Rescue-Prime STARK
Posted mutourend
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Rescue-Prime STARK相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 引言
前序博客有:
Rescue-Prime STARK 针对的场景为:
- public info: h , H h,H h,H
- private info: x x x
- 待证明relation: h = H ( x ) h=H(x) h=H(x)
其中 H ( ∗ ) H(*) H(∗) 为Rescue-Prime hash函数。
基于该Rescue-Prime STARK生成的non-interactive proof可用于构建post-quantum signature scheme。
2. Rescue-Prime
Rescue-Prime: a Standard Specification (SoK) 为面向arithmetization的hash函数,其具有a compact description in terms of AIR。
Rescue-Prime的sponge函数构建自Rescue-XLIX permutation
f
R
X
L
I
X
:
F
m
→
F
m
f_\\mathrmR^\\mathrmXLIX : \\mathbbF^m \\rightarrow \\mathbbF^m
fRXLIX:Fm→Fm,具有多个几乎完全相同的rounds。每个round包含了6个步骤:
- 1)Forward S-box:该state中的每个元素都会进行 α \\alpha α幂运算,其中 α \\alpha α为最小的invertible power。
- 2)MDS:state elements向量 会与 具有特殊属性的矩阵 进行相乘运算。
- 3)Round constants:会对该state中的每个元素 加上 预设的常量。
- 4)Backward S-box:该state中的每个元素都会进行 α − 1 \\alpha^-1 α−1幂运算,为 x → x α x\\rightarrow x^\\alpha x→xα的逆运算。
- 5)MDS:state elements向量 会与 具有特殊属性的矩阵 进行相乘运算。【与步骤2)中所用的MDS矩阵一样。】
- 6)Round constants:会对该state中的每个元素 加上 预设的常量。【不同于第3)步中的constant。每一round中,3)和6)中均会采用不同于上一轮的constant值。即round constants的取值与所在round相关。】
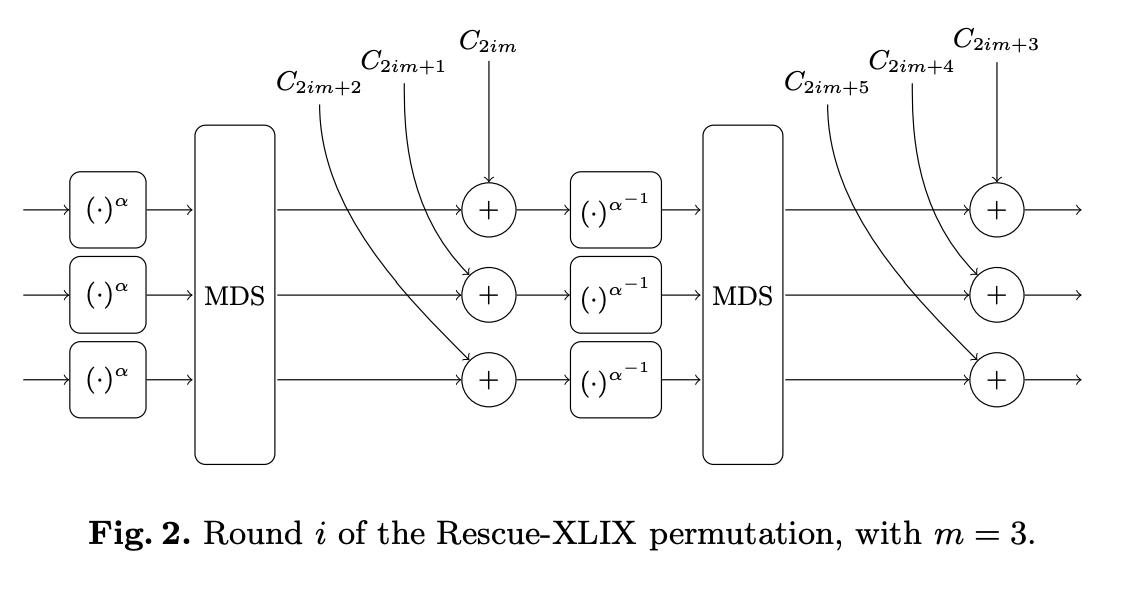
所有round几乎完全相同,不同至此在于每个round中的常量值是不同的。Backward S-box步骤看起来是high degree operation。
以上Rescue-XLIX round function中的6个步骤,可看成是non-deterministic transition constraints of degree
α
\\alpha
α。
一旦定义了Rescue-XLIX permutation,可使用a sponge function对其实例化来获得Rescue-Prime。
构建过程中,input field elements are absorbed into the top
r
r
r elements of the state in between permutations. After one final permutation, the top
r
r
r elements are read out. The Rescue-Prime hash digest consists of these
r
r
r elements.
