基于Hadoop的项目实战-职位数据综合分析 从数据采集(Selenium)数据预处理Hive分析Sqoop导入MySQL 进一步用Javaweb可视化,最后进行机器学习数据挖掘分析
Posted 小崔的金箍棒
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于Hadoop的项目实战-职位数据综合分析 从数据采集(Selenium)数据预处理Hive分析Sqoop导入MySQL 进一步用Javaweb可视化,最后进行机器学习数据挖掘分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、数据采集(selenium)
from selenium import webdriver
import time
import re
import pandas as pd
import os在爬取的过程中可能会有登陆弹窗,要先定义一个处理弹窗的函数
def close_windows():
#如果有登录弹窗,就关闭
try:
time.sleep(0.5)
if dr.find_element_by_class_name("jconfirm").find_element_by_class_name("closeIcon"):
dr.find_element_by_class_name("jconfirm").find_element_by_class_name("closeIcon").click()
except BaseException as e:
print('close_windows,没有弹窗',e)爬取部分,这里爬取维度为11列,基本上包含了职位的大部分信息
def get_current_region_job(k_index):
flag = 0
# page_num_set=0#每区获取多少条数据,对30取整
df_empty = pd.DataFrame(columns=['岗位', '地点', '薪资', '工作经验', '学历', '公司名称', '技能','工作福利','工作类型','融资情况','公司规模'])
while (flag == 0):
# while (page_num_set<151)&(flag == 0):#每次只能获取150条信息
time.sleep(0.5)
close_windows()
job_list = dr.find_elements_by_class_name("job-primary")
for job in job_list:#获取当前页的职位30条
job_name = job.find_element_by_class_name("job-name").text
# print(job_name)
job_area = job.find_element_by_class_name("job-area").text
# salary = job.find_element_by_class_name("red").get_attribute("textContent") # 获取薪资
salary_raw = job.find_element_by_class_name("red").get_attribute("textContent") # 获取薪资
salary_split = salary_raw.split('·') # 根据·分割
salary = salary_split[0] # 只取薪资,去掉多少薪
