Libevent(三)
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Libevent(三)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A每个event_base保存一堆event,而且可以测验出哪些events是激活了的
如果一个event_base是设置为用了锁,那么就是线程安全的。然而,如果你有很多个线程要进行IO操作,那么对于每个线程都需要创建一个event_base
每一个event_base都有一个工具,这些工具是:
** select poll epoll kqueue devpoll evport win32 **
你也可以关闭某个特定的工具,例如 kqueue,通过设置EVENT_NOKQUEUE环境变量关闭。如果想要在程序里关闭,可以用event_config_avoid_method
event_base_new()函数从堆分配一个默认event_base对象,返回一个event_base的指针,出错返回NULL
接口
event_config是一个保存特定event_base信息的结构体。如果要特定的event_base,将event_config传给函数event_base_new_with_config()
接口
用event_config_new()去分配一个新的event_config对象,通过调用其他函数去设置event_config,用event_config_free去回收对象。
接口
直接通过字符串名称调用event_config_avoid_method()可以让Libevent不去用特指的工具。通过event_config_require_feature()告诉Libevent不去使用不能提供特指一系列特点的工具。event_config_set_flag设置一些标签。
EV_FEATURE_ET:
需要工具支持边缘触发IO
EV_FEATURE_O1
需要工具支持插入删除激活event的复杂度是O(1)
EV_FEATURE_FDS
需要工具提供各种文件描述符,而不只是套接字。
EVENT_BASE_FLAG_NOLOCK
不给此event_base设置线程锁,多线程不安全。
示例:创建特定event_base
调用函数 void event_base_free(struct event_base* base);
默认情况下,一个event_base只支持一个优先级,可以设置多个优先级通过调用接口
优先级参数至少为1,设置后优先级为0到n_priorities-1。Libevent支持的最高优先级为EVENT_MAX_PRIORITIES.
要找到当前event_base支持多少优先级通过调用函数
在创建新进程后还要继续使用之前event_base的话,最好重新初始化
接口:
早期版本的Libevent库有个全局默认event_base,可以被所有线程访问 ,如果绑定在这个默认的event_base上,这是线程不安全的。替代event_base_new()的是:
这个将当前要绑定的base设为分配的base,而不是默认的base。
Libevent源码分析--- libevent事件机制
之前几个章节都是分析libevent的辅助功能,这一节将要详细分析libevent处理事件的流程和机制,在分析之前先看一下libevent的使用方法,本文也将以libevent的使用方式入手来分析libevent的工作机制。
void cb_func(evutil_socket_t fd, short what, void *arg)
const char *data = arg;
printf("Got an event on socket %d:%s%s%s%s [%s]",
(int) fd,
(what&EV_TIMEOUT) ? " timeout" : "",
(what&EV_READ) ? " read" : "",
(what&EV_WRITE) ? " write" : "",
(what&EV_SIGNAL) ? " signal" : "",
data);
void main_loop(evutil_socket_t fd1, evutil_socket_t fd2)
struct event *ev1, *ev2;
struct timeval five_seconds = 5,0;
struct event_base *base = event_base_new();
/* The caller has already set up fd1, fd2 somehow, and make them
nonblocking. */
ev1 = event_new(base, fd1, EV_TIMEOUT|EV_READ|EV_PERSIST, cb_func,
(char*)"Reading event");
ev2 = event_new(base, fd2, EV_WRITE|EV_PERSIST, cb_func,
(char*)"Writing event");
event_add(ev1, &five_seconds);
event_add(ev2, NULL);
event_base_dispatch(base);
使用libevent,必须先初始化一个event_base结构体,event_base结构体之前分析过,下面是它的初始化代码:
struct event_base *
event_base_new_with_config(const struct event_config *cfg)
int i;
struct event_base *base;
int should_check_environment;
#ifndef _EVENT_DISABLE_DEBUG_MODE
event_debug_mode_too_late = 1;
#endif
if ((base = mm_calloc(1, sizeof(struct event_base))) == NULL)
event_warn("%s: calloc", __func__);
return NULL;
detect_monotonic();
gettime(base, &base->event_tv);
min_heap_ctor(&base->timeheap);
TAILQ_INIT(&base->eventqueue);
base->sig.ev_signal_pair[0] = -1;
base->sig.ev_signal_pair[1] = -1;
base->th_notify_fd[0] = -1;
base->th_notify_fd[1] = -1;
event_deferred_cb_queue_init(&base->defer_queue);
base->defer_queue.notify_fn = notify_base_cbq_callback;
