项目实战心脏病患者数据分析和建模
Posted ZSYL
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了项目实战心脏病患者数据分析和建模相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
导入科学计算库
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
from pylab import mpl
# 设置显示中文字体
mpl.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ['SimHei']
# 设置正常显示符号
mpl.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
读取数据
heart_df = pd.read_csv("./data/heart.csv")
heart_df.head()
| age | sex | cp | trestbps | chol | fbs | restecg | thalach | exang | oldpeak | slope | ca | thal | target | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 63 | 1 | 3 | 145 | 233 | 1 | 0 | 150 | 0 | 2.3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 37 | 1 | 2 | 130 | 250 | 0 | 1 | 187 | 0 | 3.5 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 41 | 0 | 1 | 130 | 204 | 0 | 0 | 172 | 0 | 1.4 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 56 | 1 | 1 | 120 | 236 | 0 | 1 | 178 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 4 | 57 | 0 | 0 | 120 | 354 | 0 | 1 | 163 | 1 | 0.6 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
heart_df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 303 entries, 0 to 302
Data columns (total 14 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 age 303 non-null int64
1 sex 303 non-null int64
2 cp 303 non-null int64
3 trestbps 303 non-null int64
4 chol 303 non-null int64
5 fbs 303 non-null int64
6 restecg 303 non-null int64
7 thalach 303 non-null int64
8 exang 303 non-null int64
9 oldpeak 303 non-null float64
10 slope 303 non-null int64
11 ca 303 non-null int64