# if re.search(r'天', salary):
# continue
experience_education = job.find_element_by_class_name("job-limit").find_element_by_tag_name(
"p").get_attribute("innerhtml")
# experience_education_raw = '1-3年<em class="vline"></em>本科'
experience_education_raw = experience_education
split_str = re.search(r'[a-zA-Z =<>/"]{23}', experience_education_raw) # 搜索分割字符串<em class="vline"></em>
# print(split_str)
experience_education_replace = re.sub(r'[a-zA-Z =<>/"]{23}', ",", experience_education_raw) # 分割字符串替换为逗号
# print(experience_education_replace)
experience_education_list = experience_education_replace.split(',') # 根据逗号分割
# print('experience_education_list:',experience_education_list)
if len(experience_education_list)!=2:
print('experience_education_list不是2个,跳过该数据',experience_education_list)
break
experience = experience_education_list[0]
education = experience_education_list[1]
# print(experience)
# print(education)
company_type = job.find_element_by_class_name("company-text").find_element_by_tag_name(
"p").get_attribute("innerHTML")
company_type_size_row=company_type
split_str_2=re.search(r'[a-zA-Z =<>/"]{23}', company_type_size_row)
# print(split_str_2)
# print("split2------------------------------------------------------")
company_size_replace= re.sub(r'[a-zA-Z =<>/"]{23}', ",", company_type_size_row)
# print(company_size_replace)
company_size_list=company_size_replace.split(',')
# print(company_size_list)
if len(company_size_list) != 3:
print('company_size_list不是3个,跳过该数据', company_size_list)
break
