m );
i2 = dataLabel( m );
E( i1, i2 ) = E( i1, i2 ) + 1;
end
ConMtx=E';
E=-E;
[C,~]=hungarian(E);
nMatch=0;
for i=1:nC
nMatch=nMatch-E(C(i),i);
end
accuracy = nMatch/nData;
以上外部指标均是目前科研工作者常用指标。
2 内部指标
与外部有效性指数相比,内部有效性指数评价的是数据分区的聚类结构,目的是衡量一个集群内聚类对象的比例,评估聚类对象的分布,而没有外部信息的支持。这里外部信息指原始数据的标签。
2.1 Internal and external validation measures (NCC)
原理解释
NCC 测量的是簇内距离和簇间距离的组合。簇内距离是指一个簇内物体之间的距离。作者将两个对象的 “群内协议”(Sintra)定义为两个对象之间的属性数量和群内距离之差。
距离的测量方法如下:
如果比较的所有属性值之间存在匹配,则drs=0,否则rs= N ⁄ 1,其中N是这两个对象之间在比较过程中发现的不匹配(mismatches)数量。

簇间距离 (Dinter),是不属于同一簇的两个对象(rands)之间的距离,也就是说,这个距离可以测量两个簇之间的距离。

NCC 的表达式是针对任何聚类过程的结果而定义的,其中 T 对应于聚类中心的数量。
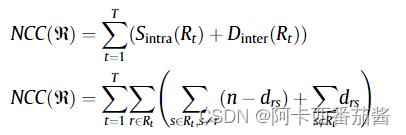
当然,NCC 度量也可以用二进制矩阵 Y 来表示,如果对象(rands)属于同一个聚类,则 yrs=1,否则 yrs=0。NCC(Y) 公式用二进制矩阵表示:

通过NCC的度量,可以观察到集群内(Sintra)和集群间(Dinter)距离之间的关系。根据作者的说法,当群内距离值较小时,群内距离就会增加。另外,当簇间距离增加时,聚类过程中的群组彼此之间变得更加异质化,即集群之间更加不相似。如果这种相似度(Sintra)和距离(Diner)增加,NCC的值就会趋于增加,否则NCC值就会减少。
Python 代码
def NCC(label, x):
m = x.shape[0]
n = x.shape[1]
Y = np.zeros((m, m))
for r in range(m):
for s in range(m):
if label[r] == label[s]:
Y[r, s] = 1
drs = np.zeros((m, m))
for r in range(m):
for s in range(m):
for att in range(n):
if x[r, att] != x[s, att]:
drs[r, s] += 1
ncc = 0.0
for r in range(m):
for s in range(m):
if r != s:
ncc += (n - 2 * drs[r, s]) * Y[r, s] + drs[r, s]
return ncc
Matlab 代码
function ncc = NCC_Y(Cluster_lable,x,n)
%%%Eq.(33)
% n is the number of attributes (categorical).
[m,~] = size(x);
Y = zeros(m,m);
for r = 1:m
for s = 1:m
if Cluster_lable(r) == Cluster_lable(s)
Y(r,s) = 1;
end
end
end
drs = zeros(m,m);
for r = 1:m
for s = 1:m
for att = 1:n
if x(r,att) ~= x(s,att)
drs(r,s) = drs(r,s) + 1;
end
end
end
end
ncc = 0;
for r = 1:m
for s = 1:m
if r~= s
ncc = ncc + (n - 2*drs(r,s))*Y(r,s) + drs(r,s);
end
end
end
注释表示论文中的公式,参考文献附文末。
2.2 Entropy
原理解释

香农熵是在2001年提出的,用于计算数据集无序性的方法。应用于聚类的方法,如果一个簇数据尽可能地有序是否可以说明,更适合聚为一类呢?基于此,有学者Rˇezanková (2009)提出使用熵来计算一个集群中属性的无序性。
p(u)lt :u表示属性l中某一个可能的值,t表示一个簇,p(u)lt表示,在簇t中在l属性上拥有u值的频率。
Entropy值越小,代表聚类效果越好~
Python 代码
def Entropy(label, x):
m = x.shape[0]
n = x.shape[1]
k = len(np.unique(label))
# 每一个属性可能出现的值
no_values = []
for i in range(n):
no_values.append(len(np.unique(x[:, i])))
# cluster 成员数
num_in_cluster = np.ones(k)
for i in range(m):
num_in_cluster[label[i]] += 1
# p_u_lt
P = []
for t in range(k):
# mt
tp = np.where(label == t)[0]
p_u_l = []
for l in range(n):
p_u_lt = []
for u in range(no_values[l]):
belong_lt = np.where(x[tp][:, l] == u)[0]
p_u_lt.append(len(belong_lt) / len(tp))
p_u_l.append(p_u_lt)
P.append(p_u_l)
# H
H = np.zeros(k)
for t in range(k):
H_lt = np.zeros(n)
for l in range(n):
H_lt_u = np.zeros(no_values[l])
for u in range(no_values[l]):
if P[t][l][u] != 0:
H_lt_u[u] = - P[t][l][u] * np.log(P
文章目录
前言
本文主要介绍聚类算法的一些常见评测指标。
假设某一种算法得到聚类结果为:
A
=
[
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
3
1
1
3
3
3
]
\\mathrmA=\\left[\\beginarraylllllllll 1 & 2 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 2 & 2 & 2 & 2 & 3 & 1 & 1 & 3 & 3 & 3 \\endarray\\right]
A=[12111112222311333]
标准的聚类结果为:
B
=
[
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
3
3
3
3
3
]
\\mathrmB=\\left[\\beginarrayllllllll 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 2 & 2 & 2 & 2 & 2 & 2 & 3 & 3 & 3 & 3 & 3 \\endarray\\right]
B=[11111122222233333]
那么如何评价该算法的聚类效果?
纯度(purity)
把每个簇中最多的类作为这个簇所代表的类,然后计算正确分配的类的数量,然后除以总数:

纯度计算如下:
purity
=
(
cluster
A
+
cluster
B
+
cluster
C
)
total
=
(
4
+
5
+
4
)
18
=
0.722
\\text purity =\\frac(\\text cluster A+\\text cluster B+\\text cluster C)\\text total =\\frac(4+5+4)18=0.722
purity = total ( cluster A+ cluster B+ cluster C)=18(4+5+4)=0.722
一般而言,纯度随着clusters数量的增加而增加。例如,将每个样本结果分为一个单独的簇,此时纯度为1。鉴于此,不能简单用纯度来衡量聚类质量与聚类数量之间的关系。
纯度的计算Python代码
def purity(result, label):
# 计算纯度
total_num = len(label)
cluster_counter = collections.Counter(result)
original_counter = collections.Counter(label)
t = []
for k in cluster_counter:
p_k = []
for j in original_counter:
count = 0
for i in range(len(result)):
if result[i] == k and label[i] == j: # 求交集
count += 1
p_k.append(count)
temp_t = max(p_k)
t.append(temp_t)
return sum(t)/total_num
标准互信息(NMI)
熵
标准互信息(Normalized mutual information, NMI)这个指标源自信息论,所以需要先了解熵(entropy)的概念。熵这个概念是用于量化不确定性,熵的定义如下:
H
(
p
)
=
−
∑
i
p
i
log
2
(
p
i
)
H(p)=-\\sum_i p_i \\log _2\\left(p_i\\right)
H(p)=−i∑pilog2(pi)
其中
P
i
P_i
Pi表示label为
i
i
i的概率。延续上述示例,可以计算其熵。
class A : 6 / 18
class B :7 / 18
class C :5 / 18
entropy
=
−
(
(
6
18
)
⋅
log
(
6
18
)
)
−
(
(
7
18
)
⋅
log
(
7
18
)
)
−
(
(
5
18
)
⋅
log
(
5
18
)
)
\\text entropy=-\\left(\\left(\\frac618\\right) \\cdot \\log \\left(\\frac618\\right)\\right)-\\left(\\left(\\frac718\\right) \\cdot \\log \\left(\\frac718\\right)\\right)-\\left(\\left(\\frac518\\right) \\cdot \\log \\left(\\frac518\\right)\\right)
entropy=−((186)⋅log(186))−((187)⋅log(187))−((185)⋅log(185))
其值为 1.089。需要注意的是:当类别或标签分布均匀时,熵值比较高。
熵随着不确定性的减小而减小。假设我们有两个类,其中类A中有9个数据点,类B中有1个数据点。在这种情况下,如果我们要预测一个随机选择的数据点的类别,我们会比之前的情况更确定。这是因为此时熵计算如下,结果值为0.325:
entropy
=
−
(
(
9
10
)
⋅
log
(
9
10
)
)
−
(
(
1
10
)
⋅
log
(
1
10
)
)
\\text entropy =-\\left(\\left(\\frac910\\right) \\cdot \\log \\left(\\frac910\\right)\\right)-\\left(\\left(\\frac110\\right) \\cdot \\log \\left(\\frac110\\right)\\right)
entropy =−((109)⋅log(109))−((101)⋅log(101))
以上即为熵的概念。
互信息
互信息是用以衡量数据分布之间的相关性。互信息越高,相关性也越高。两个离散随机变量
X
X
X 和
Y
Y
Y的互信息定义如下:
M
I
(
X
,
Y
)
=
∑
x
=
1
∣
X
∣
∑
y
=
1
∣
Y
∣
P
(
x
,
y
)
log
(
P
(
x
,
y
)
P
(
x
)
P
(
y
)
)
M I(X, Y)=\\sum_x=1^|X| \\sum_y=1^|Y| P(x, y) \\log \\left(\\fracP(x, y)P(x) P(y)\\right)
MI(X,Y)=x=1∑∣X∣y=1∑∣Y∣P(x,y)log(聚类算法指标整理