youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇148. 图像分割之线检测
Posted 小白YouCans
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇148. 图像分割之线检测相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
欢迎关注 『youcans 的 OpenCV 例程 200 篇』 系列,持续更新中
欢迎关注 『youcans 的 OpenCV学习课』 系列,持续更新中
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】148. 图像分割之线检测
2. 点、线和边缘检测
本节基于图像灰度的不连续性,讨论根据灰度的突变检测边界,以此为基础进行图像分割。
- 边缘像素是图像中灰度突变的像素,而边缘是相连边缘像素的集合。
- 线是一条细边缘线段,其两侧的背景灰度与线段的像素灰度存在显著差异。
- 孤立的点是一个被背景像素围绕的前景像素,或一个被前景像素围绕的背景像素。
导数可以用来检测灰度的局部突变:
- 一阶导数通常产生粗边缘;
- 二阶导数对精细细节(如细线、孤立点和噪声)的响应更强;
- 二阶导数在灰度斜坡和台阶过渡处会产生双边缘响应,即二阶导数在进入和离开边缘时的符号相反;
- 二阶导数的符号可用于确定边缘的过渡是从亮到暗还是从暗到亮。
计算图像中每个像素位置的一阶导数和二阶导数的方法是空间卷积。对一个 3*3 模板,计算模板区域内灰度值与模板系数的卷积。
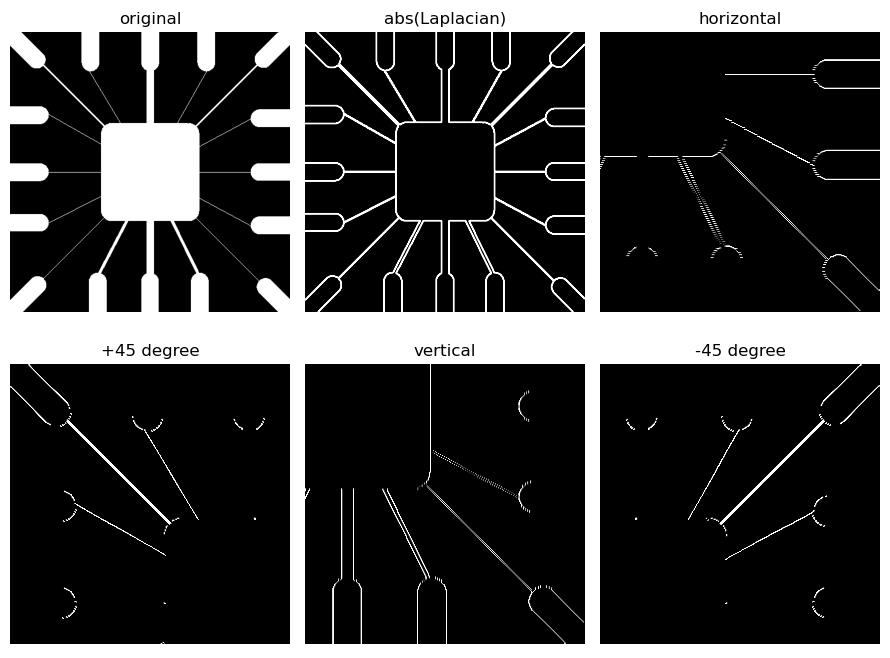
### 2.2 图像的线检测
线检测的复杂度更高。
使用二阶导数将导致更强的滤波器响应,产生比一阶导数更细的线,因此可以使用拉普拉斯核进行线检测。
由于拉普拉斯检测核是各向同性的,其响应与方向无关。如果希望检测某些特定方向的线,可以使用与方向有关的卷积核:
K
0
o
=
[
−
1
−
1
−
1
2
2
2
−
1
−
1
−
1
]
,
K
+
4
5
o
=
[
2
−
1
−
1
−
1
2
−
1
−
1
−
1
2
]
,
K
9
0
o
=
[
−
1
2
−
1
−
1
2
−
1
−
1
2
−
1
]
,
K
−
4
5
o
=
[
−
1
−
1
2
−
1
2
−
1
2
−
1
−
1
]
\\beginaligned &K_0^o = \\beginbmatrix -1 & -1 & -1\\\\ 2 & 2 & 2\\\\ -1 & -1 & -1\\\\ \\endbmatrix, \\ &K_+45^o = \\beginbmatrix 2 & -1 & -1\\\\ -1 & 2 & -1\\\\ -1 & -1 & 2\\\\ \\endbmatrix, \\\\ &K_90^o = \\beginbmatrix -1 & 2 & -1\\\\ -1 & 2 & -1\\\\ -1 & 2 & -1\\\\ \\endbmatrix, \\ &K_-45^o = \\beginbmatrix -1 & -1 & 2\\\\ -1 & 2 & -1\\\\ 2 & -1 & -1\\\\ \\endbmatrix \\endaligned
K0o=⎣⎡−12−1−12−1−12−1⎦⎤, K90o=⎣⎡−1−1−1222−1−1−1⎦⎤, K+45o=⎣⎡2−1−1−12−1−1−12⎦⎤,K−45o=⎣⎡−1−12−12−12−1−1⎦⎤
例程 11.2:图像的线检测
# 11.2 图像的线检测 (Laplace 算子)
imgGray = cv2.imread("../images/Fig0905a.tif", flags=0)
# scipy.signal 实现卷积运算 (注意:不能用 cv2.filter2D 处理)
from scipy import signal
kernelLaplace = np.array([[1, 1, 1], [1, -8, 1], [1, 1, 1]]) # Laplacian kernel
imgLaplace = signal.convolve2d(imgGray, kernelLaplace, boundary='symm', mode='same') # same 卷积
kernel1 = np.array([[-1, -1, -1], [2, 2, 2], [-1, -1, -1]]) # 0 degree, horizontal
kernel2 = np.array([[2, -1, -1], [-1, 2, -1], [-1, -1, 2]]) # +45 degree
kernel3 = np.array([[-1, 2, -1], [-1, 2, -1], [-1, 2, -1]]) # 90 degree, vertical
kernel4 = np.array([[-1, -1, 2], [-1, 2, -1], [2, -1, -1]]) # -45 degree
imgLine1 = signal.convolve2d(imgGray, kernel1, boundary='symm', mode='same') # horizontal kernel
imgLine2 = signal.convolve2d(imgGray, kernel2, boundary='symm', mode='same')
imgLine3 = signal.convolve2d(imgGray, kernel3, boundary='symm', mode='same') # vertical kernel
imgLine4 = signal.convolve2d(imgGray, kernel4, boundary='symm', mode='same')
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 7))
plt.subplot(231), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("original")
plt.imshow(imgGray, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.subplot(232), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("abs(Laplacian)")
plt.imshow(np.maximum(imgLaplace, -imgLaplace), cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.subplot(233), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("horizontal")
plt.imshow(imgLine1[200:,200:], cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.subplot(234), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("+45 degree")
plt.imshow(imgLine2[:286,:286], cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.subplot(235), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("vertical")
plt.imshow(imgLine3[200:,200:], cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.subplot(236), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("-45 degree")
plt.imshow(imgLine4[:286,200:], cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
(本节完)
版权声明:
youcans@xupt 原创作品,转载必须标注原文链接:(https://blog.csdn.net/youcans/article/details/124027129)
Copyright 2022 youcans, XUPT
Crated:2022-4-8
欢迎关注 『youcans 的 OpenCV 例程 200 篇』 系列,持续更新中