company_direct_info = company_size_list[0].split(">")[1]
company_salary_info = company_size_list[1].split(">")[1]
company_size_info=company_size_list[2]
company = job.find_element_by_class_name("company-text").find_element_by_class_name("name").text
skill_list = job.find_element_by_class_name("tags").find_elements_by_class_name("tag-item")
skill = []
job_advantage=job.find_element_by_class_name("info-desc").text
for skill_i in skill_list:
skill_i_text = skill_i.text
if len(skill_i_text) == 0:
continue
skill.append(skill_i_text)
# print(job_name)
# print(skill)
df_empty.loc[k_index, :] = [job_name, job_area, salary, experience, education, company, skill,job_advantage,company_direct_info,company_salary_info,company_size_info]
print(df_empty.loc[k_index, :])
k_index = k_index + 1
# page_num_set=page_num_set+1
print("已经读取数据{}条".format(k_index))
close_windows()
try:#点击下一页
cur_page_num=dr.find_element_by_class_name("page").find_element_by_class_name("cur").text
# print('cur_page_num',cur_page_num)
#点击下一页
element = dr.find_element_by_class_name("page").find_element_by_class_name("next")
dr.execute_script("arguments[0].click();", element)
time.sleep(1)
# print('点击下一页')
new_page_num=dr.find_element_by_class_name("page").find_element_by_class_name("cur").text
# print('new_page_num',new_page_num)
if cur_page_num==new_page_num:
flag = 1
break
except BaseException as e:
print('点击下一页错误',e)
break
print(df_empty)
if os.path.exists("ai数据.csv"):#存在追加,不存在创建
df_empty.to_csv('ai数据.csv', mode='a', header=False, index=None, encoding='gb18030')