base->defer_queue.notify_arg = base;
if (cfg)
base->flags = cfg->flags;
evmap_io_initmap(&base->io);
evmap_signal_initmap(&base->sigmap);
event_changelist_init(&base->changelist);
base->evbase = NULL;
should_check_environment =
!(cfg && (cfg->flags & EVENT_BASE_FLAG_IGNORE_ENV));
for (i = 0; eventops[i] && !base->evbase; i++)
if (cfg != NULL)
/* determine if this backend should be avoided */
if (event_config_is_avoided_method(cfg,
eventops[i]->name))
continue;
if ((eventops[i]->features & cfg->require_features)
!= cfg->require_features)
continue;
/* also obey the environment variables */
if (should_check_environment &&
event_is_method_disabled(eventops[i]->name))
continue;
base->evsel = eventops[i];
base->evbase = base->evsel->init(base);
if (base->evbase == NULL)
event_warnx("%s: no event mechanism available",
__func__);
base->evsel = NULL;
event_base_free(base);
return NULL;
if (evutil_getenv("EVENT_SHOW_METHOD"))
event_msgx("libevent using: %s", base->evsel->name);
/* allocate a single active event queue */
if (event_base_priority_init(base, 1) < 0)
event_base_free(base);
return NULL;
/* prepare for threading */
#ifndef _EVENT_DISABLE_THREAD_SUPPORT
if (EVTHREAD_LOCKING_ENABLED() &&
(!cfg || !(cfg->flags & EVENT_BASE_FLAG_NOLOCK)))
int r;
EVTHREAD_ALLOC_LOCK(base->th_base_lock,
EVTHREAD_LOCKTYPE_RECURSIVE);
base->defer_queue.lock = base->th_base_lock;
EVTHREAD_ALLOC_COND(base->current_event_cond);
r = evthread_make_base_notifiable(base);
if (r<0)
event_warnx("%s: Unable to make base notifiable.", __func__);
event_base_free(base);
return NULL;
#endif
#ifdef WIN32
if (cfg && (cfg->flags & EVENT_BASE_FLAG_STARTUP_IOCP))
event_base_start_iocp(base, cfg->n_cpus_hint);
#endif
return (base);
该初始化函数除了初始化event_base之外还要决定使用哪个io多路复用模型,所有的io多路复用模型都定义在eventops结构体中:
static const struct eventop *eventops[] =
#ifdef _EVENT_HAVE_EVENT_PORTS
&evportops,
#endif
#ifdef _EVENT_HAVE_WORKING_KQUEUE
&kqops,
#endif
#ifdef _EVENT_HAVE_EPOLL
&epollops,
#endif
#ifdef _EVENT_HAVE_DEVPOLL
&devpollops,
#endif
#ifdef _EVENT_HAVE_POLL
&pollops,
#endif
#ifdef _EVENT_HAVE_SELECT
&selectops,
#endif
#ifdef WIN32
&win32ops,
#endif
NULL
;event_base_new_with_config会从上到下进行选择,尽量选用系统支持的最高效率的模型,event_config也可以配置选择哪种模型。
初始化完event_base之后就可以开始添加事件了。
struct event * event_new(struct event_base *base, evutil_socket_t fd, short events, void (*cb)(evutil_socket_t, short, void *), void *arg)
struct event *ev;
ev = mm_malloc(sizeof(struct event));
if (ev == NULL)
return (NULL);
if (event_assign(ev, base, fd, events, cb, arg) < 0)
mm_free(ev);
return (NULL);
return (ev);
int event_assign(struct event *ev, struct event_base *base, evutil_socket_t fd, short events, void (*callback)(evutil_socket_t, short, void *), void *arg)
if (!base)
base = current_base;
_event_debug_assert_not_added(ev);
ev->ev_base = base;
ev->ev_callback = callback;
ev->ev_arg = arg;
ev->ev_fd = fd;
ev->ev_events = events;
ev->ev_res = 0;
ev->ev_flags = EVLIST_INIT;
ev->ev_ncalls = 0;
ev->ev_pncalls = NULL;
if (events & EV_SIGNAL)
if ((events & (EV_READ|EV_WRITE)) != 0)