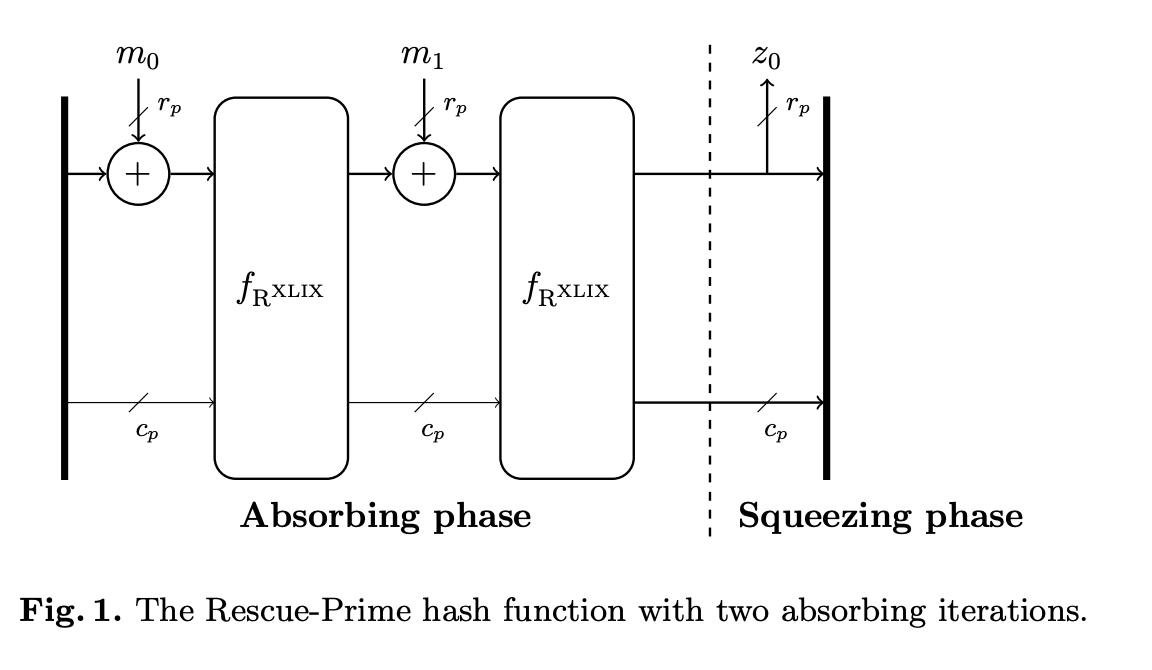
常用的STARK proof参数有:
- prime field of p = 407 ⋅ 2 119 + 1 p = 407 \\cdot 2^119 + 1 p=407⋅2119+1 elements
- α = 3 \\alpha = 3 α=3 and α − 1 = 180331931428153586757283157844700080811 \\alpha^-1 = 180331931428153586757283157844700080811 α−1=180331931428153586757283157844700080811
- m = 2 m = 2 m=2
- r = 1 r = 1 r=1.
此外,the input to the hash computation will be a single field element. So in particular, there will be only one round of absorbing and one application of the permutation。
3. Rescue-Prime AIR
The transition constraints for a single round of the Rescue-XLIX permutation are obtained expressing the state values in the middle of the round in terms of the state values at the beginning, and again in terms of the state values at the end, and then equating both expressions.