else:
df_empty.to_csv("ai数据.csv", index=False, encoding='gb18030')
return k_index自动化爬取部分 这里按照全国14个热门城市爬取 若想爬取某个固定城市,需要把for循环去掉,去网站上找到对应城市编码,剪贴url即可
def main():
# 打开浏览器
# dr = webdriver.Firefox()
global dr
dr = webdriver.Chrome()
# dr = webdriver.Ie()
# # 后台打开浏览器
# option=webdriver.ChromeOptions()
# option.add_argument('headless')
# dr = webdriver.Chrome(chrome_options=option)
# print("打开浏览器")
# 将浏览器最大化显示
dr.maximize_window()
# 转到目标网址
dr.get("https://www.zhipin.com/job_detail/?query=人工智能&city=100010000&industry=&position=")#全国
# dr.get("https://www.zhipin.com/c101010100/?query=人工智能&ka=sel-city-101010100")#北京
print("打开网址")
time.sleep(5)
k_index = 0#数据条数、DataFrame索引
flag_hot_city=0
for i in range(3,17,1):
# print('第',i-2,'页')
# try:
# 获取城市
close_windows()
hot_city_list = dr.find_element_by_class_name("condition-city").find_elements_by_tag_name("a")
close_windows()
# hot_city_list[i].click()#防止弹窗,改为下面两句
# element_hot_city_list_first = hot_city_list[i]
dr.execute_script("arguments[0].click();", hot_city_list[i])
# 输出城市名
close_windows()
hot_city_list = dr.find_element_by_class_name("condition-city").find_elements_by_tag_name("a")
print('城市:{}'.format(i-2),hot_city_list[i].text)
time.sleep(0.5)
# 获取区县
for j in range(1,50,1):
# print('第', j , '个区域')
# try:
# close_windows()
# hot_city_list = dr.find_element_by_class_name("condition-city").find_elements_by_tag_name("a")
# 在这个for循环点一下城市,不然识别不到当前页面已经更新了
close_windows()
hot_city_list = dr.find_element_by_class_name("condition-city").find_elements_by_tag_name("a")