event_warnx("%s: EV_SIGNAL is not compatible with "
"EV_READ or EV_WRITE", __func__);
return -1;
ev->ev_closure = EV_CLOSURE_SIGNAL;
else
if (events & EV_PERSIST)
evutil_timerclear(&ev->ev_io_timeout);
ev->ev_closure = EV_CLOSURE_PERSIST;
else
ev->ev_closure = EV_CLOSURE_NONE;
min_heap_elem_init(ev);
if (base != NULL)
/* by default, we put new events into the middle priority */
ev->ev_pri = base->nactivequeues / 2;
_event_debug_note_setup(ev);
return 0;
event_new用来创建一个event,event_assign用来初始化一个event。这里比较重要的是ev_flags的取值,他用来标记ev_flags的状态,EVLIST_INIT表明这是一个新创建的事件,只完成了初始化,还没有加入到任何队列中。下面是ev_flags的所有状态:
#define EVLIST_TIMEOUT 0x01
#define EVLIST_INSERTED 0x02
#define EVLIST_SIGNAL 0x04
#define EVLIST_ACTIVE 0x08
#define EVLIST_INTERNAL 0x10
#define EVLIST_INIT 0x80初始化event之后就可以添加到队列中了:
int
event_add(struct event *ev, const struct timeval *tv)
int res;
if (EVUTIL_FAILURE_CHECK(!ev->ev_base))
event_warnx("%s: event has no event_base set.", __func__);
return -1;
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(ev->ev_base, th_base_lock);
res = event_add_internal(ev, tv, 0);
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(ev->ev_base, th_base_lock);
return (res);
static inline int
event_add_internal(struct event *ev, const struct timeval *tv,
int tv_is_absolute)
struct event_base *base = ev->ev_base;
int res = 0;
int notify = 0;
EVENT_BASE_ASSERT_LOCKED(base);
_event_debug_assert_is_setup(ev);
event_debug((
"event_add: event: %p (fd "EV_SOCK_FMT"), %s%s%scall %p",
ev,
EV_SOCK_ARG(ev->ev_fd),
ev->ev_events & EV_READ ? "EV_READ " : " ",
ev->ev_events & EV_WRITE ? "EV_WRITE " : " ",
tv ? "EV_TIMEOUT " : " ",
ev->ev_callback));
EVUTIL_ASSERT(!(ev->ev_flags & ~EVLIST_ALL));
/*
* prepare for timeout insertion further below, if we get a
* failure on any step, we should not change any state.
*/
if (tv != NULL && !(ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_TIMEOUT))
if (min_heap_reserve(&base->timeheap,
1 + min_heap_size(&base->timeheap)) == -1)
return (-1); /* ENOMEM == errno */
/* If the main thread is currently executing a signal event's
* callback, and we are not the main thread, then we want to wait
* until the callback is done before we mess with the event, or else
* we can race on ev_ncalls and ev_pncalls below. */
#ifndef _EVENT_DISABLE_THREAD_SUPPORT
if (base->current_event == ev && (ev->ev_events & EV_SIGNAL)
&& !EVBASE_IN_THREAD(base))
++base->current_event_waiters;
EVTHREAD_COND_WAIT(base->current_event_cond, base->th_base_lock);
#endif
if ((ev->ev_events & (EV_READ|EV_WRITE|EV_SIGNAL)) &&
!(ev->ev_flags & (EVLIST_INSERTED|EVLIST_ACTIVE)))
if (ev->ev_events & (EV_READ|EV_WRITE))
res = evmap_io_add(base, ev->ev_fd, ev);
else if (ev->ev_events & EV_SIGNAL)
res = evmap_signal_add(base, (int)ev->ev_fd, ev);
if (res != -1)
event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_INSERTED);
if (res == 1)
/* evmap says we need to notify the main thread. */
notify = 1;
res = 0;
/*
* we should change the timeout state only if the previous event
* addition succeeded.