12 thal 303 non-null int64
13 target 303 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(1), int64(13)
memory usage: 33.3 KB
- age - 年龄
- sex - (1 = male(男性); 0 = (女性))
- cp - chest pain type(胸部疼痛类型)(1:典型的心绞痛-typical,2:非典型心绞痛-atypical,3:没有心绞痛-non-anginal,4:无症状-asymptomatic)
- trestbps - 静息血压 (in mm Hg on admission to the hospital)
- chol - 胆固醇 in mg/dl
- fbs - (空腹血糖 > 120 mg/dl) (1 = true; 0 = false)
- restecg - 静息心电图测量(0:普通,1:ST-T波异常,2:可能左心室肥大)
- thalach - 最高心跳率
- exang - 运动诱发心绞痛 (1 = yes; 0 = no)
- oldpeak - 运动相对于休息引起的ST抑制
- slope - 运动ST段的峰值斜率(1:上坡-upsloping,2:平的-flat,3:下坡-downsloping)
- ca - 主要血管数目(0-4)
- thal - 一种叫做地中海贫血的血液疾病(3 = normal; 6 = 固定的缺陷-fixed defect; 7 = 可逆的缺陷-reversable defect)
- target - 是否患病 (1=yes, 0=no)
患病的分布情况
fig,axes = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(10,5), dpi=100)
ax = heart_df.target.value_counts().plot(kind="bar",ax=axes[0])
ax.set_title("患病分布")
ax.set_xlabel("1:患病,0:未患病")
heart_df.target.value_counts().plot(kind="pie",autopct="%.2f%%",labels=['患病','未患病'],ax=axes[1])
plt.show()

性别和患病的分布
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5), dpi=100)
ax1 = plt.subplot(121)
ax = sns.countplot(x="sex",hue='target',data=heart_df,ax=ax1)
ax.set_xlabel("0:女性,1:男性")
ax2 = plt.subplot(222)
heart_df[heart_df['target'] == 0].sex.value_counts().plot(kind="pie",autopct="%.2f%%",labels=['男性','女性'],ax=ax2)
ax2.set_title("未患病性别比例")
ax2 = plt.subplot(224)
heart_df[heart_df['target'] == 1].sex.value_counts().plot(kind="pie",autopct="%.2f%%",labels=['男性','女性'],ax=ax2)
ax2.set_title("患病性别比例")
Text(0.5, 1.0, '患病性别比例')