close_windows()
# hot_city_list[i].click()#防止弹窗,改为下面
dr.execute_script("arguments[0].click();", hot_city_list[i])
#输出区县名称
close_windows()
city_district = dr.find_element_by_class_name("condition-district").find_elements_by_tag_name("a")
if len(city_district)==j:
print('遍历完所有区县,没有不可点击的,跳转下一个城市')
break
print('区县:',j, city_district[j].text)
# city_district_value=city_district[j].text#当前页面的区县值
# 点击区县
close_windows()
city_district= dr.find_element_by_class_name("condition-district").find_elements_by_tag_name("a")
close_windows()
# city_district[j].click()]#防止弹窗,改为下面两句
# element_city_district = city_district[j]
dr.execute_script("arguments[0].click();", city_district[j])
#判断区县是不是点完了
close_windows()
hot_city_list = dr.find_element_by_class_name("condition-city").find_elements_by_tag_name("a")
print('点击后这里应该是区县', hot_city_list[1].text)#如果是不限,说明点完了,跳出
hot_city_list = dr.find_element_by_class_name("condition-city").find_elements_by_tag_name("a")
print('如果点完了,这里应该是不限:',hot_city_list[1].text)
hot_city_list = dr.find_element_by_class_name("condition-city").find_elements_by_tag_name("a")
if hot_city_list[1].text == '不限':
print('当前区县已经点完了,点击下一个城市')
flag_hot_city=1
break
close_windows()
k_index = get_current_region_job(k_index)#获取职位,爬取数据
# 重新点回城市页面,再次获取区县。但此时多了区县,所以i+1
close_windows()
hot_city_list = dr.find_element_by_class_name("condition-city").find_elements_by_tag_name("a")
close_windows()
# hot_city_list[i+1].click()#防止弹窗,改为下面两句
# element_hot_city_list_again = hot_city_list[i+1]
dr.execute_script("arguments[0].click();", hot_city_list[i+1])
