Codeforces Round #705 (Div. 2) D. GCD of an Array
Posted TURNINING
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Codeforces Round #705 (Div. 2) D. GCD of an Array相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
传送门
题意:给你一个数组含有n个数,同时进行q次操作,每次操作让x位置上的数乘上v,每次操作后输出给个数组的gcd。
最大公约数:
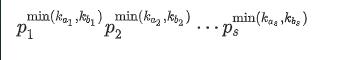
于是我们有这样的想法,对于每个素数,我们维护n个数中的最小值。显然区间最小值可以用线段树维护,但那样我们不是要开s课线段树?内存显然不够用。
1.考虑离线处理 每次算乘上这个数后对结果的贡献(指数是相加的),同样对于刚开始的n个数,我们可以看作最开始每个数都是1,然后依次乘上ai。
每次算贡献 我们可以一次把所有p的贡献算完,算完后再清空线段树就可以重复利用了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define lsn (u << 1)
#define rsn (u << 1 | 1)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
typedef pair<double, double> PD;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
const int MAX_LEN = 100000 + 10;
const int MAX_LOG_V = 22;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const ull B = 100000007;
int n, q;
struct Node {
int id, t, v;
};
vector<Node> a[MAXN];
int tr[4*MAXN];
ll ans[2*MAXN];
ll qpow(ll x, int y) {
ll res = 1;
while(y) {
if(y & 1) res = res * x % mod;
y >>= 1;
x = x * x % mod;
}
return res;
}
void pushup(int u) {
tr[u] = min(tr[lsn], tr[rsn]);
}
void add(int u, int l, int r, int p, int v) {
if(l == r && l == p) tr[u] += v;
else {
if(p <= mid) add(lsn, l, mid, p, v);
else add(rsn, mid+1, r, p, v);
pushup(u);
}
}
void solve() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &q);
for(int i = 1; i <= n + q; i++) ans[i] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x; scanf("%d", &x);
for(int j = 2; j * j <= x; j++) {
if(x % j != 0) continue;
int cnt = 0;
while(x % j == 0) {
cnt++;
x /= j;
}
a[j].emplace_back(Node{i, i, cnt});
}
if(x != 1) a[x].emplace_back(Node{i, i, 1});
}
for(int i = n+1; i <= n+q; i++) {
int id, x; scanf("%d %d", &id, &x);
for(int j = 2; j * j <= x; j++) {
if(x % j != 0) continue;
int cnt = 0;
while(x % j == 0) {
cnt++;
x /= j;
}
a[j].emplace_back(Node{id, i, cnt});
}
if(x != 1) a[x].emplace_back(Node{id, i, 1});
}
for(int i = 2; i < MAXN; i++) {
int last = 0;
for(auto p : a[i]) {
add(1, 1, n, p.id, p.v);
if(tr[1] == last) continue;
ans[p.t] = ans[p.t] * qpow(i, tr[1]-last) % mod; //在p.t时刻素数i对结果的贡献。
last = tr[1];
}
for(auto p : a[i]) {
add(1, 1, n, p.id, -p.v);
}
}
for(int i = 2; i <= n + q; i++) {
ans[i] = ans[i] * ans[i-1] % mod;
}
for(int i = n+1; i <= n+q; i++) {
printf("%lld\\n", ans[i]);
}
}
int main() {
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t = 1; //scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
2.动态开点线段树。
就非要开2e5个线段树
引用真是个好东西
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define lsn (u << 1)
#define rsn (u << 1 | 1)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
typedef pair<double, double> PD;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
const int MAX_LEN = 100000 + 10;
const int MAX_LOG_V = 22;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const ull B = 100000007;
int n, q;
ll qpow(ll x, ll y) {
ll res = 1;
while(y) {
if(y & 1) res = res * x % mod;
y >>= 1;
x = x * x % mod;
}
return res;
}
const int maxm = 1e7 + 5;
int ls[maxm], rs[maxm], tr[maxm], rt[maxm], tot;
void pushup(int u) {
tr[u] = min(tr[ls[u]], tr[rs[u]]);
}
void add(int &u, int l, int r, int p, int v) {
if(!u) u = ++tot;
if(l == r) { tr[u] += v; return ; }
else {
if(p <= mid) add(ls[u], l, mid, p, v);
else add(rs[u], mid+1, r, p, v);
pushup(u);
}
}
void solve() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &q);
ll ans = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x; scanf("%d", &x);
for(int j = 2; j * j <= x; j++) {
if(x % j != 0) continue;
int cnt = 0;
while(x % j == 0) {
cnt++;
x /= j;
}
int pre = tr[rt[j]];
add(rt[j], 1, n, i, cnt);
ans = ans * qpow(j, tr[rt[j]]-pre) % mod;
}
if(x != 1) {
int pre = tr[rt[x]];
add(rt[x], 1, n, i, 1);
ans = ans * qpow(x, tr[rt[x]]-pre) % mod;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++) {
int p, x; scanf("%d %d", &p, &x);
for(int j = 2; j * j <= x; j++) {
if(x % j != 0) continue;
int cnt = 0;
while(x % j == 0) {
cnt++;
x /= j;
}
int pre = tr[rt[j]];
add(rt[j], 1, n, p, cnt);
ans = ans * qpow(j, tr[rt[j]]-pre) % mod;
}
if(x != 1) {
int pre = tr[rt[x]];
add(rt[x], 1, n, p, 1);
ans = ans * qpow(x, tr[rt[x]]-pre) % mod;
}
printf("%lld\\n", ans);
}
}
int main() {
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t = 1; //scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
以上是关于Codeforces Round #705 (Div. 2) D. GCD of an Array的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Codeforces Round #705 (Div. 2) D. GCD of an Array
Codeforces Round #436 E. Fire(背包dp+输出路径)