*/
if (res != -1 && tv != NULL)
struct timeval now;
int common_timeout;
/*
* for persistent timeout events, we remember the
* timeout value and re-add the event.
*
* If tv_is_absolute, this was already set.
*/
if (ev->ev_closure == EV_CLOSURE_PERSIST && !tv_is_absolute)
ev->ev_io_timeout = *tv;
/*
* we already reserved memory above for the case where we
* are not replacing an existing timeout.
*/
if (ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_TIMEOUT)
/* XXX I believe this is needless. */
if (min_heap_elt_is_top(ev))
notify = 1;
event_queue_remove(base, ev, EVLIST_TIMEOUT);
/* Check if it is active due to a timeout. Rescheduling
* this timeout before the callback can be executed
* removes it from the active list. */
if ((ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_ACTIVE) &&
(ev->ev_res & EV_TIMEOUT))
if (ev->ev_events & EV_SIGNAL)
/* See if we are just active executing
* this event in a loop
*/
if (ev->ev_ncalls && ev->ev_pncalls)
/* Abort loop */
*ev->ev_pncalls = 0;
event_queue_remove(base, ev, EVLIST_ACTIVE);
gettime(base, &now);
common_timeout = is_common_timeout(tv, base);
if (tv_is_absolute)
ev->ev_timeout = *tv;
else if (common_timeout)
struct timeval tmp = *tv;
tmp.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK;
evutil_timeradd(&now, &tmp, &ev->ev_timeout);
ev->ev_timeout.tv_usec |=
(tv->tv_usec & ~MICROSECONDS_MASK);
else
evutil_timeradd(&now, tv, &ev->ev_timeout);
event_debug((
"event_add: timeout in %d seconds, call %p",
(int)tv->tv_sec, ev->ev_callback));
event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_TIMEOUT);
if (common_timeout)
struct common_timeout_list *ctl =
get_common_timeout_list(base, &ev->ev_timeout);
if (ev == TAILQ_FIRST(&ctl->events))
common_timeout_schedule(ctl, &now, ev);
else
/* See if the earliest timeout is now earlier than it
* was before: if so, we will need to tell the main
* thread to wake up earlier than it would
* otherwise. */
if (min_heap_elt_is_top(ev))
notify = 1;
/* if we are not in the right thread, we need to wake up the loop */
if (res != -1 && notify && EVBASE_NEED_NOTIFY(base))
evthread_notify_base(base);
_event_debug_note_add(ev);
return (res);
事件的添加和删除需要添加锁,因为操作可能是通过其他线程调用的。event_add_internal的第二个参数代表这是一个和时间相关的值,第三个参数则用来表示第二个参数是绝对值还是相对值,即是具体的某一个时间点还是一个时间间隔。如果时间不为空并且EVLIST_TIMEOUT没有被设置,则需要在小根堆中预留一个位置。base->current_event代表主线程正在处理该event的callback,此时的添加和删除操作都需要等待处理完成的通知。之后就要把事件插入到对应的数据结构中了,如果是EV_READ或者EV_WRITE事件,则插入到evmap_io中,如果是EV_SIGNAL事件则插入到evmap_signal中。EV_SIGNAL事件和其他两个事件是互斥的。之后调用event_queue_insert方法把事件插入到event_base中的双向链表中,event_queue_insert根据传入的queue标记把event添加相应的状态并且插入到对应的数据结构中。此时改event的ev_flags标记变为了EVLIST_INIT|EVLIST_INSERTED,下面是event_queue_insert函数:
static void
event_queue_insert(struct event_base *base, struct event *ev, int queue)
EVENT_BASE_ASSERT_LOCKED(base);
if (ev->ev_flags & queue)
/* Double insertion is possible for active events */
if (queue & EVLIST_ACTIVE)
return;
event_errx(1, "%s: %p(fd "EV_SOCK_FMT") already on queue %x", __func__,
ev, EV_SOCK_ARG(ev->ev_fd), queue);
return;