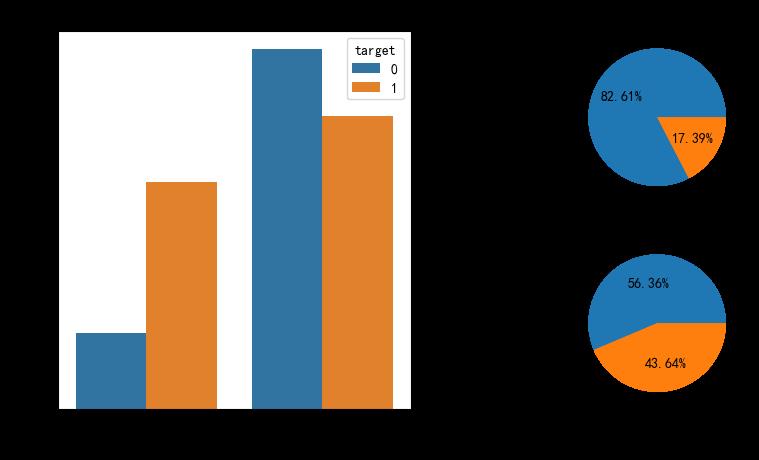
年龄分布情况
fig,axes = plt.subplots(2,1,figsize=(20,10), dpi=100)
ax = sns.countplot(x="age",hue="target",data=heart_df,ax=axes[0])
ax.set_xlabel("0:女性,1:男性")
# 0-45:青年人,45-59:中年人,60-100:老年人
age_type = pd.cut(heart_df.age,bins=[0,45,60,100],include_lowest=True,right=False,labels=['青年人','中年人','老年人'])
age_target_df = pd.concat([age_type,heart_df.target],axis=1)
sns.countplot(x="age",hue='target',data=age_target_df)
plt.show()

统一看下所有特征的分布情况
fig,axes = plt.subplots(7,2,figsize=(10,20), dpi=100)
for x in range(0,14):
plt.subplot(7,2,x+1)
sns.distplot(heart_df.iloc[:,x],kde=True)
plt.tight_layout()
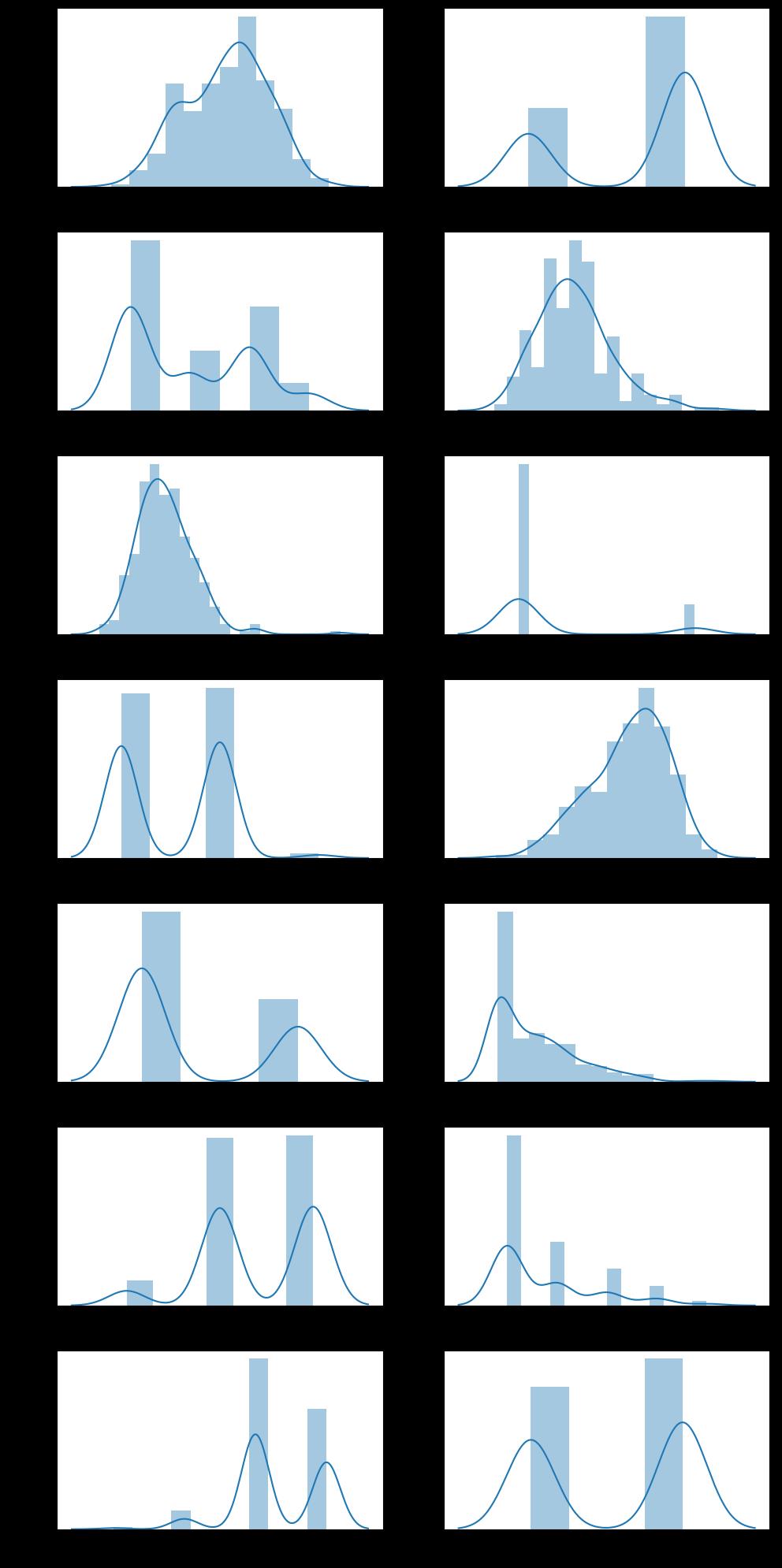
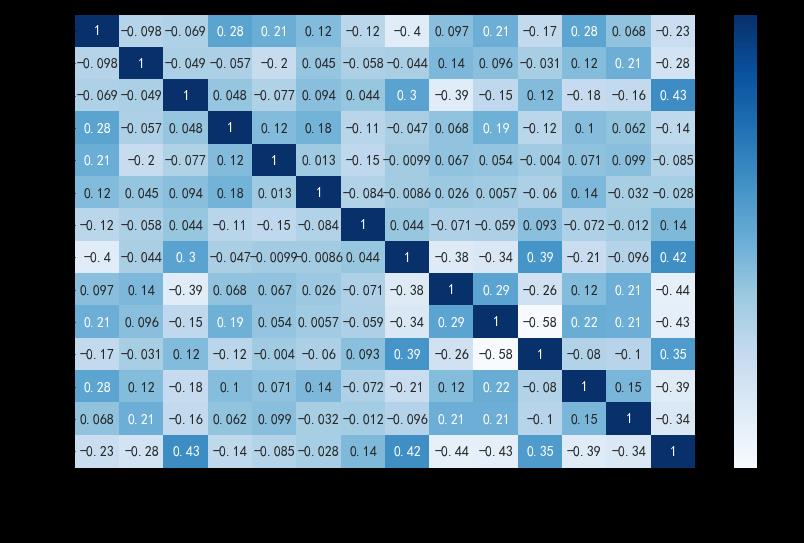
# 绘制热力图
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6), dpi=100)
sns.heatmap(heart_df.corr(),cmap="Blues",annot=True)
plt.show()
建模操作
数据预处理
features = heart_df.drop(columns=['target'])
targets = heart_df['target']
features.head()
| age | sex | cp | trestbps | chol | fbs | restecg | thalach | exang | oldpeak | slope | ca | thal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 63 | 1 | 3 | 145 | 233 | 1 | 0 | 150 | 0 | 2.3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 37 | 1 | 2 | 130 | 250 | 0 | 1 | 187 | 0 | 3.5 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 2 | 41 | 0 | 1 | 130 | 204 | 0 | 0 | 172 | 0 | 1.4 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 3 | 56 | 1 | 1 | 120 | 236 | 0 | 1 | 178 | 0 | 0.8 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 4 | 57 | 0 | 0 | 120 | 354 | 0 | 1 | 163 | 1 | 0.6 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