令
s
i
\\boldsymbols_ i
si 为round
i
i
i的初始state values,
c
2
i
\\boldsymbolc_ 2i
c2i 和
c
2
i
+
1
\\boldsymbolc_2i+1
c2i+1 分别为该round步骤3)和步骤6)中所用的round constants,
M
M
M为MDS矩阵,令下图的superscript表示的是element-wise powering。则有:
s
i
+
1
=
M
(
(
M
(
s
i
α
)
+
c
2
i
)
1
α
)
+
c
2
i
+
1
\\boldsymbols_i+1 =M(( M (\\boldsymbols_i^\\alpha) + \\boldsymbolc_2i)^\\frac1\\alpha )+ \\boldsymbolc_2i+1
si+1=M((M(siα)+c2i)α1)+c2i+1
从而可将single round的transition以如下等式表示:
M
(
s
i
α
)
+
c
2
i
=
(
M
−
1
(
s
i
+
1
−
c
2
i
+
1
)
)
α
.
M (\\boldsymbols_i^\\alpha) + \\boldsymbolc_2i = \\left(M^-1 (\\boldsymbols_i+1 - \\boldsymbolc_2i+1)\\right)^\\alpha \\enspace .
M(siα)+c2i=(M−1(si+1−c2i+1))α.
为了将其用于STARK,transition constraints 应与round无关,换句话说,即需要用一个单独的等式来描述所有round,而不是值针对某round
i
i
i。
令
X
\\boldsymbolX
X为表示current state(beginning of the round)的变量向量,
Y
\\boldsymbolY
Y 为表示 next state (at the end of the round)的变量向量。
令
f
c
2
i
(
W
)
\\mathbff_ \\boldsymbolc_ 2i(W)
fc2i(W) 表示 the vector of
m
m
m polynomials that take the value
c
2
i
\\boldsymbolc_ 2i
c2i on
ο
i
\\omicron^i
οi,
f
c
2
i
+
1
(
W
)
\\mathbff_ \\boldsymbolc_2i+1(W)
fc2i+1(W) 表示the vector of
m
m
m polynomials that take the value
c
2
i
+
1
\\boldsymbolc_ 2i+1
c2i+1 on
ο
i
\\omicron^i
οi。
execution trace 的插值domain为
ο
i
∣
0
≤
i
≤
T
\\lbrace \\omicron^i \\vert 0 \\leq i \\leq T\\rbrace
οi∣0≤i≤T for some
T
T
T。
以上 arithmetic transition constraints 等价为:【一共有
2
m
+
1
2m+1
2m+1个变量,
m
=
w
m= \\mathsfw
m=w 个 registers。】
M
(
X
α
)
+
f
c
2
i
(
W
)
=
(
M
−
1
(
Y
−
f
c
2
i
+
1
(
W
)
)
)
α
M(\\boldsymbolX^\\alpha) + \\mathbff_ \\boldsymbolc_ 2i(W) = \\left(M^-1(\\boldsymbolY - \\mathbff_ \\boldsymbolc_2i+1(W))\\right)^\\alpha
M(Xα)+fc2i(W)=(M−1(Y−fc2i+1(W)))α
这样,boundary constraints就要简单很多了。
# absorb。最开始
state = [input_element] + [self.field.zero()] * (self.m - 1)
# permutation。N round处理。
for r in range(self.N):
.........
# squeeze。最后
return state[0]
初始,根据sponge construction的定义,第一个state element是unknown secret,第二个state element为0。
最后(after all
N
N
N rounds或
T
T
T cycles),第一个state element即为已知的hash digest
[
h
]
[h]
[h] 中的一个元素,第二个state element不做限制。但是,这第二个state element必须keep secret to be secure,否则attacker可invert该permutation。
从而有boundary constraints
(
c
,
r
,
e
)
∈
0
,
…
,
T
×
0
,
…
,
w
−
1
×
F
(c, r, e) \\in \\lbrace 0, \\ldots, T \\rbrace \\times \\lbrace 0, \\ldots, \\mathsfw-1 \\rbrace \\times \\mathbbF
(c,r,e)