目标检测MMDetection的安装与基础使用
Posted zstar-_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了目标检测MMDetection的安装与基础使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
MMDetection是商汤和港中文大学针对目标检测任务推出的一个开源工具包,统一标准化了很多前沿模型,为研究者复现代码提供了便利。本篇就来尝试安装一下MMDetection并简单跑一下官方的示例教程。
官方文档:https://mmdetection.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/get_started.html
官方仓库:https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection
MMDetection架构
首先安装之前,需要先简单了解一下MMDetection的架构,整体架构如下图所示[1]:
MMDetection的底层是使用PyTorch进行编写,再上一层是MMCV,这个工具包提供了一些通用工具类和训练,检测工具。
MMDetection仅仅是多个Codebases中的其中一个,除此之外,还有专用于图像分类的MMClassification,用于目标追踪的MMTracking等。

安装
有了项目的概念之后,我们就知道需要安装两个库:MMCV和MMDetection
和Pytorch和torchvision一样,这两个库的版本必须要对应,官网给出这张版本对应参考表。

这里官方提供了一个比较简介的方案,首先查看自己的cuda版本和pytorch版本,比如我的cuda版本是11.5,torch版本是1.11.0,那么可以这样进行快速安装mmcv:
pip install mmcv-full -f https://download.openmmlab.com/mmcv/dist/cu115/torch1.11.0/index.html
注:这样安装的是mmcv1.6.1版本,对照表似乎没及时进行更新。
稳妥起见,我直接访问https://download.openmmlab.com/mmcv/dist/cu115/torch1.11.0/index.html下载mmcv_full-1.5.0-cp37-cp37m-win_amd64.whl进行安装。
MMDetection安装很简单,查阅对照表,安装2.25.1版本即可。
pip install mmdet==2.25.1
安装完成之后,运行下面的程序进行检测。
# Check Pytorch installation
import torch, torchvision
print(torch.__version__, torch.cuda.is_available())
# Check MMDetection installation
import mmdet
print(mmdet.__version__)
# Check mmcv installation
from mmcv.ops import get_compiling_cuda_version, get_compiler_version
print(get_compiling_cuda_version())
print(get_compiler_version())
输出:
1.11.0+cu115 True
2.25.1
11.5
MSVC 192930140
说明安装成功。
显示图片
在官方仓库的demo文件夹下,提供了三个示例教程,这里就跟着来跑一下。

首先需要将源码中的configs文件夹复制到测试工程路径下,这个文件夹包含了各种算法的结构。

使用mmcv.imread读取图片,并用matplotlib进行显示。
import mmcv
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
img = mmcv.imread('kitti_tiny/training/image_2/000073.jpeg')
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
plt.imshow(mmcv.bgr2rgb(img))
plt.show()

模型推理
第二个示例程序是加载模型进行推理。
首先需要根据官方教程指引,下载faster_rcnn的权重文件faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco_20200130-047c8118.pth,放置在checkpoints文件夹下。
from mmdet.apis import init_detector, inference_detector, show_result_pyplot
config_file = 'configs/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py'
checkpoint_file = 'checkpoints/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco_20200130-047c8118.pth'
device = 'cuda:0'
# 初始化检测器
model = init_detector(config_file, checkpoint_file, device=device)
# 推理演示图像
img = 'img/demo.jpg'
result = inference_detector(model, img)
show_result_pyplot(model, img, result, score_thr=0.3)
加载模型主要通过init_detector这个函数,注意模型的config_file文件和模型权重必须对应。
运行之后,输出下图。