if (~ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_INTERNAL)
base->event_count++;
ev->ev_flags |= queue;
switch (queue)
case EVLIST_INSERTED:
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&base->eventqueue, ev, ev_next);
break;
case EVLIST_ACTIVE:
base->event_count_active++;
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&base->activequeues[ev->ev_pri],
ev,ev_active_next);
break;
case EVLIST_TIMEOUT:
if (is_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout, base))
struct common_timeout_list *ctl =
get_common_timeout_list(base, &ev->ev_timeout);
insert_common_timeout_inorder(ctl, ev);
else
min_heap_push(&base->timeheap, ev);
break;
default:
event_errx(1, "%s: unknown queue %x", __func__, queue);
继续看event_add_internal,当调用event_queue_insert之后需要设置notify标记,该标记用于在非主线程操作时唤醒主线乘。因为可能新的event设置的timeout时间小于当前io模型的timeout时间,唤醒的方式依旧是通过socketpair,因为socketpari中的其中一个套接字已经作为一个内部event添加到event_base中,只要有写事件会马上返回,停止睡眠。
接下来的代码都是处理时间相关的,首先如果这是一个persist事件并且时间设置的是相对时间,则需要保存这个相对时间,ev_io_timeout用于存储该时间,persist和signal事件是互斥的。ev_timeout会存储一个相对值,之后再次调用event_queue_insert将event存储到小跟堆或者是common list列表中。这里需要注意的是因为新加入到的时间时间如果是common时间并且新加入的event在commonlist 列表的第一个则需要调整common_timeout_list的timeout_event,timeout_event可能之前在小根堆中(队列之前不为空,并且新加入的event的timeout时间小于timeout_event的过期时间,在前面的章节中分析过这在理论上是不可能的,但是libevent还是做了一次检查),也可能不在小根队中。
static void
common_timeout_schedule(struct common_timeout_list *ctl,
const struct timeval *now, struct event *head)
struct timeval timeout = head->ev_timeout;
timeout.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK;
event_add_internal(&ctl->timeout_event, &timeout, 1);
event_add_internal方法中有判断,如果ev_flags有标记EVLIST_TIMEOUT,则会调用 event_queue_remove(base, ev, EVLIST_TIMEOUT)先从小根堆(common_timeout_list的timeout_event在小根堆中)中移除,然后重新添加到小根堆中。
最后event_add_internal会根据情况判断是否唤醒主线程。
event_add分析完成之后就是event_base_dispatch函数了,该函数是event_base的主循环。内部实际运行的是event_base_loop方法:
int
event_base_loop(struct event_base *base, int flags)
const struct eventop *evsel = base->evsel;
struct timeval tv;
struct timeval *tv_p;
int res, done, retval = 0;
/* Grab the lock. We will release it inside evsel.dispatch, and again
* as we invoke user callbacks. */
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
if (base->running_loop)
event_warnx("%s: reentrant invocation. Only one event_base_loop"
" can run on each event_base at once.", __func__);
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
return -1;
base->running_loop = 1;
clear_time_cache(base);
if (base->sig.ev_signal_added && base->sig.ev_n_signals_added)
evsig_set_base(base);
done = 0;
#ifndef _EVENT_DISABLE_THREAD_SUPPORT
base->th_owner_id = EVTHREAD_GET_ID();
#endif
base->event_gotterm = base->event_break = 0;
while (!done)
base->event_continue = 0;
/* Terminate the loop if we have been asked to */
if (base->event_gotterm)
break;
if (base->event_break)
break;
timeout_correct(base, &tv);
tv_p = &tv;
if (!N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base) && !(flags & EVLOOP_NONBLOCK))
timeout_next(base, &tv_p);
else
/*
* if we have active events, we just poll new events
* without waiting.
