数据结构之双链表
Posted 小倪同学 -_-
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构之双链表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
为什么需要双链表
单链表相对于顺序表在空间复杂度上有了很大的提升,但是它在时间复杂度上还有很大缺陷
- 尾插,尾删时需要遍历整个链表找到尾结点或其前一个结点,这样就造成了时间上的浪费
- 在指定位置插入数据时需要找到前一个结点,有种多此一举的感觉
为了解决上述问题,我们引入了双链表
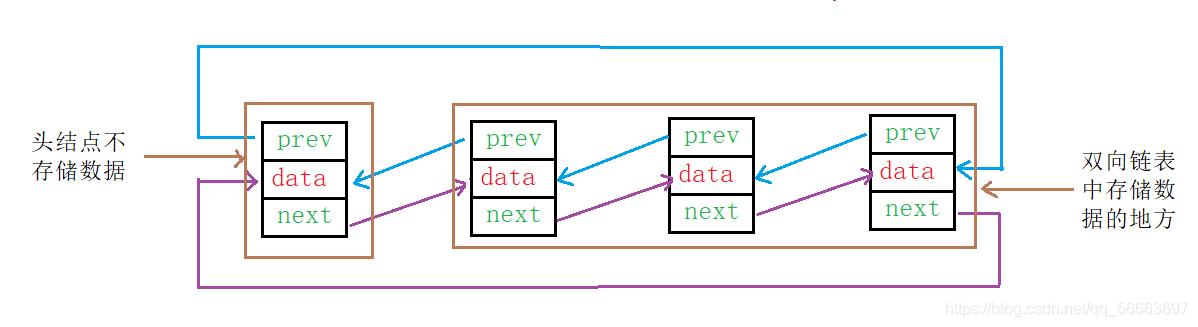
双链表的结构
项目的创建
创建三个文件SList.h , SList.c , test.c
- SList.h:头文件的包含,结构体定义,函数的声明
- SList.c:函数的实现
- test.c:测试程序

双链表的功能实现
结点的定义
从上面的结构图我们可以知道结构体内容
- 指向前一结点的指针
- 存放数据的空间
- 指向后一结点的指针
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{
LTDataType data;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* prev;
}ListNode;
双链表初始化
创建一个头结点,并使其头指针和尾指针都指向其自己
ListNode* ListCreate(LTDataType x)
{
//创建
ListNode* node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\\n");
exit(-1);
}
node->data = x;
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = NULL;
return node;
}
ListNode* ListInit()
{
ListNode* phead = ListCreate(0);
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
return phead;
}
双链表打印
遍历打印头结点之后的数据
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\\n");
}
双链表判空
判断双链表是否不存储数据
bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
return phead->next == phead;
}
双链表查找
遍历链表找到指定数值,将其结点地址返回
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
//遍历
while (cur != pHead)
{
//找到返回地址
if (cur->data == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
//找不到返回空指针
return NULL;
}
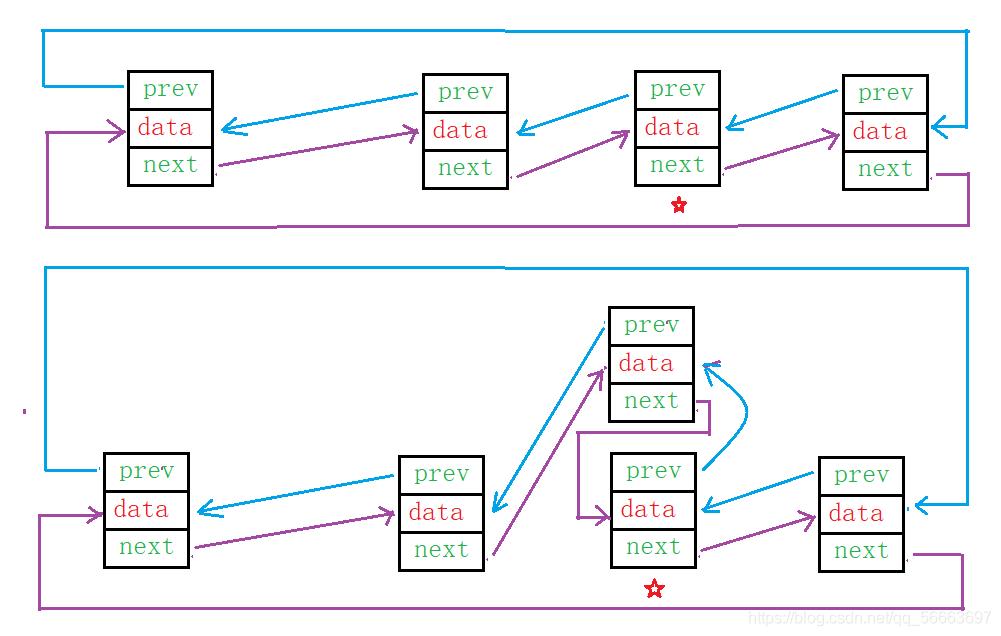
指定位置插入
思路
- 记录该结点前一个结点
- 创建一个新节点
- 将新结点连入双链表
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* newnode = ListCreate(x);
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = prev;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
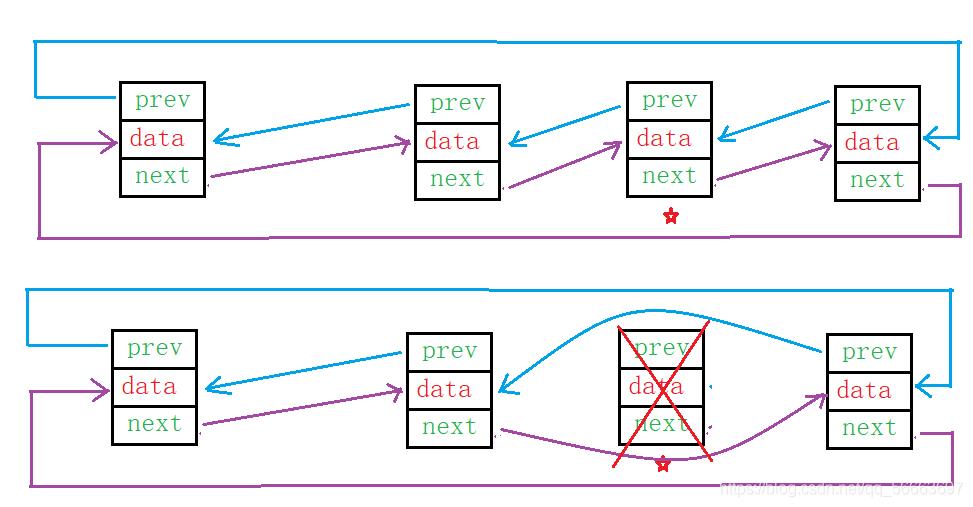
指定位置删除
思路
- 记录指定结点的前后结点
- 删除指定结点
- 将前后结点相连
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
//记录指定结点前后结点
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
ListNode* next = pos->next;
free(pos);
//连接前后结点
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
}
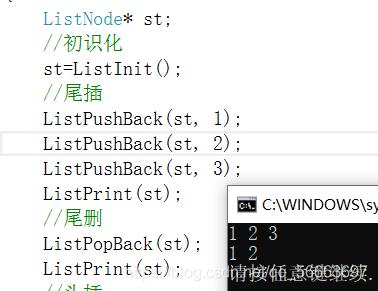
双链表尾插,尾删
上文在指定结点插入删除,尾插,尾删可利用该函数
尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
ListInsert(pHead, x);
}
检测
尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
assert(!ListEmpty(pHead));
ListErase(pHead->prev);
}
检测
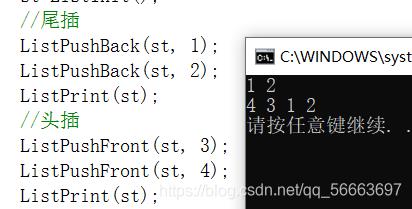
双链表头插,头删
和尾插,尾删类似
头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
ListInsert(pHead->next, x);
}
检测
头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
assert(!ListEmpty(pHead));
ListErase(pHead->next);
}
检测

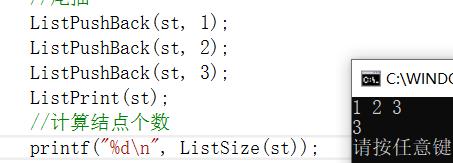
计算结点个数
遍历计数
size_t ListSize(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
size_t n = 0;
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur!=phead)
{
++n;
cur = cur->next;
}
return n;
}
检测
双链表的销毁
遍历释放即可
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead)