欢迎关注 『youcans 的 OpenCV学习课』 系列,持续更新中【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】01. 图像的读取(cv2.imread)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】02. 图像的保存(cv2.imwrite)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】03. 图像的显示(cv2.imshow)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】04. 用 matplotlib 显示图像(plt.imshow)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】05. 图像的属性(np.shape)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】06. 像素的编辑(img.itemset)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】07. 图像的创建(np.zeros)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】08. 图像的复制(np.copy)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】09. 图像的裁剪(cv2.selectROI)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】10. 图像的拼接(np.hstack)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】11. 图像通道的拆分(cv2.split)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】12. 图像通道的合并(cv2.merge)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】13. 图像的加法运算(cv2.add)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】14. 图像与标量相加(cv2.add)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】15. 图像的加权加法(cv2.addWeight)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】16. 不同尺寸的图像加法
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】17. 两张图像的渐变切换
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】18. 图像的掩模加法
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】19. 图像的圆形遮罩
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】20. 图像的按位运算
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】21. 图像的叠加
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】22. 图像添加非中文文字
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】23. 图像添加中文文字
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】24. 图像的仿射变换
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】25. 图像的平移
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】26. 图像的旋转(以原点为中心)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】27. 图像的旋转(以任意点为中心)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】28. 图像的旋转(直角旋转)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】29. 图像的翻转(cv2.flip)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】30. 图像的缩放(cv2.resize)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】31. 图像金字塔(cv2.pyrDown)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】32. 图像的扭变(错切)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】33. 图像的复合变换
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】34. 图像的投影变换
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】35. 图像的投影变换(边界填充)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】36. 直角坐标与极坐标的转换
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】37. 图像的灰度化处理和二值化处理
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】38. 图像的反色变换(图像反转)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】39. 图像灰度的线性变换
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】40. 图像分段线性灰度变换
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】41. 图像的灰度变换(灰度级分层)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】42. 图像的灰度变换(比特平面分层)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】43. 图像的灰度变换(对数变换)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】44. 图像的灰度变换(伽马变换)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】45. 图像的灰度直方图
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】46. 直方图均衡化
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】47. 图像增强—直方图匹配
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】48. 图像增强—彩色直方图匹配
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】49. 图像增强—局部直方图处理
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】50. 图像增强—直方图统计量图像增强
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】51. 图像增强—直方图反向追踪
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】52. 图像的相关与卷积运算
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】53. Scipy 实现图像二维卷积
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】54. OpenCV 实现图像二维卷积
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】55. 可分离卷积核
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】56. 低通盒式滤波器
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】57. 低通高斯滤波器
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】58. 非线性滤波—中值滤波
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】59. 非线性滤波—双边滤波
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】60. 非线性滤波—联合双边滤波
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】61. 导向滤波(Guided filter)
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】62. 图像锐化——钝化掩蔽
【youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇】63. 图像锐化——Laplaci以上是关于youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇148. 图像分割之线检测的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
OpenCV 例程200篇236. 特征提取之主成分分析(OpenCV)
youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇184.鼠标交互标记的分水岭算法
youcans 的 OpenCV 例程200篇183.基于轮廓标记的分水岭算法
OpenCV 例程200篇236. 特征提取之主成分分析(OpenCV)