*/
evutil_timerclear(&tv);
/* If we have no events, we just exit */
if (!event_haveevents(base) && !N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base))
event_debug(("%s: no events registered.", __func__));
retval = 1;
goto done;
/* update last old time */
gettime(base, &base->event_tv);
clear_time_cache(base);
res = evsel->dispatch(base, tv_p);
if (res == -1)
event_debug(("%s: dispatch returned unsuccessfully.",
__func__));
retval = -1;
goto done;
update_time_cache(base);
timeout_process(base);
if (N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base))
int n = event_process_active(base);
if ((flags & EVLOOP_ONCE)
&& N_ACTIVE_CALLBACKS(base) == 0
&& n != 0)
done = 1;
else if (flags & EVLOOP_NONBLOCK)
done = 1;
event_debug(("%s: asked to terminate loop.", __func__));
done:
clear_time_cache(base);
base->running_loop = 0;
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
return (retval);
evsig_set_base方法使得libevent中只有最后调用event_base_dispatch的event_base才能支持信号量事件。在进入到while循环之前,event_base_loop会获取全局锁:EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);进入while循环之后会进行时间的校正,这在之前的博客中分析过。之后是一些状态的判断和时间的设置,接着就调用了evsel->dispatch(base, tv_p),如果当前有激活事件,tv_p则为空,如果没有tv_p则设置为小根堆中的最小时间。 该方法会调用对应的io模型的dispach方法用于检测io事件,如果有事件则调用 evmap_io_active(base, i, res),该方法定义如下:
void
evmap_io_active(struct event_base *base, evutil_socket_t fd, short events)
struct event_io_map *io = &base->io;
struct evmap_io *ctx;
struct event *ev;
#ifndef EVMAP_USE_HT
EVUTIL_ASSERT(fd < io->nentries);
#endif
GET_IO_SLOT(ctx, io, fd, evmap_io);
EVUTIL_ASSERT(ctx);
TAILQ_FOREACH(ev, &ctx->events, ev_io_next)
if (ev->ev_events & events)
event_active_nolock(ev, ev->ev_events & events, 1);
evmap_io_active会遍历所有与该fd相关的event,如果fd上的事件是event监听的事件,则调用event_active_nolock方法:
void
event_active_nolock(struct event *ev, int res, short ncalls)
struct event_base *base;
event_debug(("event_active: %p (fd "EV_SOCK_FMT"), res %d, callback %p",
ev, EV_SOCK_ARG(ev->ev_fd), (int)res, ev->ev_callback));
/* We get different kinds of events, add them together */
if (ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_ACTIVE)
ev->ev_res |= res;
return;
base = ev->ev_base;
EVENT_BASE_ASSERT_LOCKED(base);
ev->ev_res = res;
if (ev->ev_pri < base->event_running_priority)
base->event_continue = 1;
if (ev->ev_events & EV_SIGNAL)
#ifndef _EVENT_DISABLE_THREAD_SUPPORT
if (base->current_event == ev && !EVBASE_IN_THREAD(base))
++base->current_event_waiters;
EVTHREAD_COND_WAIT(base->current_event_cond, base->th_base_lock);
#endif
ev->ev_ncalls = ncalls;
ev->ev_pncalls = NULL;
event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_ACTIVE);
if (EVBASE_NEED_NOTIFY(base))
evthread_notify_base(base);
该函数会调用event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_ACTIVE),用于把event添加到激活列表中,event_queue_insert内部会判断是否已经有了EVLIST_ACTIVE标记,如果有则不会重复添加。
继续看event_base_loop函数,处理完IO事件之后会接着处理小根堆定时器事件。
/* Activate every event whose timeout has elapsed. */
static void
timeout_process(struct event_base *base)
/* Caller must hold lock. */
struct timeval now;
struct event *ev;
if (min_heap_empty(&base->timeheap))
return;
gettime(base, &now);
while ((ev = min_heap_top(&base->timeheap)))
if (evutil_timercmp(&ev->ev_timeout, &now, >))
break;
/* delete this event from the I/O queues */
event_del_internal(ev);
event_debug(("timeout_process: call %p",
ev->ev_callback));
event_active_nolock(ev, EV_TIMEOUT, 1);
timeout_process会把小根堆中所有超时事件都调用event_del_internal,如果这是一个EV_PERSIST事件,之后在event_persist_closure还会添加回来,最后调用event_active_nolock把事件加入到激活事件链表。最后当激活链表中有事件时会调用event_process_active(base)来处理所有的激活事件:
static int
event_process_active(struct event_base *base)
/* Caller must hold th_base_lock */