# except BaseException as e:
# print('main的j循环-获取区县发生错误:', e)
# close_windows()
time.sleep(0.5)
# except BaseException as e:
# print('main的i循环发生错误:',e)
# close_windows()
time.sleep(0.5)
# 退出浏览器
dr.quit()
# p1.close()最后调用main即可,爬取结果如下 数据量共计一万(人工智能职位)
数据为两部分:分别为全国人工智能职位爬取 热门城市人工职位数据爬取
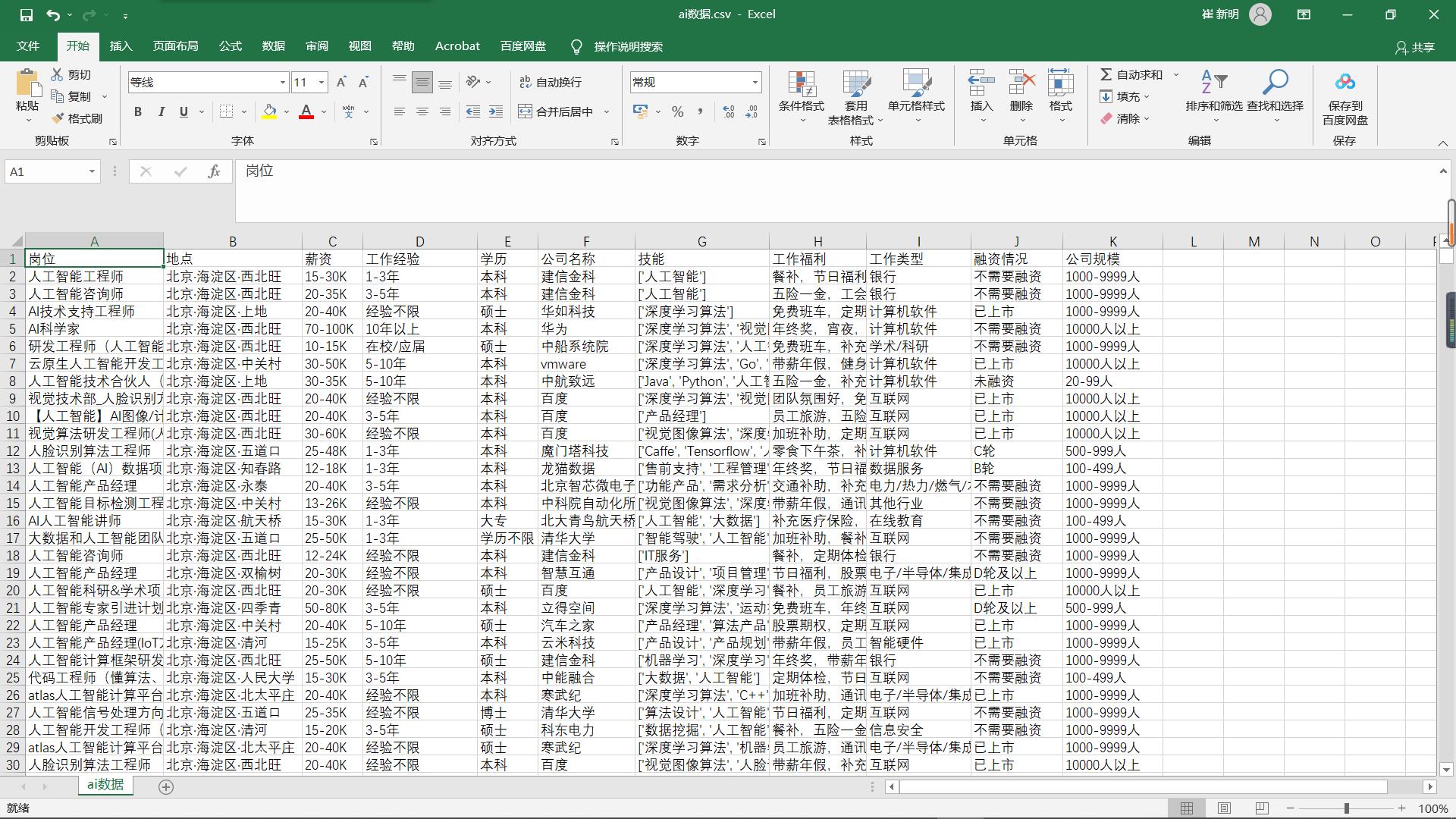
二、数据预处理
简单做一些缺失值和规范化的处理 具体分析部分在Hive中
# coding=utf-8
import collections
import wordcloud
import re
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 设置正常显示符号
def create_dir_not_exist(path): # 判断文件夹是否存在,不存在-新建
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.mkdir(path)
create_dir_not_exist(r'./image')
create_dir_not_exist(r'./image/city')
data = pd.read_csv('ai数据.csv', encoding='gb18030')
data_df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print("\\n查看是否有缺失值\\n", data_df.isnull().sum())
data_df_del_empty = data_df.dropna(subset=['岗位'], axis=0)
# print("\\n删除缺失值‘岗位'的整行\\n",data_df_del_empty)
data_df_del_empty = data_df_del_empty.dropna(subset=['公司名称'], axis=0)
# print("\\n删除缺失值‘公司'的整行\\n",data_df_del_empty)
print("\\n查看是否有缺失值\\n", data_df_del_empty.isnull().sum())
print('去除缺失值后\\n', data_df_del_empty)
data_df_python_keyword = data_df_del_empty.loc[data_df_del_empty['岗位'].str.contains('人工智能|AI')]
# print(data_df_python_keyword)#筛选带有python的行
# 区间最小薪资
data_df_python_keyword_salary = data_df_python_keyword['薪资'].str.split('-', expand=True)[0]
print(data_df_python_keyword_salary) # 区间最小薪资
