[leetcode][46] Permutations
Posted ekoeko
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[leetcode][46] Permutations相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
46. Permutations
Given a collection of distinct integers, return all possible permutations.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3]
Output:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]解析
给定一个数组(没有重复元素),返回所有可能的排序。
参考答案
自己写的:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> lists = new LinkedList<>();
addList(nums, lists, new ArrayList<>());
return lists;
}
public void addList(int[] nums, List<List<Integer>> lists, List<Integer> list) {
if (list.size() == nums.length) {
lists.add(list);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (!list.contains(nums[i])) {
List newList = new ArrayList<>(list);
newList.add(nums[i]);
addList(nums, lists, newList);
}
}
}
}别人写的:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
// Arrays.sort(nums); // not necessary
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums);
return list;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> tempList, int [] nums){
if(tempList.size() == nums.length){
list.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));
} else{
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(tempList.contains(nums[i])) continue; // element already exists, skip
tempList.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(list, tempList, nums);
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}我的答案是简单粗暴的,递归遍历找到数组每个位置上可能的数字,然后复制上次的数组,加上新的位置上可能存在的数字然后用新的数组进行下个位置的查询,效率低,主要是因为每次迭代都要复制数组。
别人这里用了回朔,一直到到最终结果才会复制数组,然后回退,寻找下个结果,没有再向上回退,一直到最上面的递归执行完毕,就对所有结果查找完毕。下面画了两种方法的流程图,帮助理解。
不用回朔的情况:
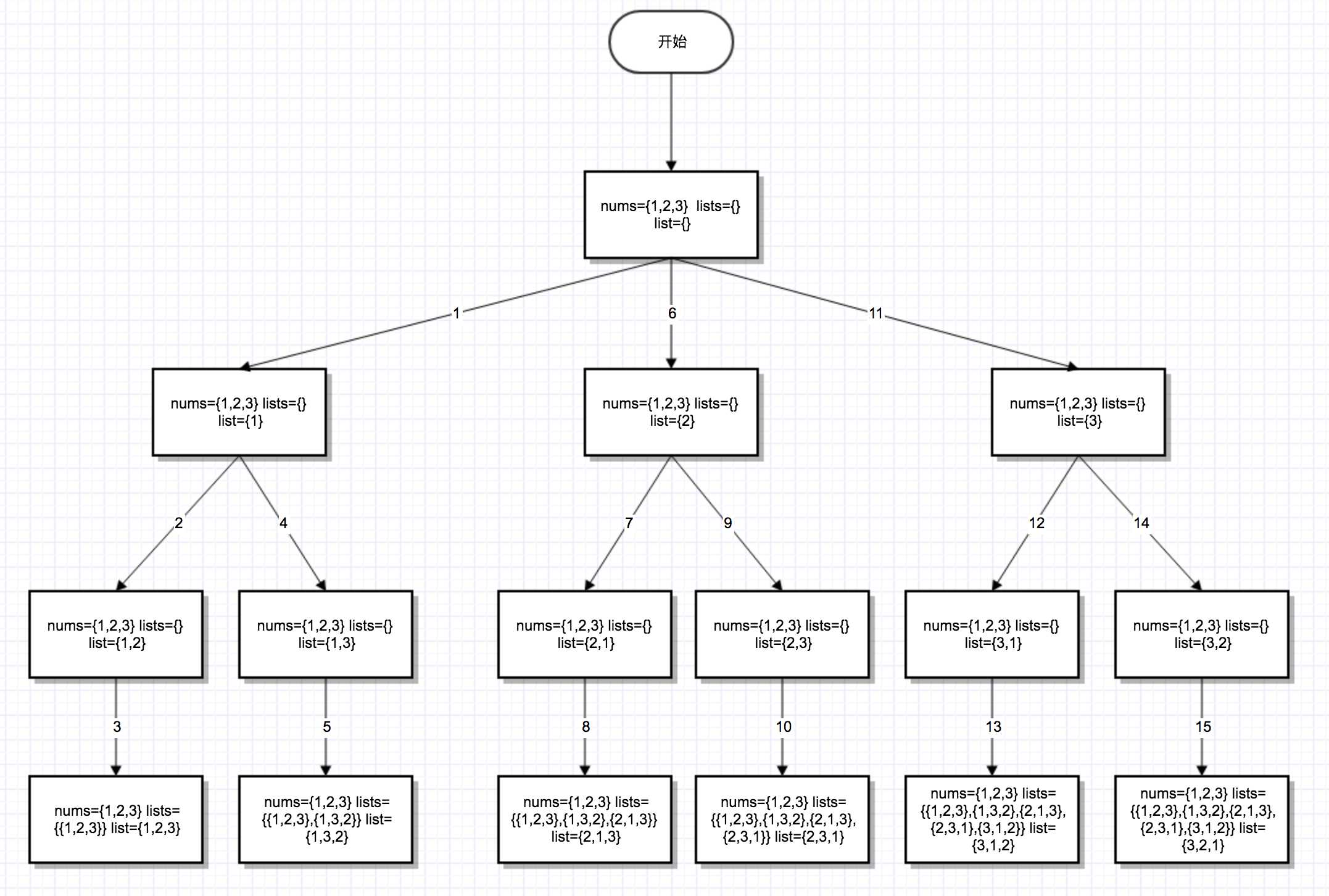
每层递归都要复制数组,效率低下。
用回朔的情况:
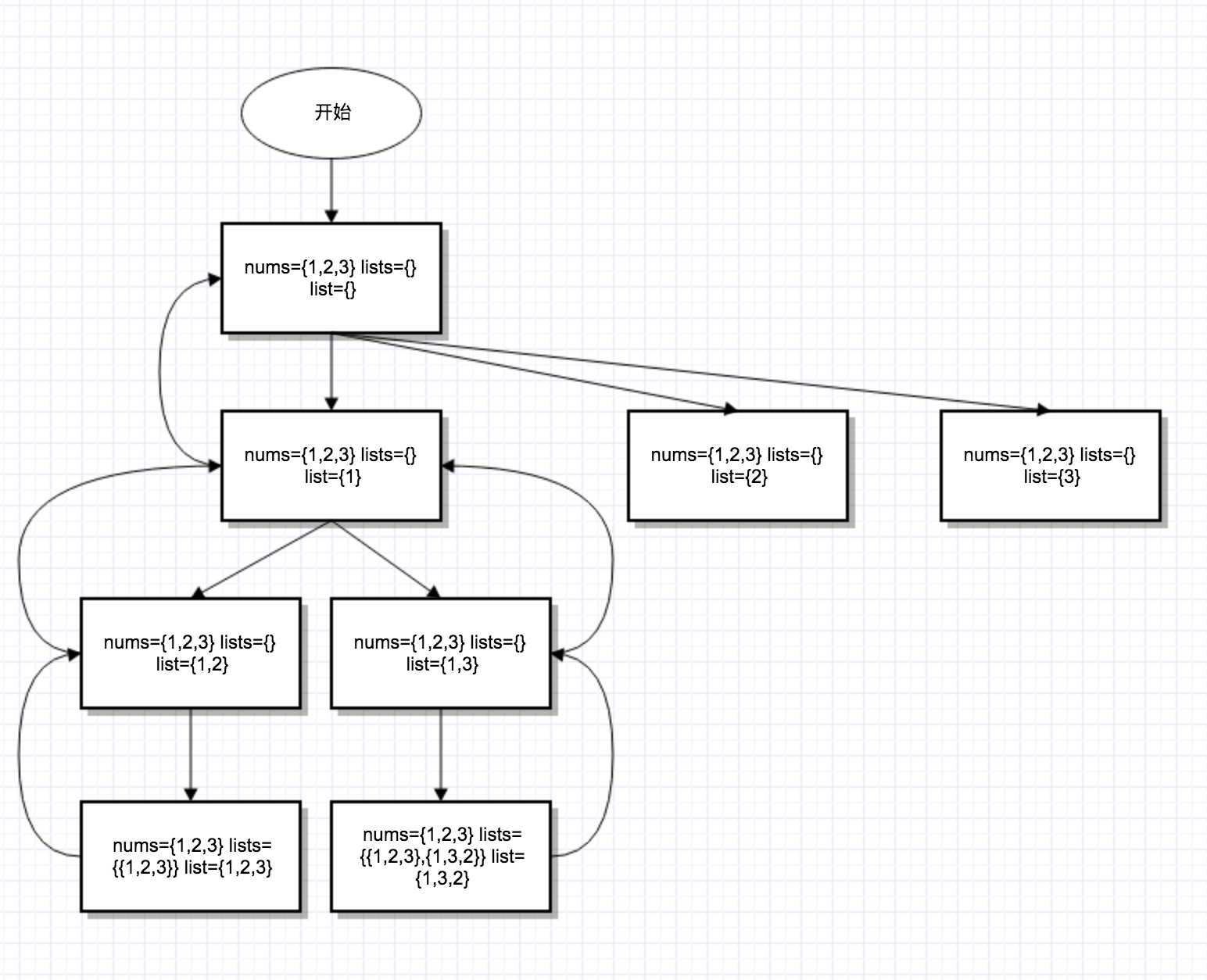
底层递归执行完之后返回上层,上层会删除底层增加的元素,然后继续遍历,不需要复制数组,只会在最终得到结果时,复制数组,加入结果数组。
以上是关于[leetcode][46] Permutations的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
[LeetCode] 46. Permutations(全排列)