{
ListNode* cur = pHead;
while (cur != pHead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(pHead);
pHead = NULL;
}
总结
SList.h文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
// 带头+双向+循环链表增删查改实现
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{
LTDataType data;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* prev;
}ListNode;
//初始化
//void ListInit(ListNode** pphead);
ListNode* ListInit();
// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate(LTDataType x);
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead);
//判空
bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead);
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
//计算链表的个数
size_t ListSize(ListNode* phead);
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead);
SList.c文件
#include "SList.h"
ListNode* ListCreate(LTDataType x)
{
//创建
ListNode* node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\\n");
exit(-1);
}
node->data = x;
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = NULL;
return node;
}
ListNode* ListInit()
{
ListNode* phead = ListCreate(0);
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
return phead;
}
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\\n");
}
bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
return phead->next == phead;
}
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
//遍历
while (cur != pHead)
{
//找到返回地址
if (cur->data == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
//找不到返回空指针
return NULL;
}
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* newnode = ListCreate(x);
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = prev;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
//记录指定结点前后结点
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
ListNode* next = pos->next;
free(pos);
//连接前后结点
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
}
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
ListInsert(pHead, x);
}
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
assert(!ListEmpty(pHead));
//ListNode* tail = pHead->prev;
//ListNode* tailPrev = tail->next;
//free(tail);
//tailPrev->next = pHead;
//pHead->prev = tailPrev;
ListErase(pHead->prev);
}
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
ListInsert(pHead->next, x);
}
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
assert(!ListEmpty(pHead));
ListErase(pHead->next);
}
size_t ListSize(ListNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
size_t n = 0;
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur!=phead)
{
++n;
cur = cur->next;
}
return n;
}
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead)
{
ListNode* cur = pHead;
while (cur != pHead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(pHead);
pHead = NULL;
}
以上是关于数据结构之双链表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章