# 将离散型数据,从普通的0,1,2这些,转换成真正的字符串表示
# sex
features.loc[features['sex']==0,'sex'] = 'female'
features.loc[features['sex']==1,'sex'] = 'male'
# cp
features.loc[features['cp'] == 1,'cp'] = 'typical'
features.loc[features['cp'] == 2,'cp'] = 'atypical'
features.loc[features['cp'] == 3,'cp'] = 'non-anginal'
features.loc[features['cp'] == 4,'cp'] = 'asymptomatic'
# fbs
features.loc[features['fbs'] == 1,'fbs'] = 'true'
features.loc[features['fbs'] == 0,'fbs'] = 'false'
# exang
features.loc[features['exang'] == 1,'exang'] = 'true'
features.loc[features['exang'] == 0,'exang'] = 'false'
# slope
features.loc[features['slope'] == 1,'slope'] = 'true'
features.loc[features['slope'] == 2,'slope'] = 'true'
features.loc[features['slope'] == 3,'slope'] = 'true'
# thal
features.loc[features['thal'] == 3,'thal'] = 'normal'
features.loc[features['thal'] == 3,'thal'] = 'fixed'
features.loc[features['thal'] == 3,'thal'] = 'reversable'
# restecg
# 0:普通,1:ST-T波异常,2:可能左心室肥大
features.loc[features['restecg'] == 0,'restecg'] = 'normal'
features.loc[features['restecg'] == 1,'restecg'] = 'ST-T abnormal'
features.loc[features['restecg'] == 2,'restecg'] = 'Left ventricular hypertrophy'
# ca
features['ca'].astype("object")
# thal
features.thal.astype("object")
features.head()
| age | sex | cp | trestbps | chol | fbs | restecg | thalach | exang | oldpeak | slope | ca | thal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 63 | male | non-anginal | 145 | 233 | true | normal | 150 | false | 2.3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 37 | male | atypical | 130 | 250 | false | ST-T abnormal | 187 | false | 3.5 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 2 | 41 | female | typical | 130 | 204 | false | normal | 172 | false | 1.4 | true | 0 | 2 |