# Dataframe新增一列 在第 列新增一列名为' ' 的一列 数据
data_df_python_keyword.insert(7, '区间最小薪资(K)', data_df_python_keyword_salary)
print(data_df_python_keyword)
# 城市地区
data_df_python_keyword_location_city = data_df_python_keyword['地点'].str.split('·', expand=True)[0]
print(data_df_python_keyword_location_city) # 北京
data_df_python_keyword_location_district = data_df_python_keyword['地点'].str.split('·', expand=True)[1]
print(data_df_python_keyword_location_district) # 海淀区
data_df_python_keyword_location_city_district = []
for city, district in zip(data_df_python_keyword_location_city, data_df_python_keyword_location_district):
city_district = city + district
data_df_python_keyword_location_city_district.append(city_district)
print(data_df_python_keyword_location_city_district) # 北京海淀区
# Dataframe新增一列 在第 列新增一列名为' ' 的一列 数据
data_df_python_keyword.insert(8, '城市地区', data_df_python_keyword_location_city_district)
print(data_df_python_keyword)
data_df_python_keyword.insert(9, '城市', data_df_python_keyword_location_city)
data_df_python_keyword.insert(10, '地区', data_df_python_keyword_location_district)
data_df_python_keyword.to_csv("data_df_python_keyword.csv", index=False, encoding='gb18030')
print('-------------------------------------------')三、Hadoop数据处理
首先需要配置好hadoop环境 通过jps查看当前状态
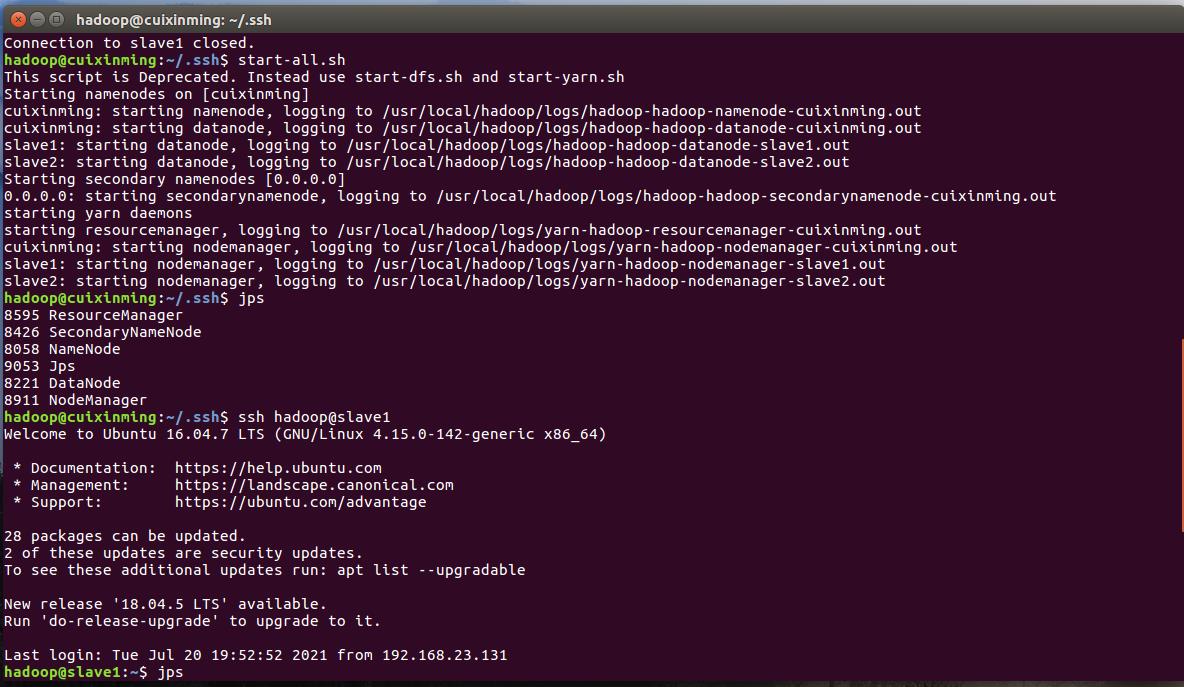
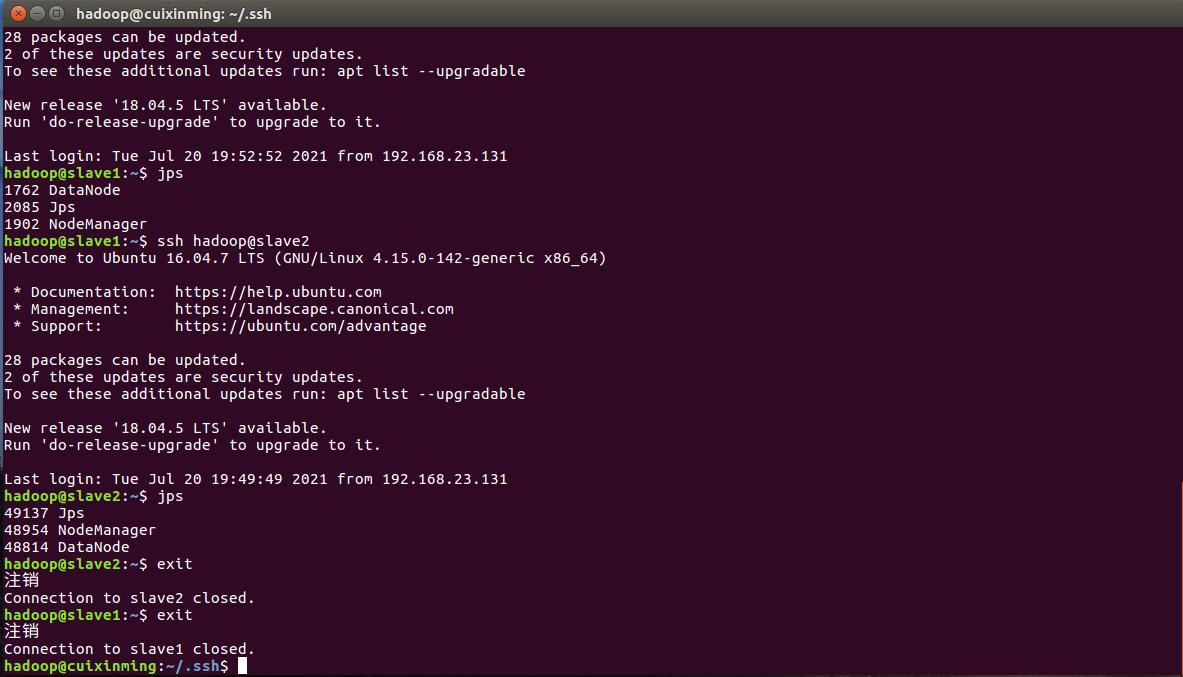
然后进入到Hive分析阶段,进行词频统计等等操作
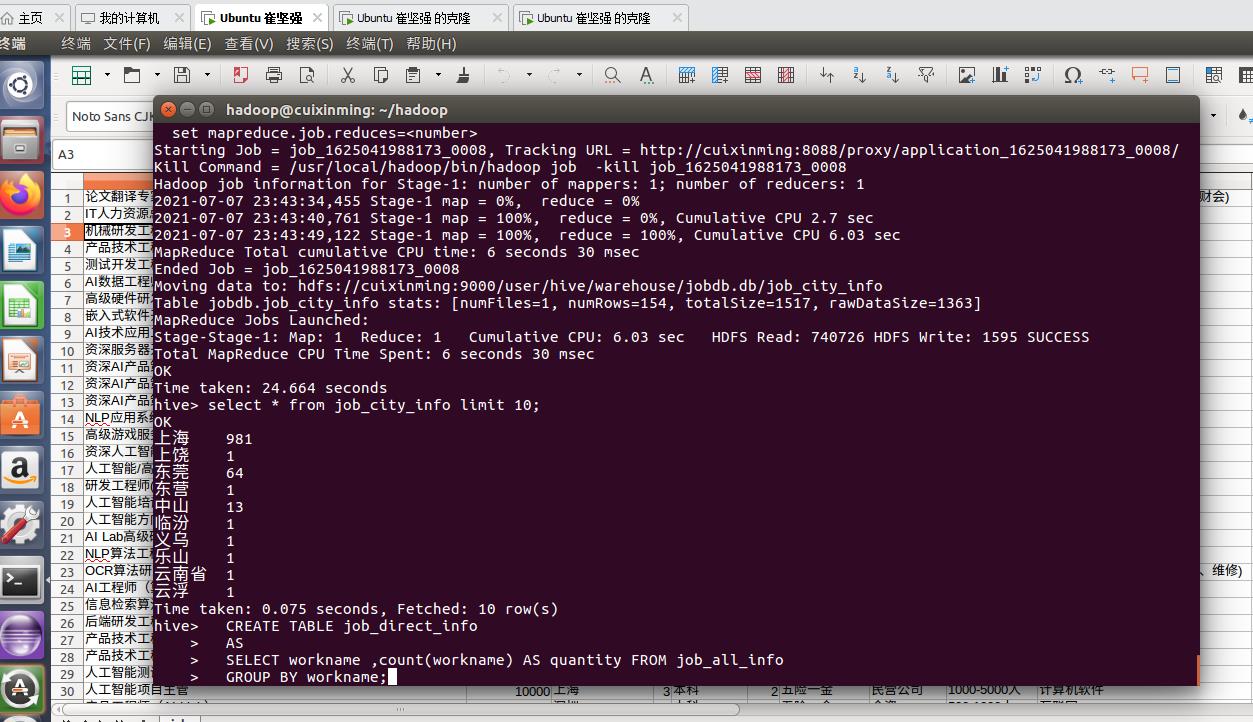
这里可以看到Hive表的最终分析后出来的表
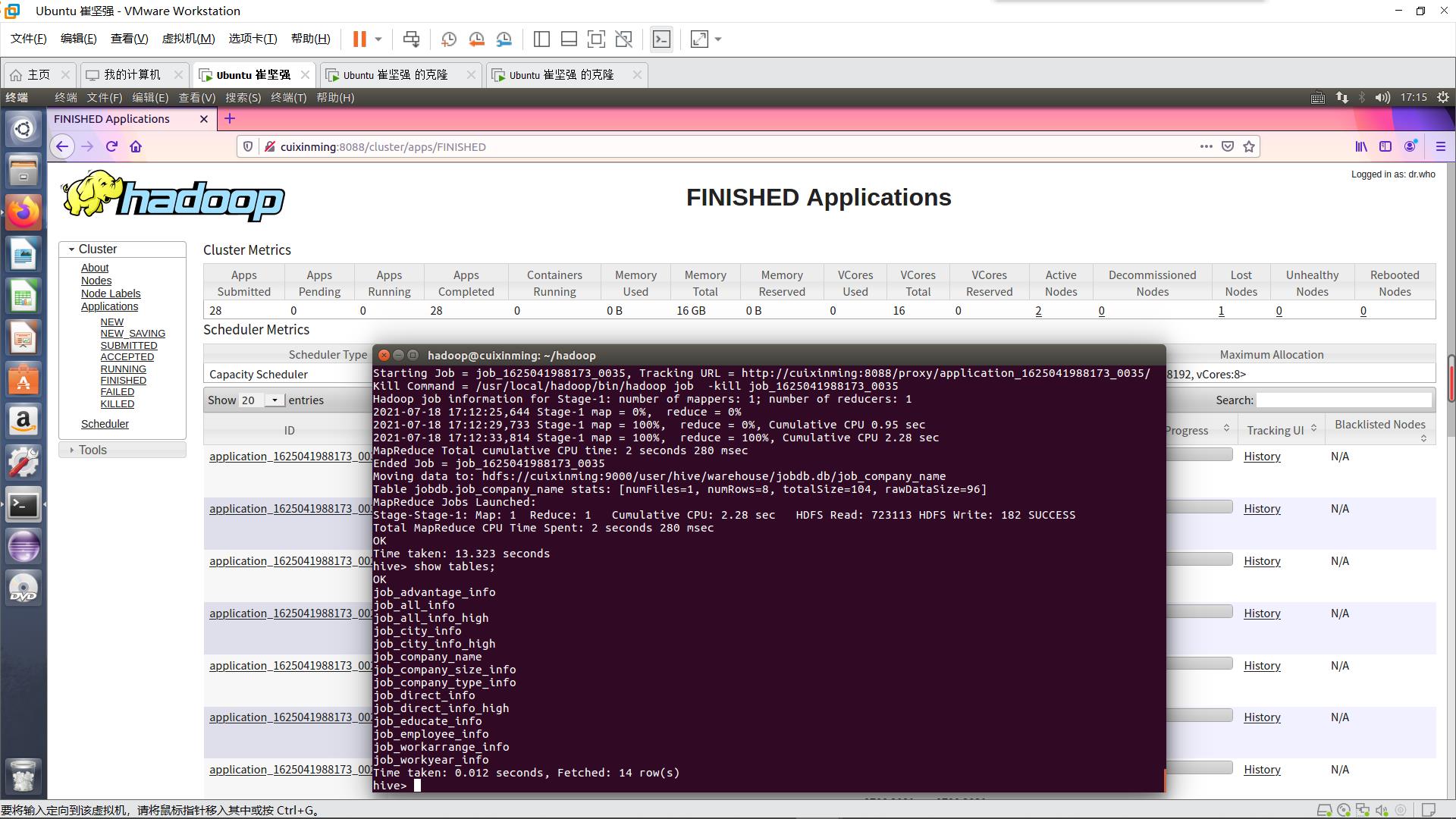
进一步通过Sqoop导入到MySQL中(MySQL需要提前建好表)
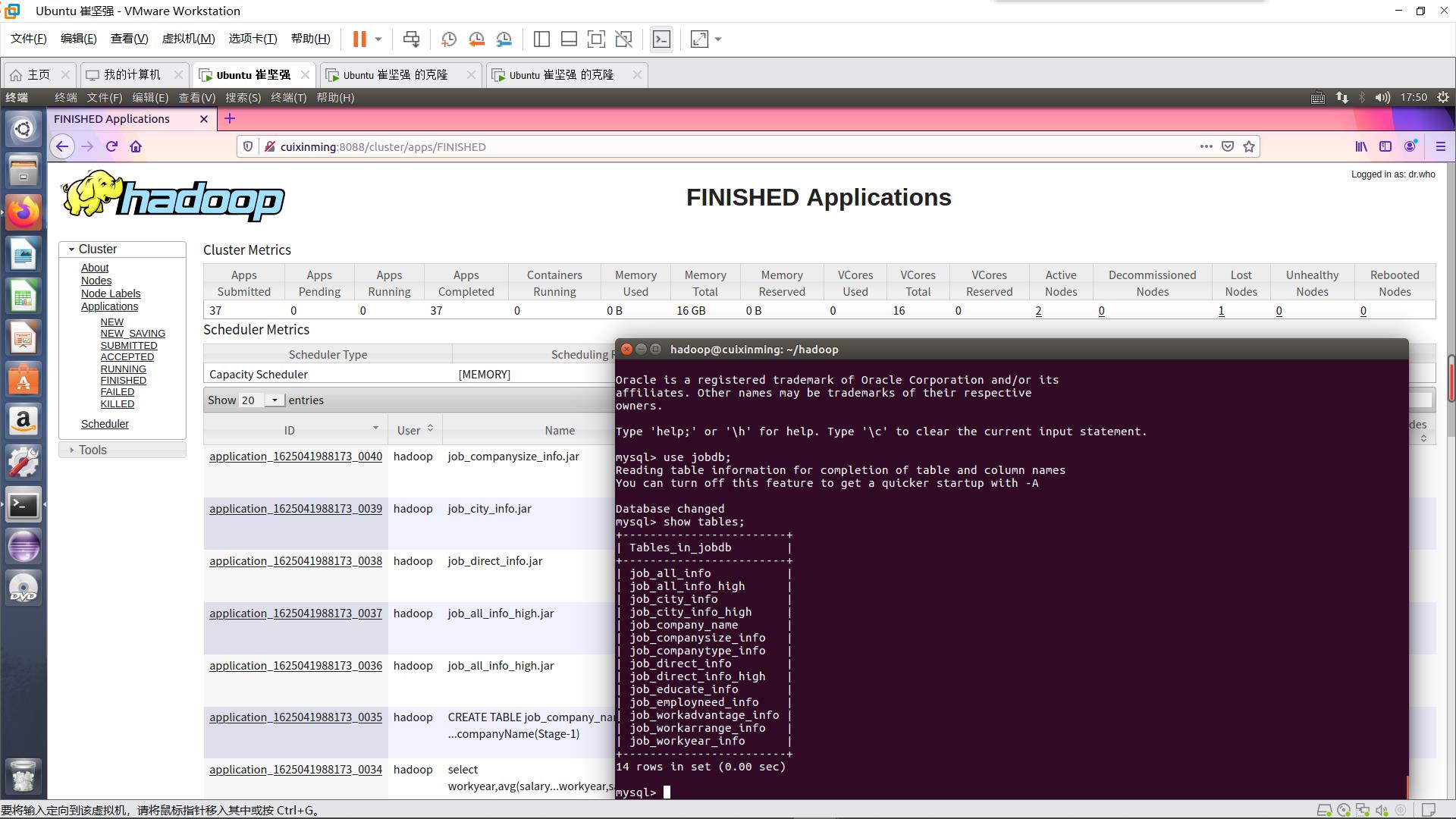
