《算法图解》读书笔记 - 狄克斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)
Posted Leida_wanglin
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了《算法图解》读书笔记 - 狄克斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
《算法图解》读书笔记 - 狄克斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)
应用于有向加权图中前往X的最短路径。

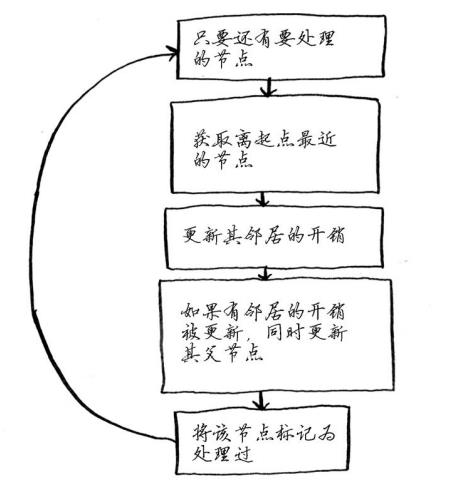
狄克斯特拉算法步骤:
(1)找出“最便宜”的节点,即可在最短时间内到达的节点。
(2)更新该节点的邻居的开销。
(3)重复这个过程,直到对图中的每个节点都这样做了。
(4)计算最终路径。
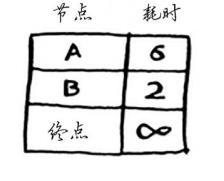
第一步:找出最便宜的节点。你站在起点,不知道该前往节点A还是前往节点B。前往这两个节点都要多长时间呢?

前往节点A需要6分钟,而前往节点B需要2分钟。至于前往其他节点,你
还不知道需要多长时间。
由于你还不知道前往终点需要多长时间,因此你假设为无穷大(这样做的
原因你马上就会明白)。节点B是最近的——2分钟就能达到。
第二步:计算经节点B前往其各个邻居所需的时间。
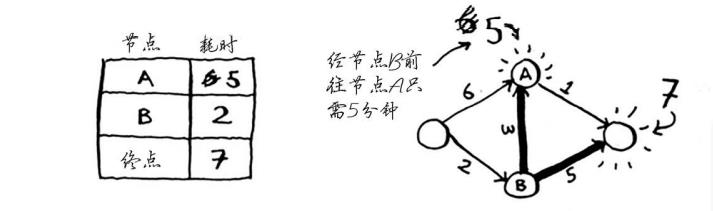
你刚找到了一条前往节点A的更短路径!直接前往节点A需要6分钟。

但经由节点B前往节点A只需5分钟!

对于节点B的邻居,如果找到前往它的更短路径,就更新其开销。在这里,你找到了:
前往节点A的更短路径(时间从6分钟缩短到5分钟);
前往终点的更短路径(时间从无穷大缩短到7分钟)。
第三步:重复!
重复第一步:找出可在最短时间内前往的节点。你对节点B执行了第二步,除节点B外,可在最短时间内前往的节点是节点A。

重复第二步:更新节点A的所有邻居的开销。
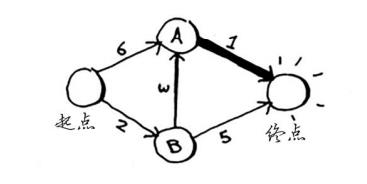
你发现前往终点的时间为6分钟!
你对每个节点都运行了狄克斯特拉算法(无需对终点这样做)。现在,你知道:
前往节点B需要2分钟;
前往节点A需要5分钟;
前往终点需要6分钟。

最后一步——计算最终路径将留到下一节去介绍,这里先直接将最终路径告诉你。

Java代码实现Dijkstra算法

我在这建立三个散列表

1.graph存节点与节点和节点之间的边的值
2.costs存起点与各个节点的权重
3.parents存父节点
小编在这里写的是Java思想,存在一个问题就是HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>>会出现相同Key的Value会被覆盖的问题还没有解决,所以此代码只提供思路。
public class Dijkstra
private static HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
private static HashMap<String, Integer> costs = new HashMap<>();
private static HashMap<String, String> parents = new HashMap<>();
private static List<String> processed = new ArrayList<>();
public static void dijkstra()
//在未处理的节点中找出开销最小的节点
String node = findLowestCostNode(costs);
//这个while循环在所有节点都被处理过后结束
while (node != null)
Integer cost = costs.get(node);
HashMap<String, Integer> neighbors = graph.get(node);
//遍历当前节点的所有邻居
for (String n : neighbors.keySet())
Integer new_cost = cost + neighbors.get(n);
//如果经当前节点前往该邻居更近
if (costs.get(n) > new_cost)
//就更新该邻居的开销
costs.put(n, new_cost);
//同时将该邻居的父节点设置为当前节点
parents.put(n, node);
//将当前节点标记为处理过
processed.add(node);
//找出接下来要处理的节点,并循环
node = findLowestCostNode(costs);
//找出开销最低的节点
public static String findLowestCostNode(HashMap<String, Integer> costs)
Integer lowest_cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
String lowest_cost_node = null;
//遍历所有的节点
for (String node : costs.keySet())
Integer cost = costs.get(node);
//如果当前节点的开销更低且未处理过
if (cost < lowest_cost && parents.containsKey(node) == false)
//就将其视为开销最低的节点
lowest_cost = cost;
lowest_cost_node = node;
return lowest_cost_node;
public static void main(String[] args)
graph.put("start", new HashMap<String, Integer>()put("a", 6););
graph.put("start", new HashMap<String, Integer>()put("b", 2););
graph.put("a", new HashMap<String, Integer>()put("fin", 1););
graph.put("b", new HashMap<String, Integer>()put("a", 3););
graph.put("b", new HashMap<String, Integer>()put("fin", 5););
graph.put("fin", new HashMap<>());
costs.put("a", 6);
costs.put("b", 2);
costs.put("fin", Integer.MAX_VALUE);
parents.put("a", "start");
parents.put("b", "start");
parents.put("fin", null);
dijkstra();
System.out.println(costs.get("fin"));
以上是关于《算法图解》读书笔记 - 狄克斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章