| 3 | 56 | male | typical | 120 | 236 | false | ST-T abnormal | 178 | false | 0.8 | true | 0 | 2 |
| 4 | 57 | female | 0 | 120 | 354 | false | ST-T abnormal | 163 | true | 0.6 | true | 0 | 2 |
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
features = pd.get_dummies(features) # 文本特征onehot表示
features_temp = StandardScaler().fit_transform(features)
# features_temp = StandardScaler().fit_transform(pd.get_dummies(features))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(features_temp,targets,test_size=0.25)
- K近邻
- 决策树
- 随机森林
- 逻辑回归
- SGD分类
K近邻
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score,recall_score,f1_score
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve,roc_curve,average_precision_score,auc
# https://www.jianshu.com/p/c61ae11cc5f6
def plotting(estimator,y_test):
fig,axes = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(10,5), dpi=100)
y_predict_proba = estimator.predict_proba(X_test)
precisions,recalls,thretholds = precision_recall_curve(y_test,y_predict_proba[:,1])
axes[0].plot(precisions,recalls)
axes[0].set_title("平均精准率:%.2f"%average_precision_score(y_test,y_predict_proba[:,1]))
axes[0].set_xlabel("召回率")
axes[0].set_ylabel("精准率")
fpr,tpr,thretholds = roc_curve(y_test,y_predict_proba[:,1])
axes[1].plot(fpr,tpr)
axes[1].set_title("AUC值:%.2f"%auc(fpr,tpr))
axes[1].set_xlabel("FPR")
axes[1].set_ylabel("TPR")