struct event_list *activeq = NULL;
int i, c = 0;
for (i = 0; i < base->nactivequeues; ++i)
if (TAILQ_FIRST(&base->activequeues[i]) != NULL)
base->event_running_priority = i;
activeq = &base->activequeues[i];
c = event_process_active_single_queue(base, activeq);
if (c < 0)
base->event_running_priority = -1;
return -1;
else if (c > 0)
break; /* Processed a real event; do not
* consider lower-priority events */
/* If we get here, all of the events we processed
* were internal. Continue. */
event_process_deferred_callbacks(&base->defer_queue,&base->event_break);
base->event_running_priority = -1;
return c;
event_process_active会根据优先级顺序调用event_process_active_single_queue处理已激活状态的事件,deferred_callbacks将在后面event_buffer中详细分析:
static int
event_process_active_single_queue(struct event_base *base, struct event_list *activeq)
struct event *ev;
int count = 0;
EVUTIL_ASSERT(activeq != NULL);
for (ev = TAILQ_FIRST(activeq); ev; ev = TAILQ_FIRST(activeq))
if (ev->ev_events & EV_PERSIST)
event_queue_remove(base, ev, EVLIST_ACTIVE);
else
event_del_internal(ev);
if (!(ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_INTERNAL))
++count;
event_debug((
"event_process_active: event: %p, %s%scall %p",
ev,
ev->ev_res & EV_READ ? "EV_READ " : " ",
ev->ev_res & EV_WRITE ? "EV_WRITE " : " ",
ev->ev_callback));
#ifndef _EVENT_DISABLE_THREAD_SUPPORT
base->current_event = ev;
base->current_event_waiters = 0;
#endif
switch (ev->ev_closure)
case EV_CLOSURE_SIGNAL:
event_signal_closure(base, ev);
break;
case EV_CLOSURE_PERSIST:
event_persist_closure(base, ev);
break;
default:
case EV_CLOSURE_NONE:
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
(*ev->ev_callback)(
ev->ev_fd, ev->ev_res, ev->ev_arg);
break;
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
#ifndef _EVENT_DISABLE_THREAD_SUPPORT
base->current_event = NULL;
if (base->current_event_waiters)
base->current_event_waiters = 0;
EVTHREAD_COND_BROADCAST(base->current_event_cond);
#endif
if (base->event_break)
return -1;
if (base->event_continue)
break;
return count;
如果事件是EV_PERSIST类型只需要从激活队列中移除即可,否则就会执行event_del_internal。如果事件是定时器事件,那么该事件在timeout_process中已经移除过一次了,但是当时事件不是激活状态的。所以此时的event_queue_remove和event_del_internal作用相同,都是从激活列表中移除。接下来需要特殊处理的就是信号量事件和EV_PERSIST事件,信号量事件需要使用event_signal_closure关闭,EV_PERSIST需要调用event_persist_closure进行清理,普通事件直接调用回调即可:
static inline void
event_persist_closure(struct event_base *base, struct event *ev)
/* reschedule the persistent event if we have a timeout. */
if (ev->ev_io_timeout.tv_sec || ev->ev_io_timeout.tv_usec)
/* If there was a timeout, we want it to run at an interval of
* ev_io_timeout after the last time it was _scheduled_ for,
* not ev_io_timeout after _now_. If it fired for another
* reason, though, the timeout ought to start ticking _now_. */
struct timeval run_at, relative_to, delay, now;
ev_uint32_t usec_mask = 0;
EVUTIL_ASSERT(is_same_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout,
&ev->ev_io_timeout));
gettime(base, &now);
if (is_common_timeout(&ev->ev_timeout, base))
delay = ev->ev_io_timeout;
usec_mask = delay.tv_usec & ~MICROSECONDS_MASK;
delay.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK;
if (ev->ev_res & EV_TIMEOUT)
relative_to = ev->ev_timeout;
relative_to.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK;
else
relative_to = now;
else
delay = ev->ev_io_timeout;
if (ev->ev_res & EV_TIMEOUT)
relative_to = ev->ev_timeout;
else
relative_to = now;
evutil_timeradd(&relative_to, &delay, &run_at);
if (evutil_timercmp(&run_at, &now, <))
/* Looks like we missed at least one invocation due to
* a clock jump, not running the event loop for a
* while, really slow callbacks, or
* something. Reschedule relative to now.