Sqoop导出过程部分如下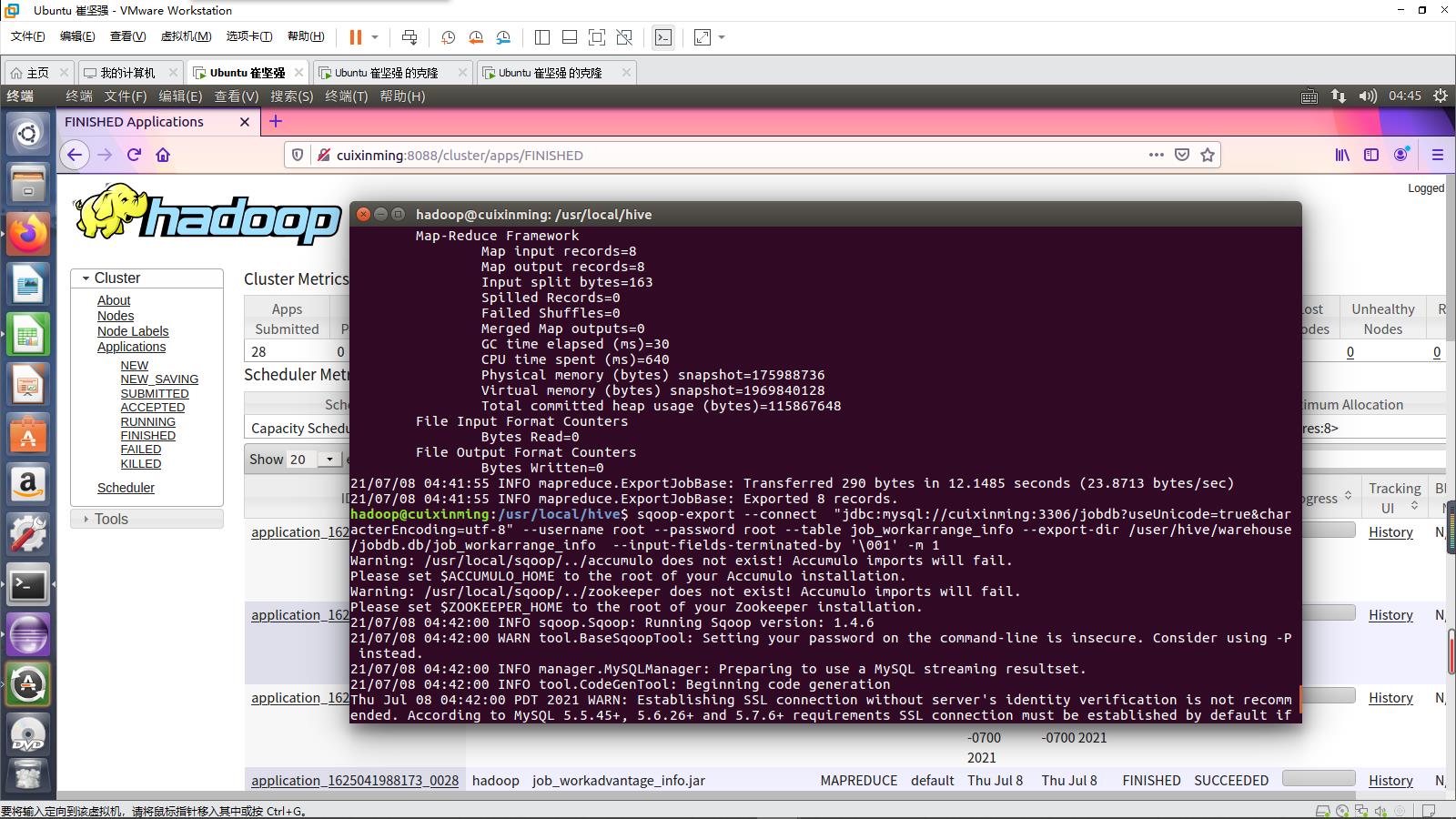
MySQL表如下
可以通过Navicat访问数据库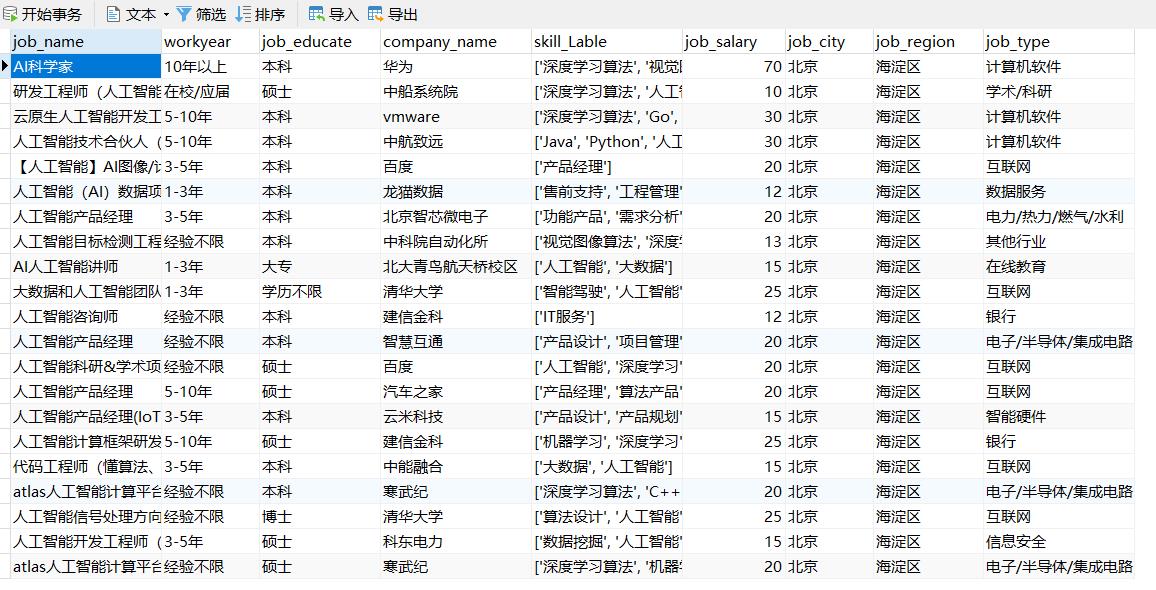
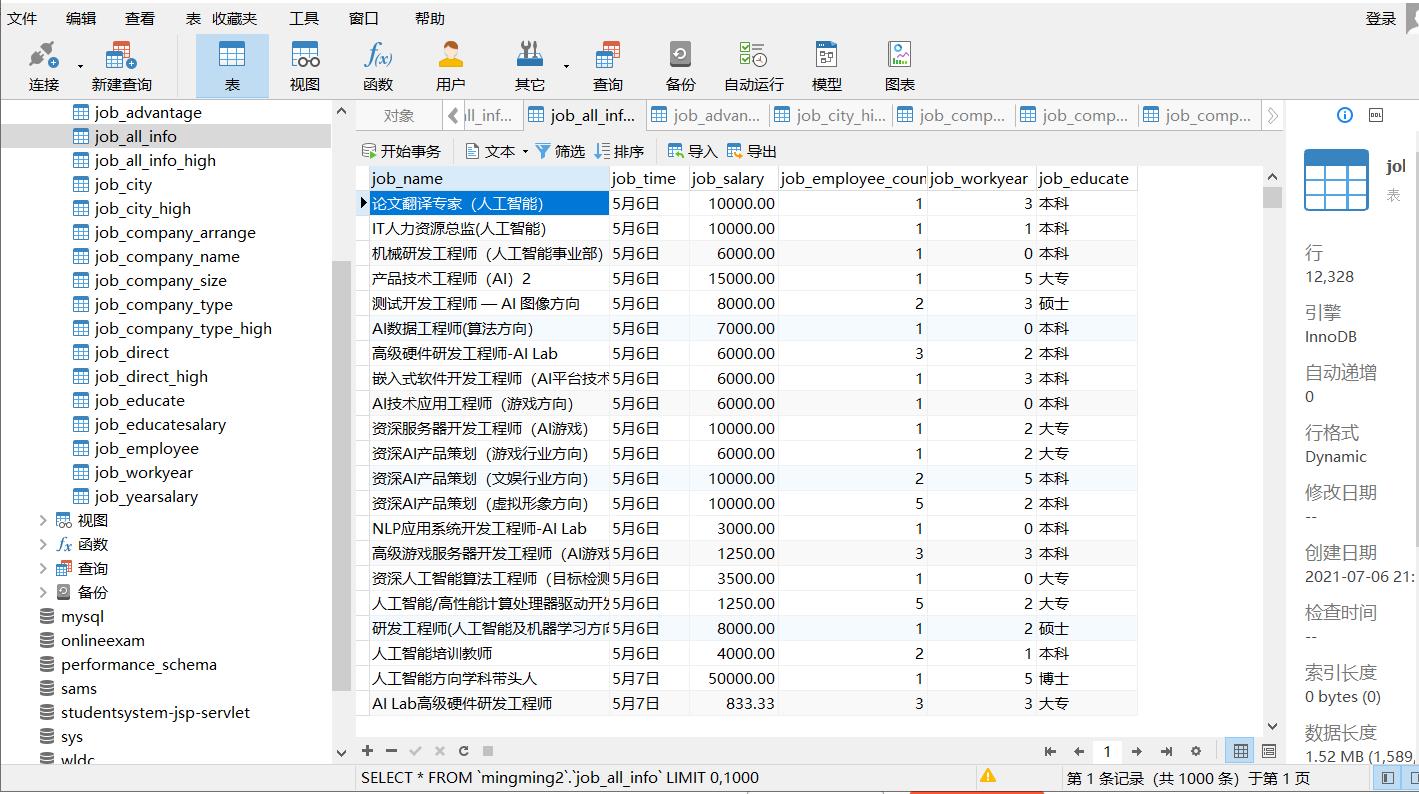
四、数据可视化
使用MVC模式架构 分层完成可视化大屏
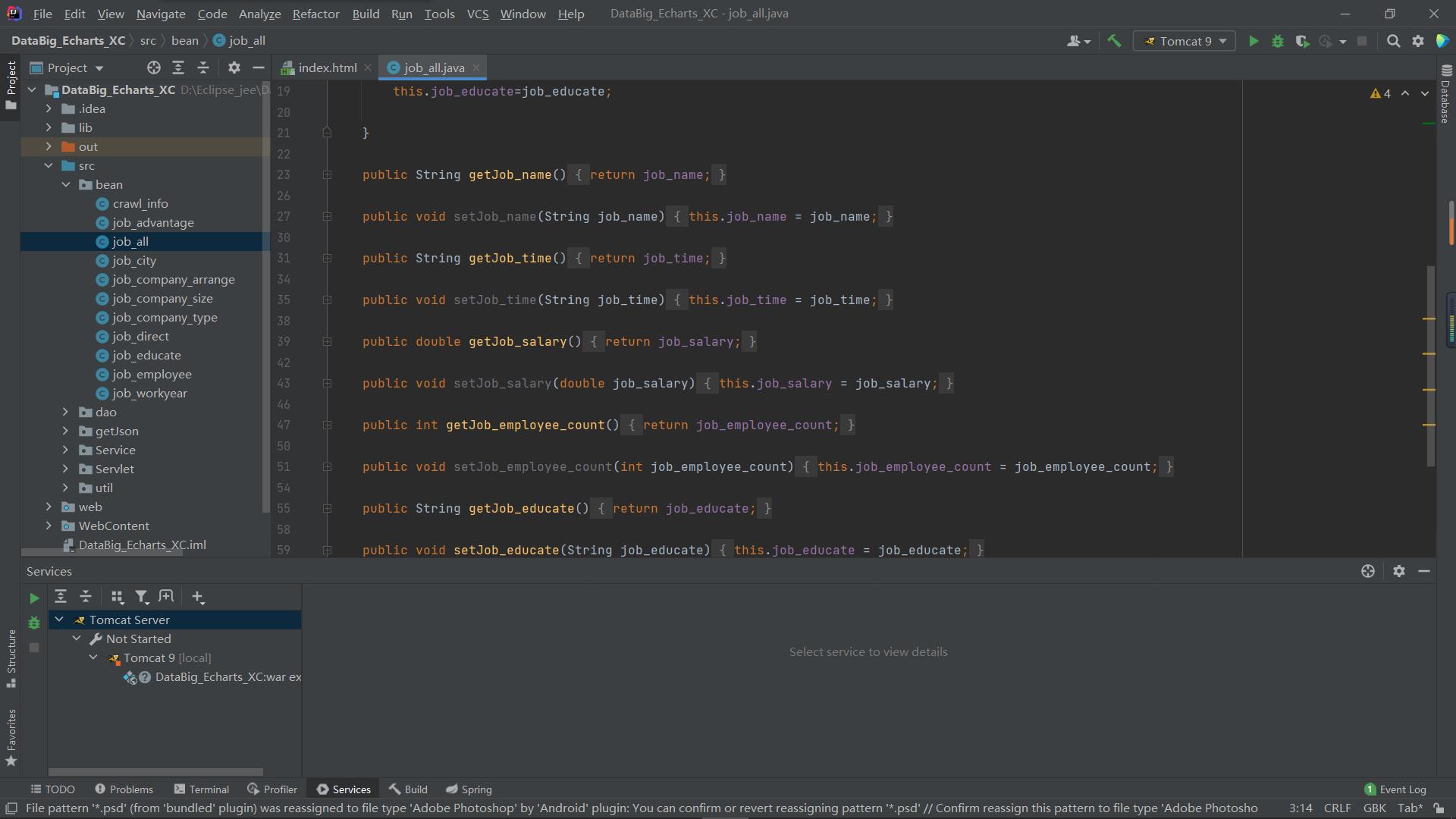
首先需要定义bean类 与数据库中 表对应
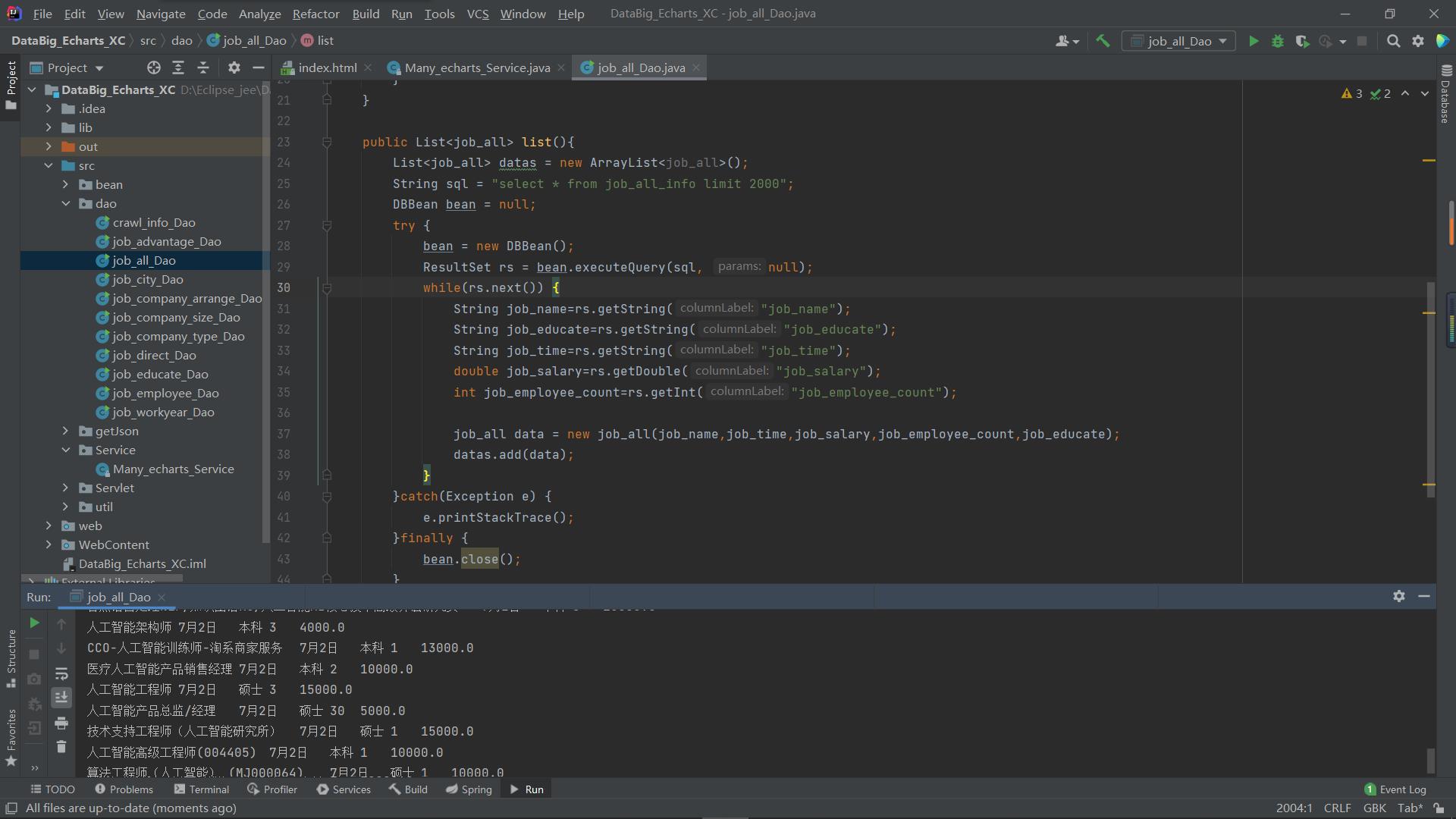
然后定义dao类 获取数据库中对应表的数据(连接数据库部分这里不再赘述)这样一个表的数据就得到了
接着我们需要定义service类将dao中获取的不同表的数据汇总到一起 完成数据聚合 获取数据列表
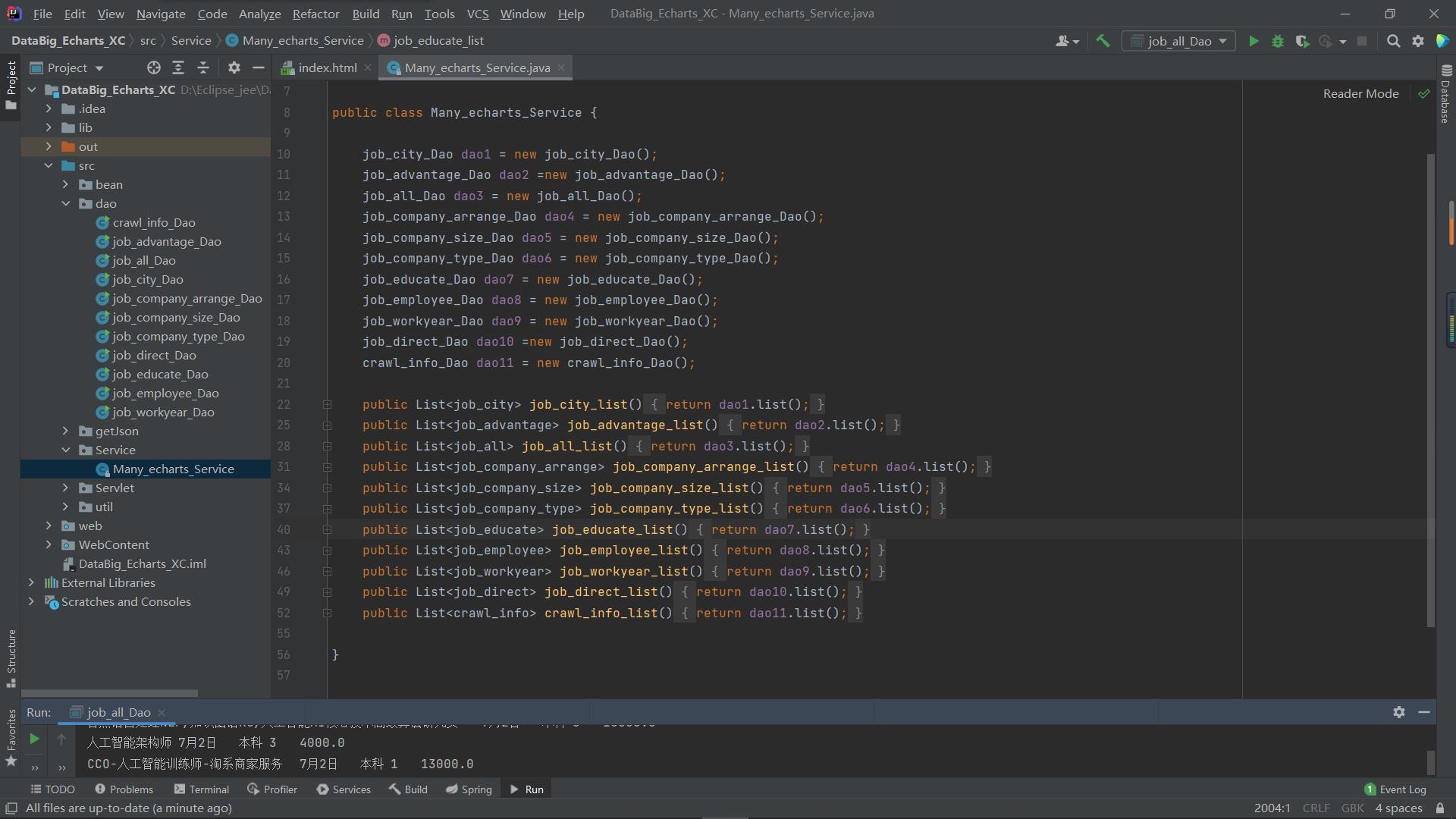
最后的servlet类负责调用service 将获取的数据发送到指定位置
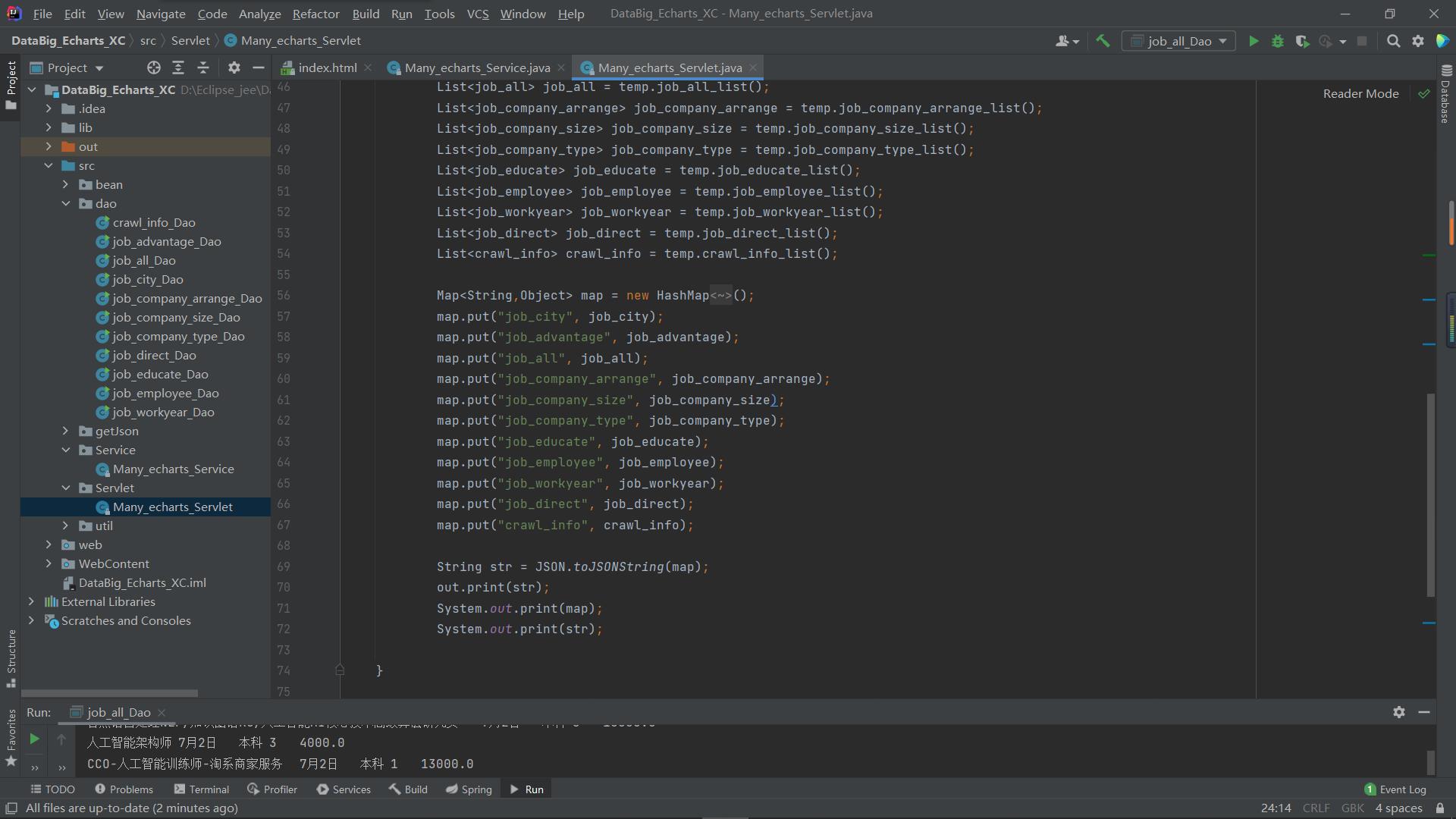
这样数据获取传输部分就完成啦
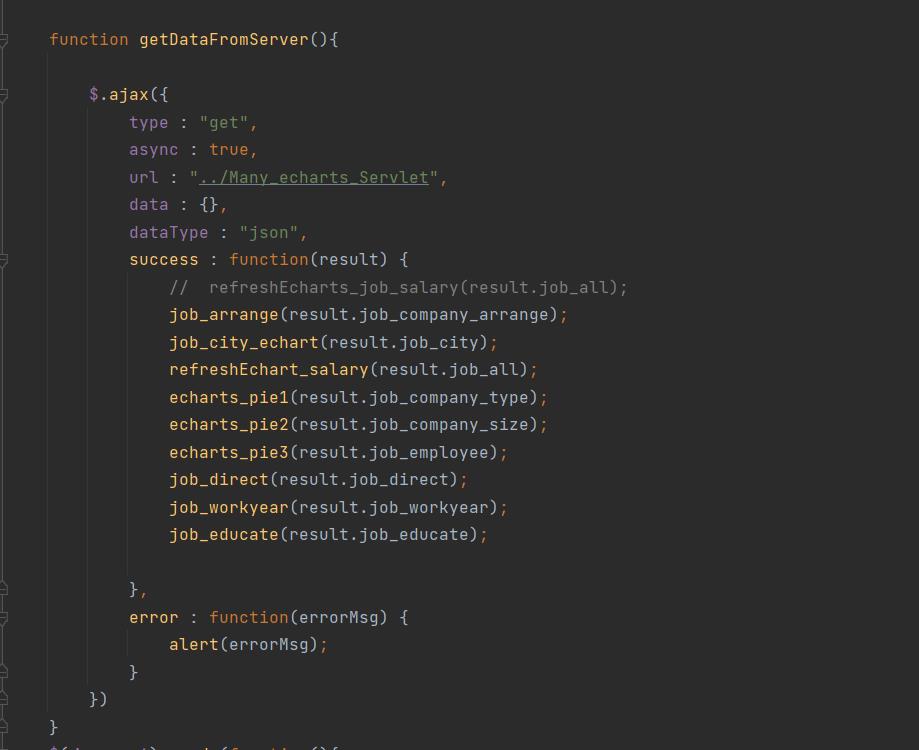
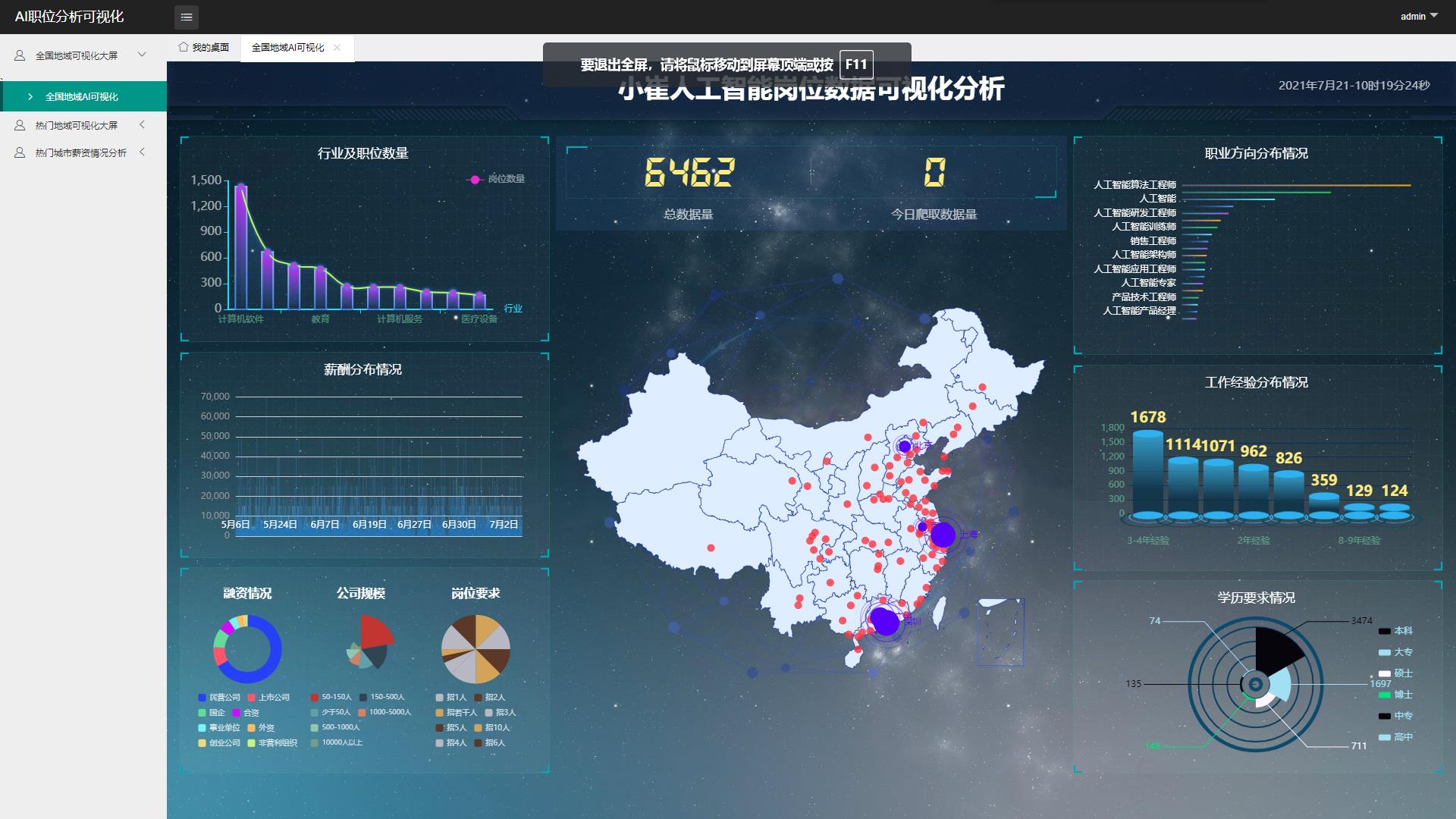
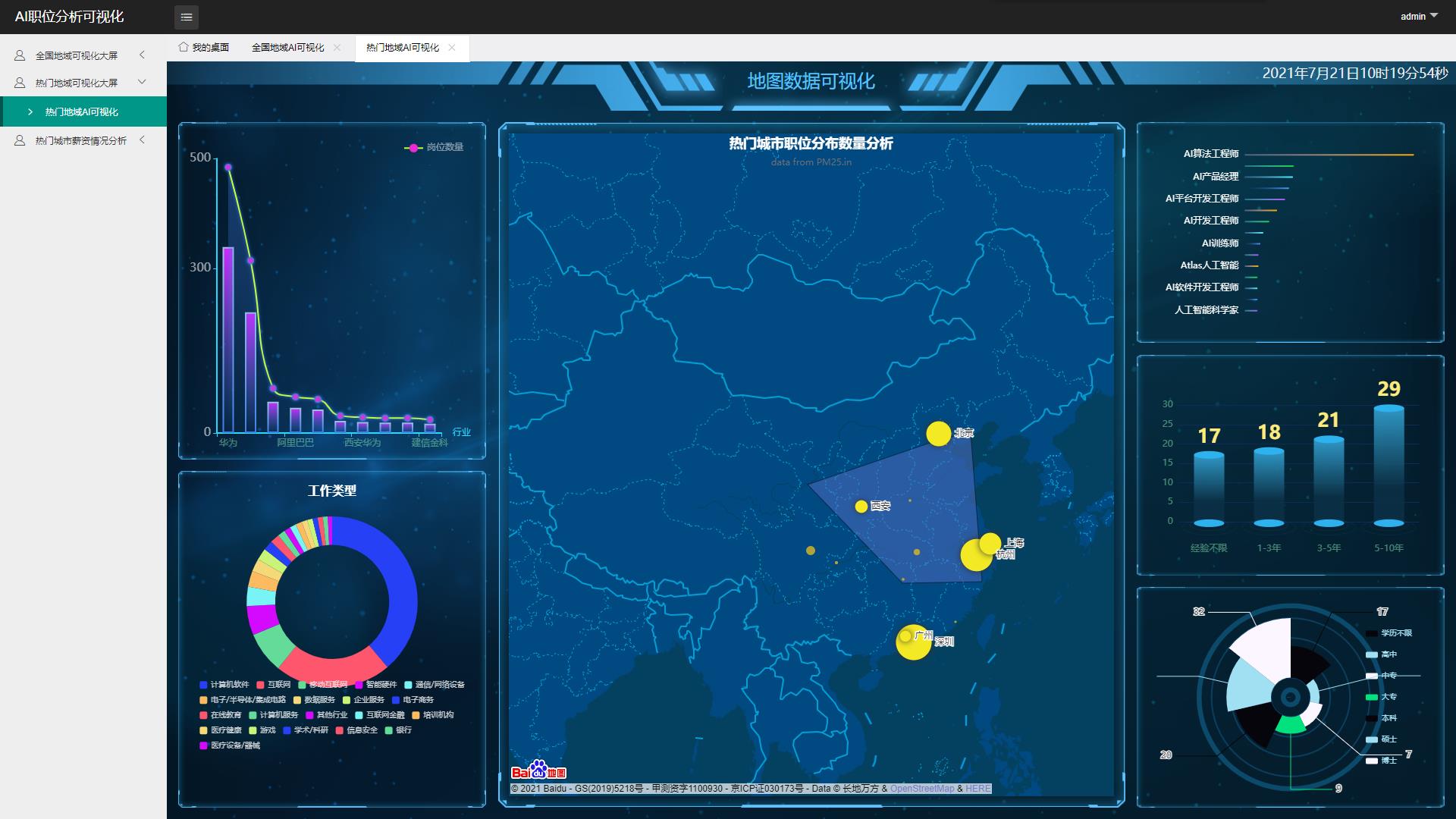
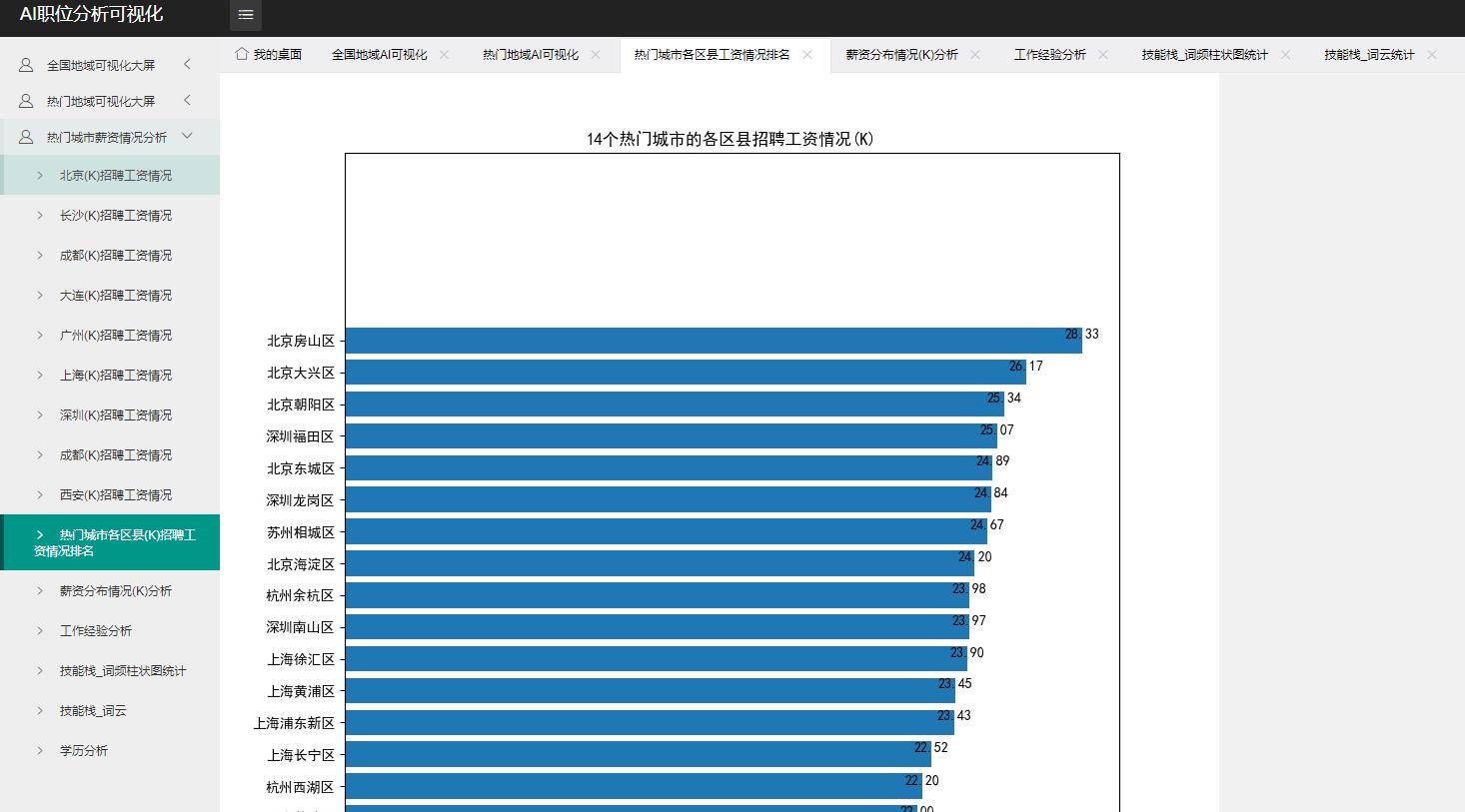
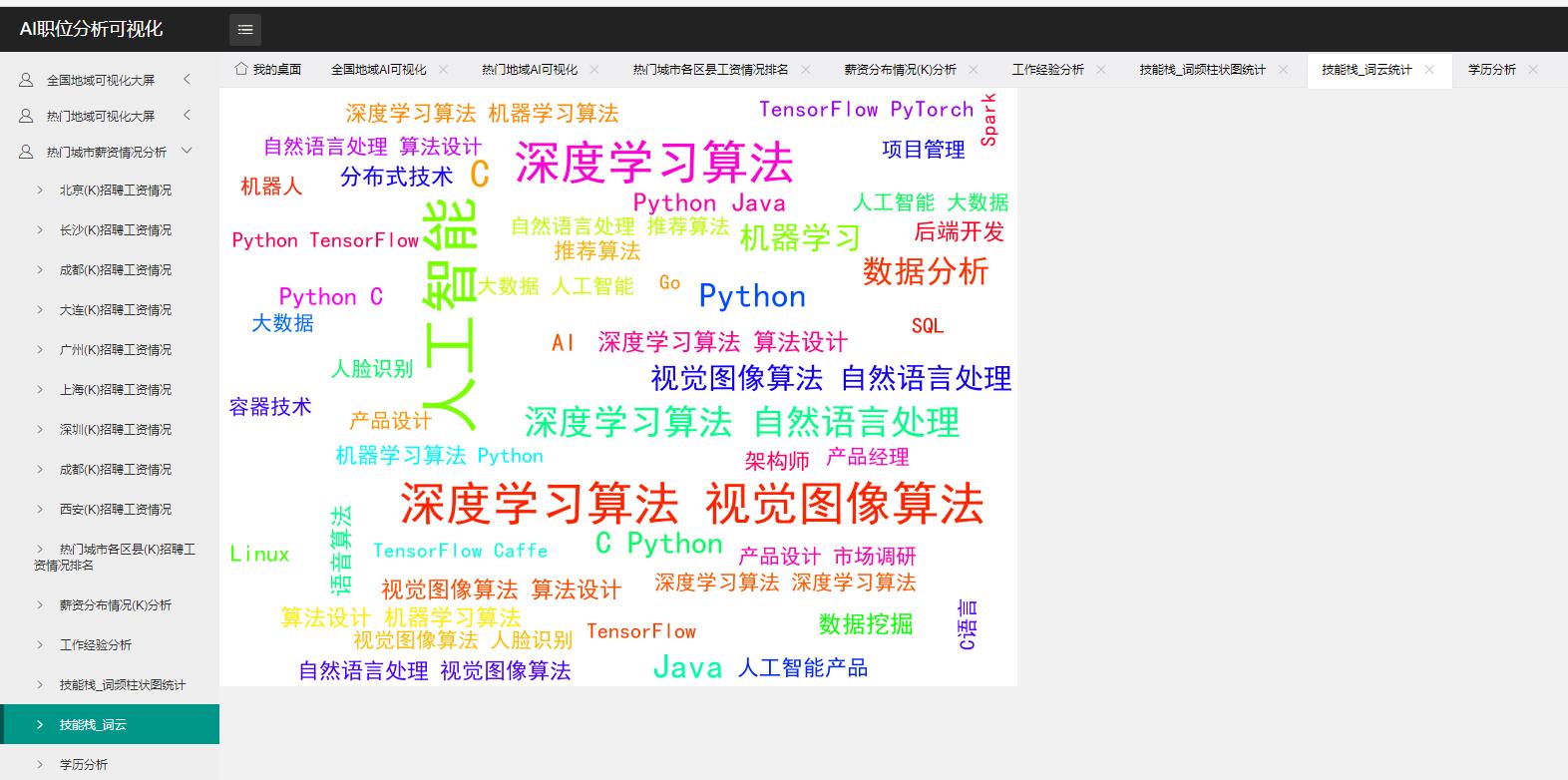
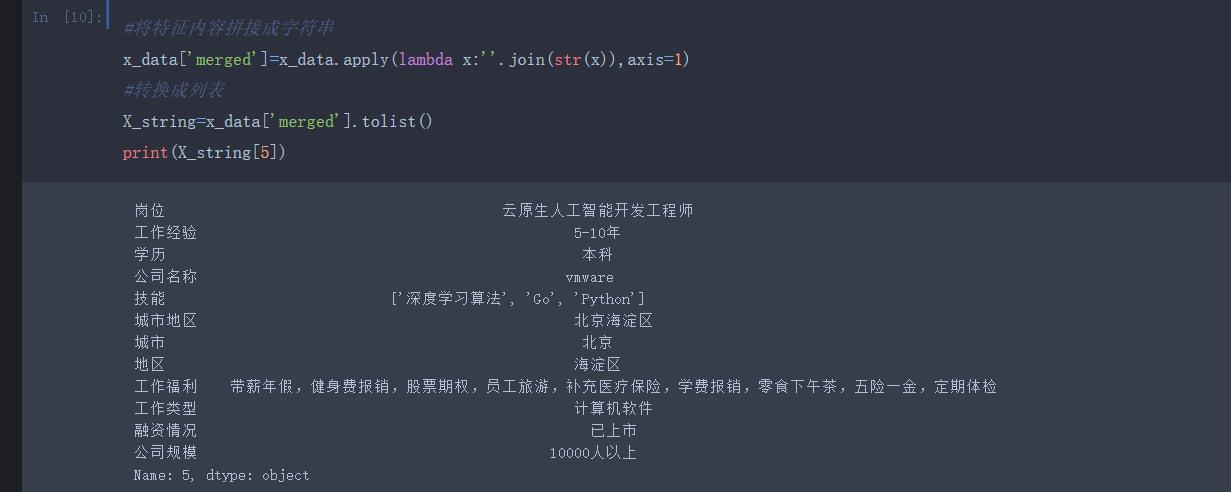
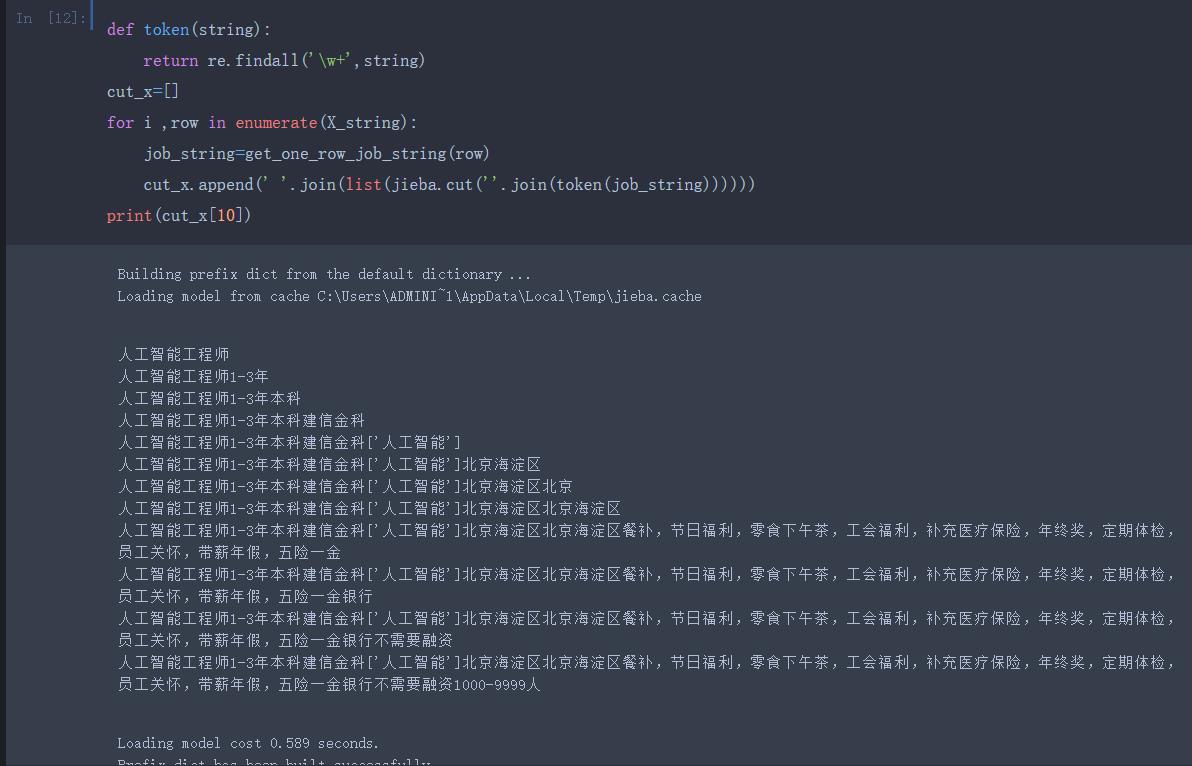
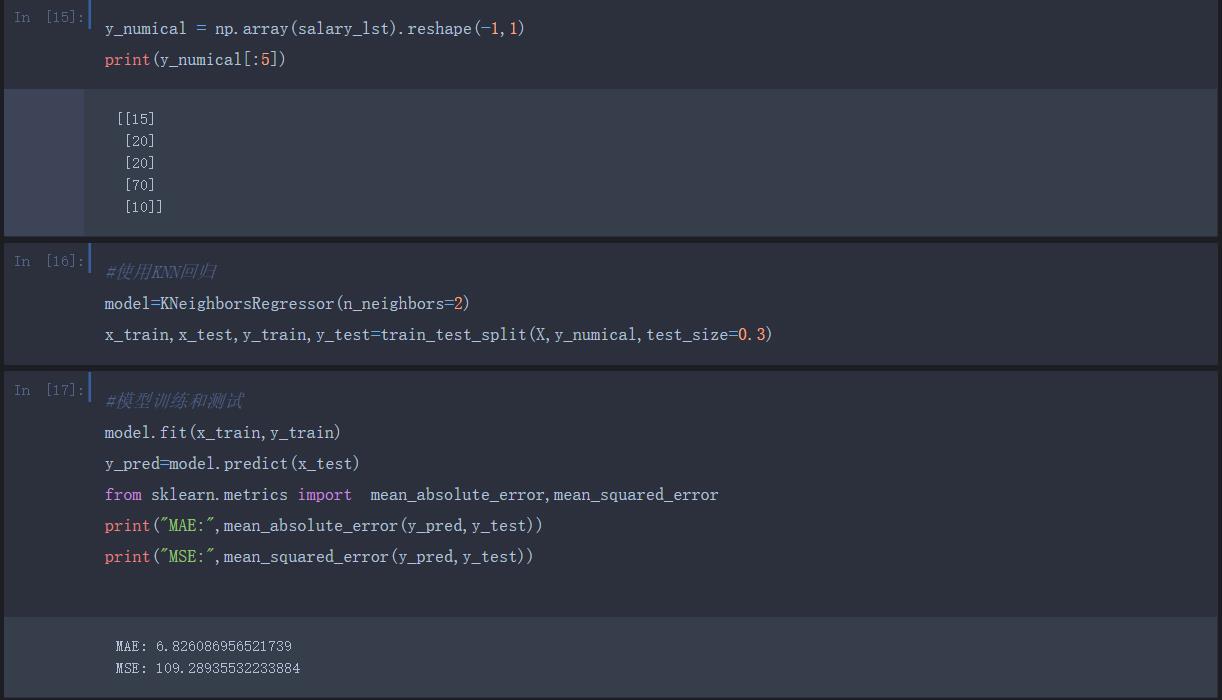
五、职位薪资预测(PageRank+TF-IDF+KNN)及职位搜索推荐
处理好的职位数据进行薪资预测
技术点:
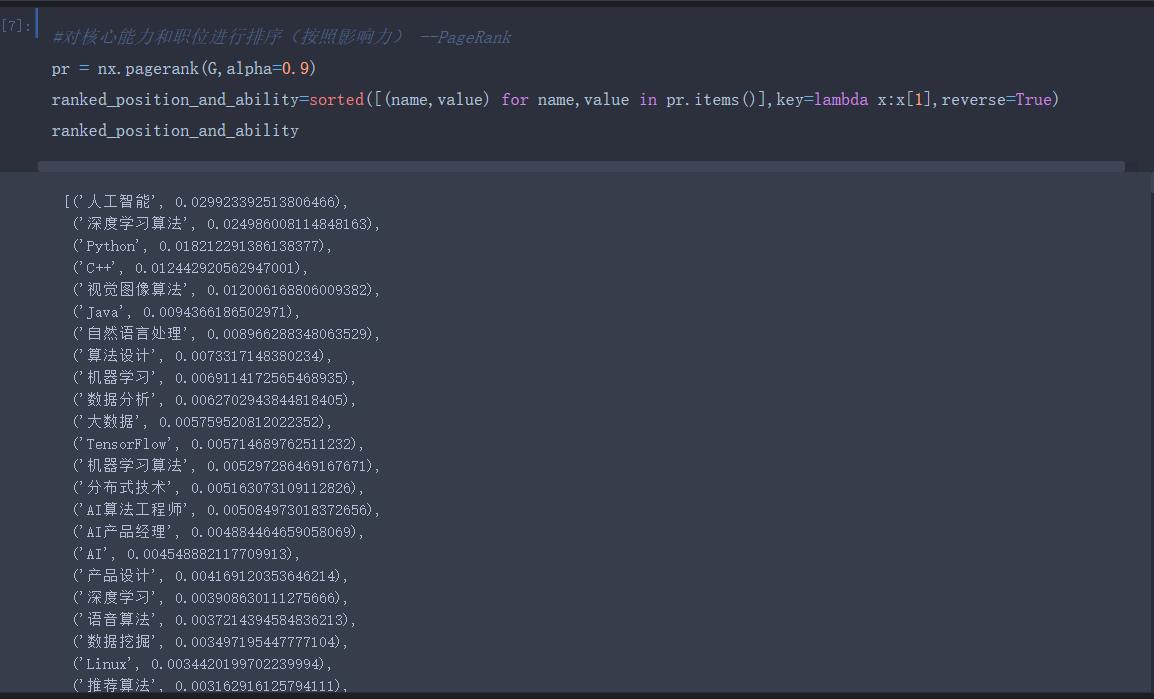
对核心能力和职位进行排序(按照影响力)-PageRank算法
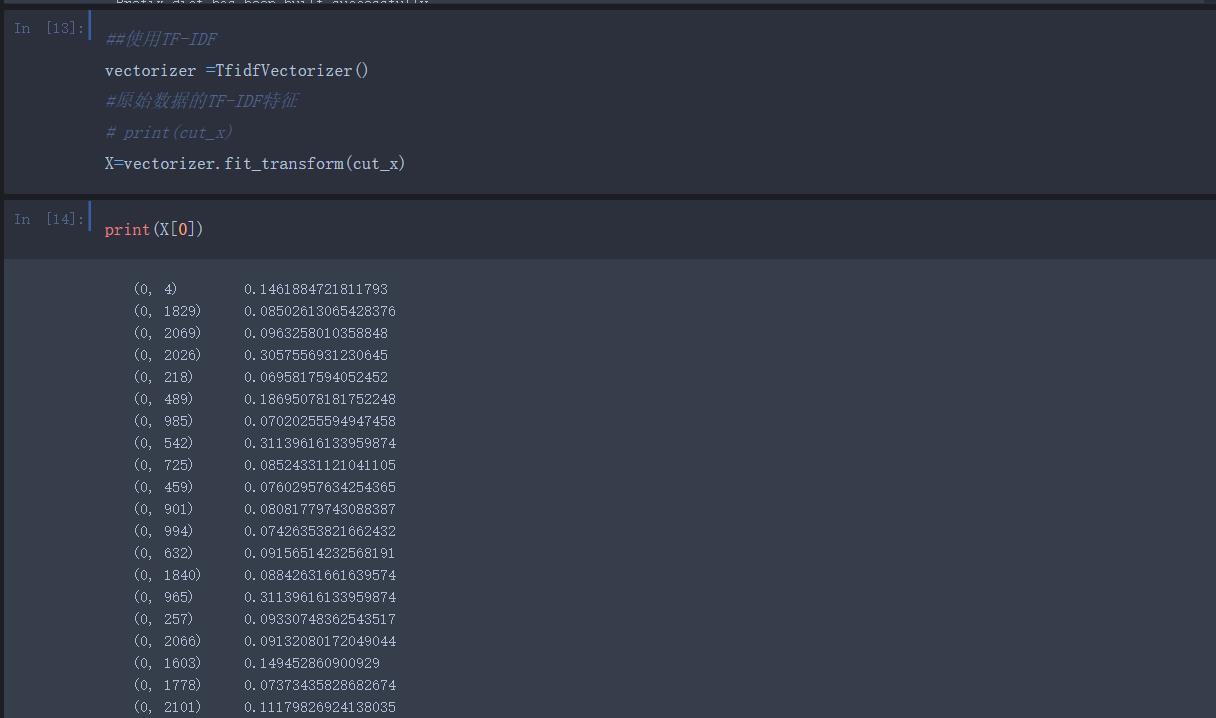
将每个特征占有的比重计算出来 -TFIDF算法
训练数据与模型预测 -KNN回归
流程如下,代码附有注释 欢迎交流~
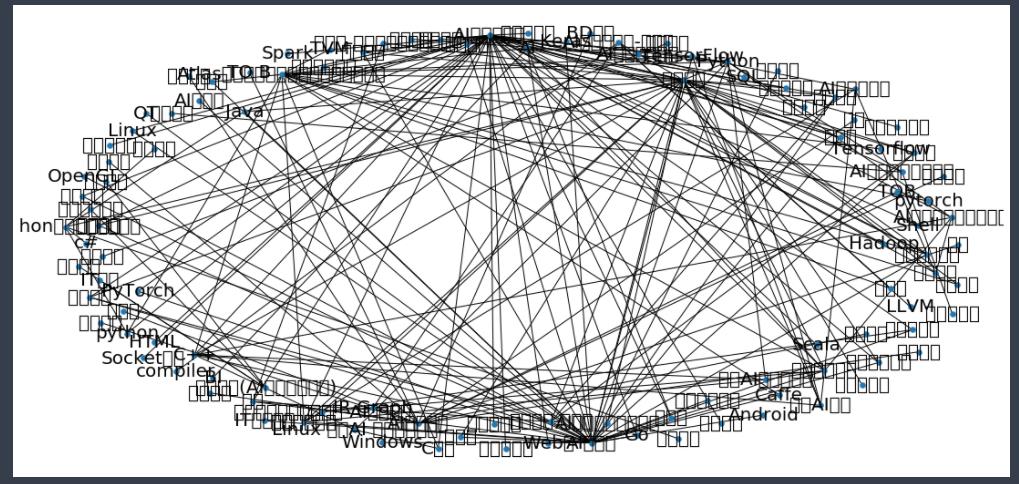
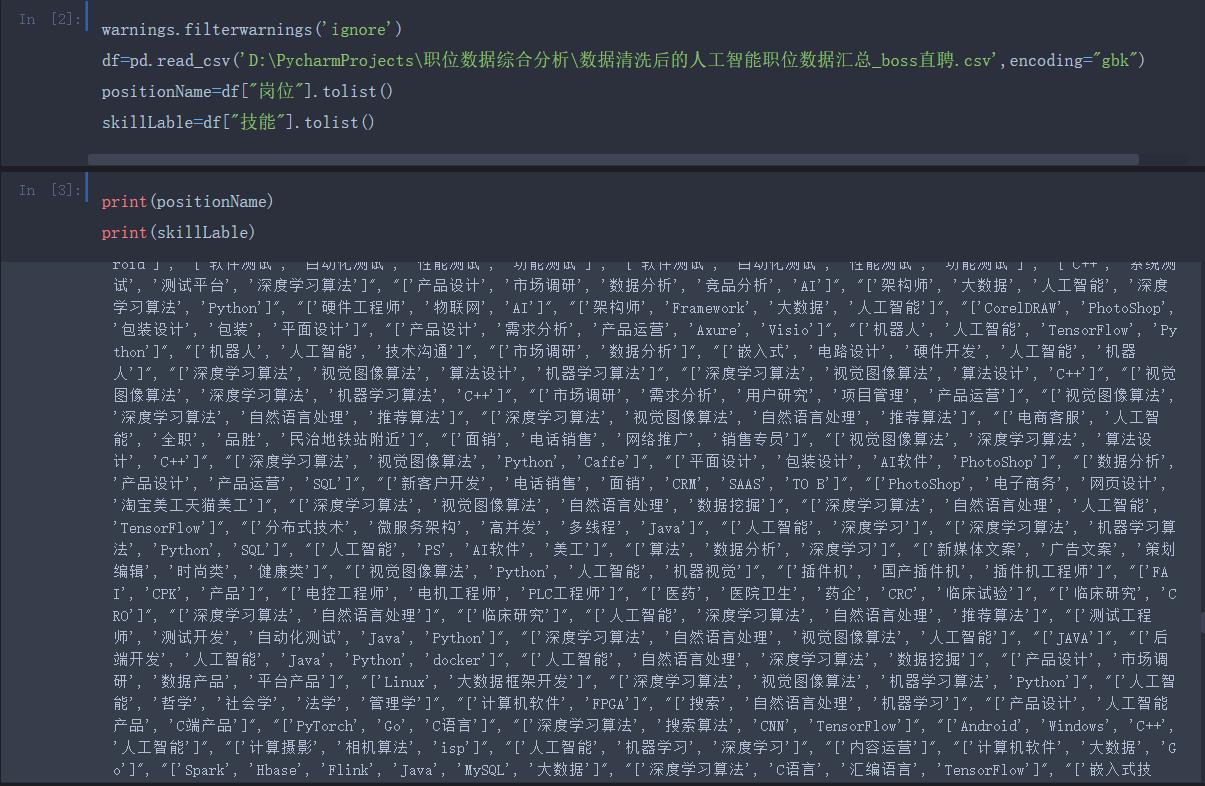
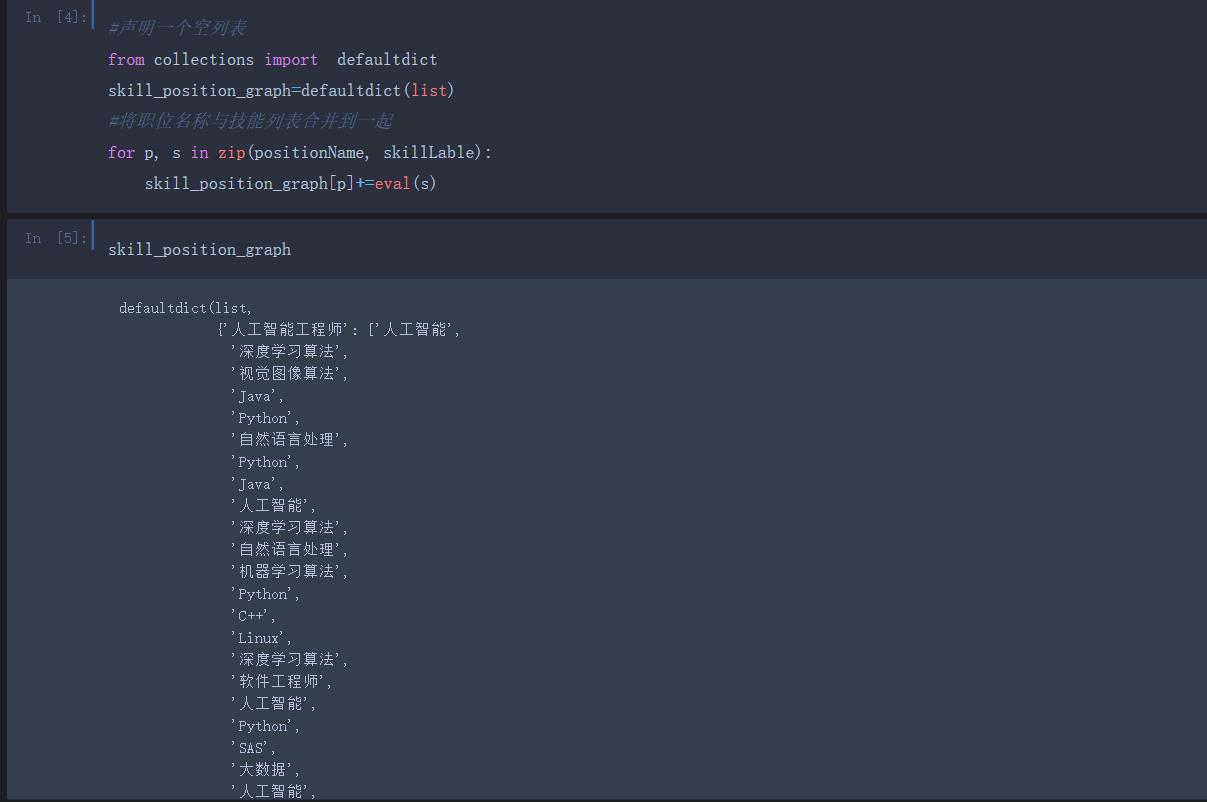
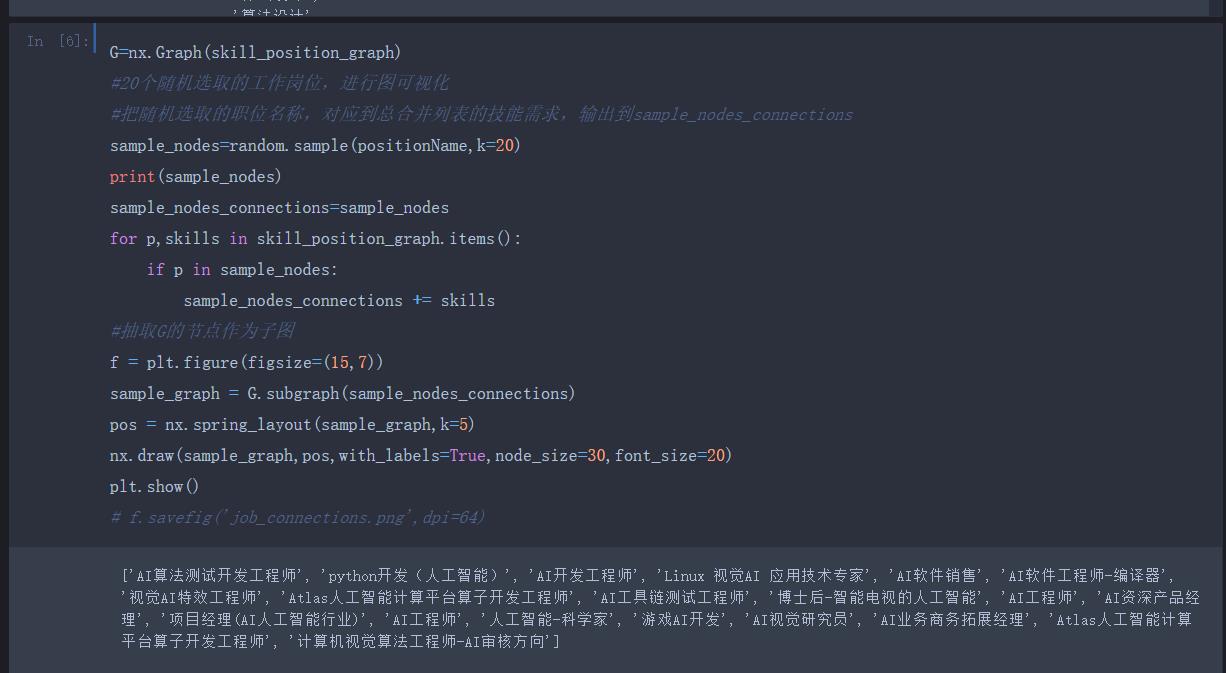

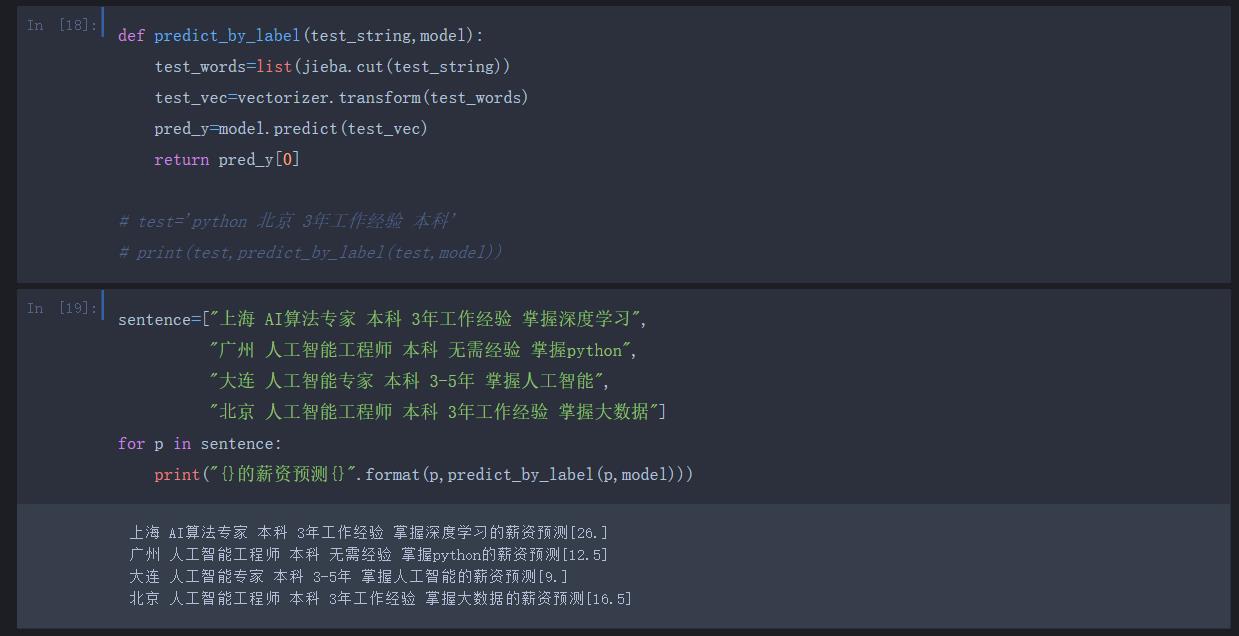
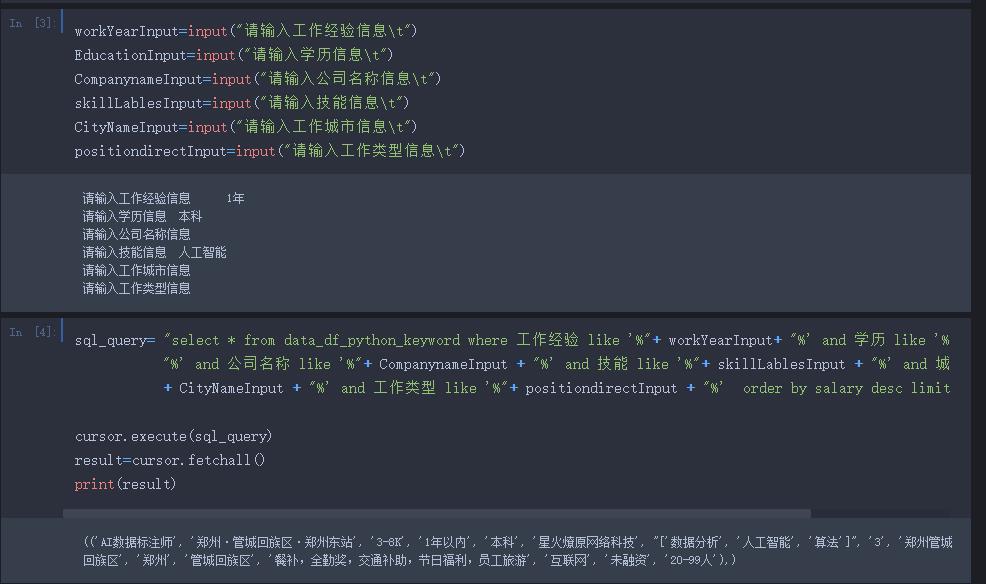
这里简单的使用模糊查询搜索薪资最高的职位 若有更好的推荐职位的算法欢迎交流~~
以上是关于基于Hadoop的项目实战-职位数据综合分析 从数据采集(Selenium)数据预处理Hive分析Sqoop导入MySQL 进一步用Javaweb可视化,最后进行机器学习数据挖掘分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章