# 1. K近邻
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
scores = cross_val_score(knn,features_temp,targets,cv=5)
print("准确率:",scores.mean())
knn.fit(X_train,y_train)
y_predict = knn.predict(X_test)
# 精准率
print("精准率:",precision_score(y_test,y_predict))
# 召回率
print("召回率:",recall_score(y_test,y_predict))
# F1-Score
print("F1得分:",f1_score(y_test,y_predict))
plotting(knn,y_test)
准确率: 0.8317486338797814
精准率: 0.8260869565217391
召回率: 0.8837209302325582
F1得分: 0.853932584269663

决策树
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=10)
tree.fit(X_train,y_train)
plotting(tree,y_test)
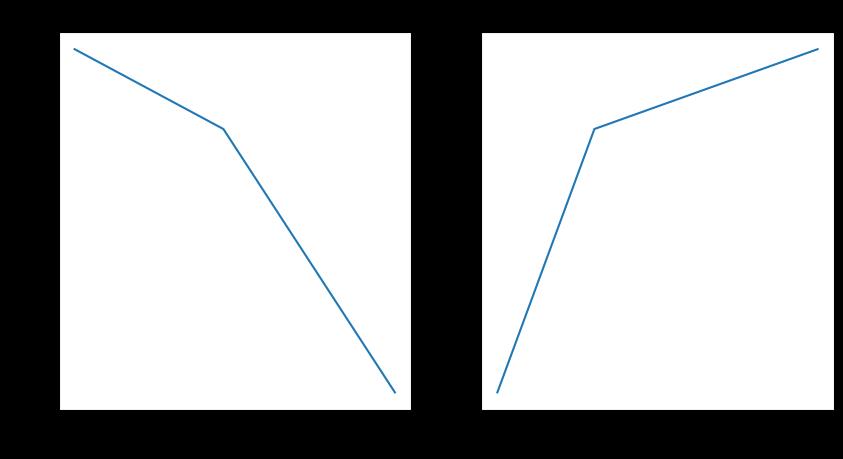
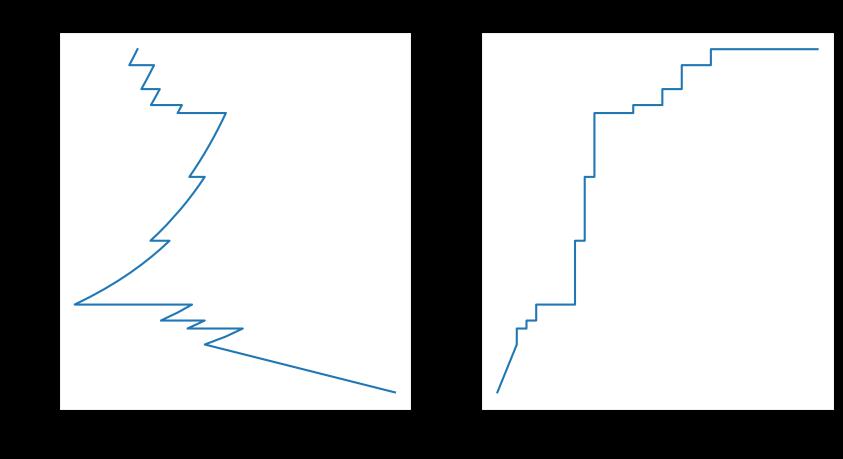
随机森林
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)
rf.fit(X_train,y_train)
plotting(rf,y_test)
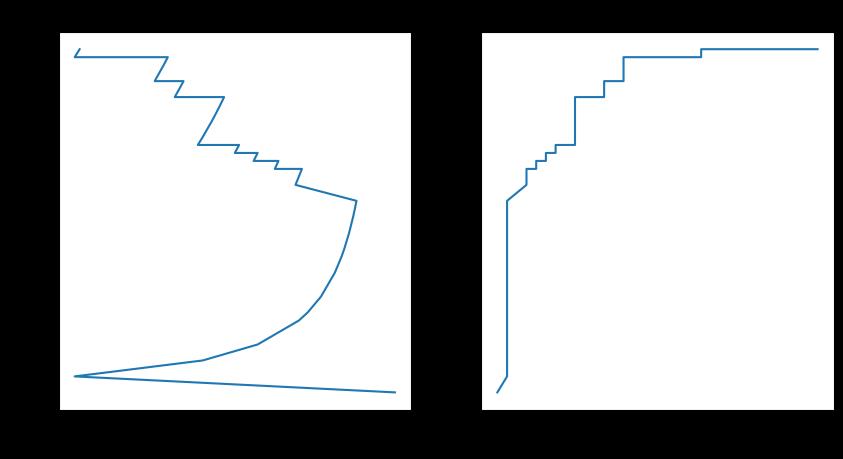
逻辑回归
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
logic = LogisticRegression(tol=1e-10)
logic.fit(X_train,y_train)
plotting(logic,y_test)
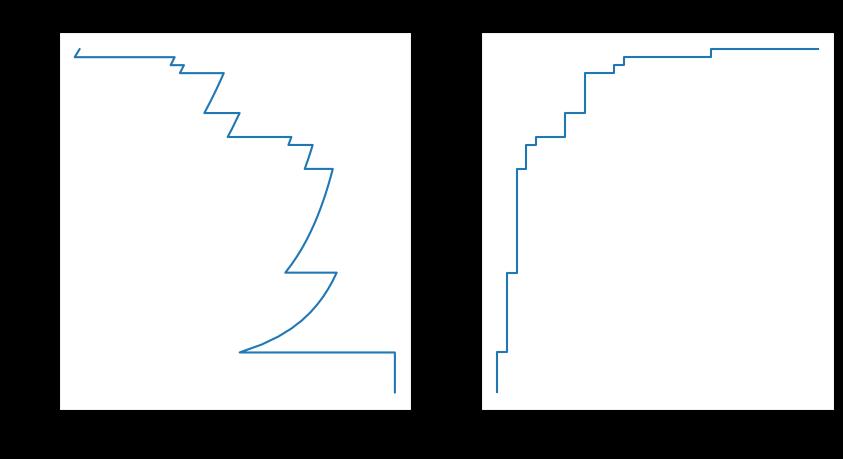
SGD分类
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
sgd = SGDClassifier(loss="log")
sgd.fit(X_train,y_train)
plotting(sgd,y_test)
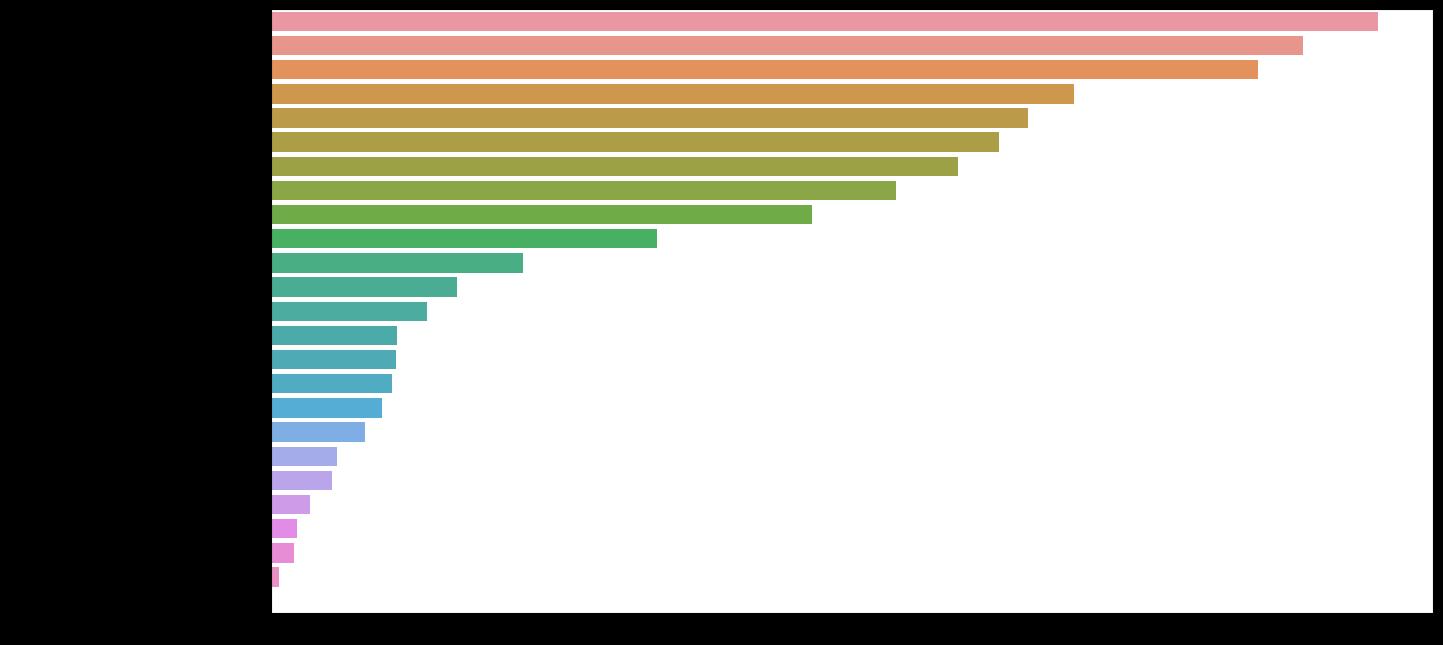
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8), dpi=100)
importances = pd.Series(data=rf.feature_importances_,index=features.columns).sort_values(ascending=False)
sns.barplot(y=importances.index,x=importances.values,orient='h')
plt.show()
加油!
感谢!
努力!
以上是关于项目实战心脏病患者数据分析和建模的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
R语言基于Bagging分类的逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)决策树森林分析心脏病患者