*/
evutil_timeradd(&now, &delay, &run_at);
run_at.tv_usec |= usec_mask;
event_add_internal(ev, &run_at, 1);
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
(*ev->ev_callback)(ev->ev_fd, ev->ev_res, ev->ev_arg);
该函数主要是重置时间,不管激活事件是不是因为timeout引起的都需要重置时间然后重新添加事件。event_add_internal会进行判断如果事件已经在evmap_io中或者evmap_signal中则不处理,但是如果在小根堆活着commonlist中则需要移除在添加。
以上就是libevent处理事件的流程,下面是作者在网上找的一幅流程图:
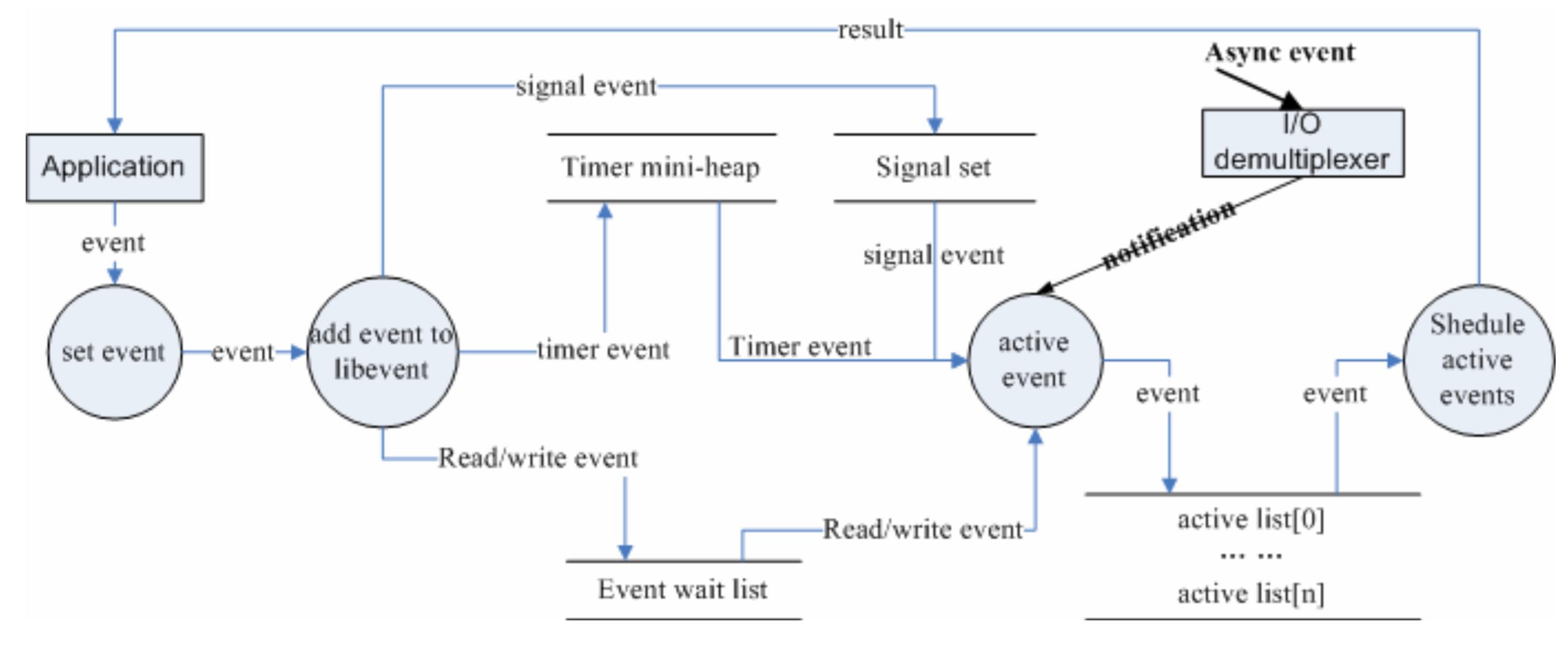
以上是关于Libevent(三)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章