这里顺便对config_file文件进行一个解析:
configs/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py文件内容:
_base_ = './faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py'
model = dict(
backbone=dict(
norm_cfg=dict(requires_grad=False),
norm_eval=True,
style='caffe',
init_cfg=dict(
type='Pretrained',
checkpoint='open-mmlab://detectron2/resnet50_caffe')))
# use caffe img_norm
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[103.530, 116.280, 123.675], std=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0], to_rgb=False)
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True),
dict(
type='Resize',
img_scale=[(1333, 640), (1333, 672), (1333, 704), (1333, 736),
(1333, 768), (1333, 800)],
multiscale_mode='value',
keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip', flip_ratio=0.5),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_bboxes', 'gt_labels']),
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(1333, 800),
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='Resize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
data = dict(
train=dict(pipeline=train_pipeline),
val=dict(pipeline=test_pipeline),
test=dict(pipeline=test_pipeline))
在MMDetection中,所有的参数都使用字典dict的形式构建。
先看主要模型model,这里指定了backbone的结构,init_cfg为默认参数,后续载入模型会将其进行覆盖。
后面是train_pipeline和test_pipeline,定义了数据预处理的各种方式。
最后看第一行的_base_,这里相当于引用了另一个文件./faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py的内容
./faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py
_base_ = [
'../_base_/models/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn.py',
'../_base_/datasets/coco_detection.py',
'../_base_/schedules/schedule_1x.py', '../_base_/default_runtime.py'
]
这个文件非常简单,直接调用了另外四个文件。
- …/base/models/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn.py :包含faster_rcnn的整体结构
- …/base/datasets/coco_detection.py:包含数据集预处理策略,后面写的会将其进行覆盖
- …/base/schedules/schedule_1x.py:包含学习率的调度策略
- …/base/default_runtime.py:模型运行时通用策略
可以发现,MMDetection的文件加载方式是一层层读取和覆盖,这样就不需要重复写相同的内容,只需要注意后面需要修改的参数。
如果需要预览模型整体架构,可以运行下面的代码:
import mmcv
from mmcv.runner import load_checkpoint
from mmdet.models import build_detector
# Choose to use a config and initialize the detector
config = 'configs/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain_3x_coco.py'
# Setup a checkpoint file to load
checkpoint = 'checkpoints/faster_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain_3x_coco_20210526_095054-1f77628b.pth'
# Set the device to be used for evaluation
device = 'cuda:0'
# Load the config
config = mmcv.Config.fromfile(config)
# Set pretrained to be None since we do not need pretrained model here
config.model.pretrained = None
# Initialize the detector
model = build_detector(config.model)
# Load checkpoint
checkpoint = load_checkpoint(model, checkpoint, map_location=device)
# Set the classes of models for inference
model.CLASSES = checkpoint['meta']['CLASSES']
# We need to set the model's cfg for inference
model.cfg = config
# Convert the model to GPU
model.to(device)
# Convert the model into evaluation mode
model.eval()
print(model)
模型训练
第三个示例关于模型训练,使用的是kitti_tiny数据集
训练过程不做详解,各注释已写在代码中。
import copy
import os.path as osp
import mmcv
import numpy as np
from mmdet.datasets.builder import DATASETS
from mmdet.datasets.custom import CustomDataset
from mmcv import Config
from mmdet.apis import set_random_seed
from mmdet.datasets import build_dataset
from mmdet.models import build_detector
from mmdet.apis import train_detector
from mmdet.utils import get_device
@DATASETS.register_module()
class KittiTinyDataset(CustomDataset):
CLASSES = ('Car', 'Pedestrian', 'Cyclist')
def load_annotations(self, ann_file):
cat2label = k: i for i, k in enumerate(self.CLASSES)
# load image list from file
image_list = mmcv.list_from_file(self.ann_file)
data_infos = []
# convert annotations to middle format
for image_id in image_list:
filename = f'self.img_prefix/image_id.jpeg'
image = mmcv.imread(filename)
height, width = image.shape[:2]
data_info = dict(filename=f'image_id.jpeg', width=width, height=height)
# load annotations
label_prefix = self.img_prefix.replace('image_2', 'label_2')
lines = mmcv.list_from_file(osp.join(label_prefix, f'image_id.txt'))
content = [line.strip().split(' ') for line in lines]
bbox_names = [x[0] for x in content]
bboxes = [[float(info) for info in x[4:8]] for x in content]
gt_bboxes = []
gt_labels = []
gt_bboxes_ignore = []
gt_labels_ignore = []
# filter 'DontCare'
# 过滤不关心类别标签,需要筛选的类别在上面CLASSES中进行了指定
for bbox_name, bbox in zip(bbox_names, bboxes):
if bbox_name in cat2label:
gt_labels.append(cat2label[bbox_name])
gt_bboxes.append(bbox)
else:
gt_labels_ignore.append(-1)
gt_bboxes_ignore.append(bbox)
data_anno = dict(
bboxes=np.array(gt_bboxes, dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 4),
labels=np.array(gt_labels, dtype=np.int64),
bboxes_ignore=np.array(gt_bboxes_ignore,
dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 4),
labels_ignore=np.array(gt_labels_ignore, dtype=np.int64))
data_info.update(ann=data_anno)
data_infos.append(data_info)
return data_infos
# 加载配置文件
cfg = Config.fromfile('./configs/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain_1x_coco.py')
# 获取设备状态
cfg.device = get_device()
# 指定数据集类型,这里对应的是上面注册的KittiTinyDataset类
cfg.dataset_type = 'KittiTinyDataset'
cfg.data_root = 'kitti_tiny/'
# 测试
cfg.data.test.type = 'KittiTinyDataset'
cfg.data.test.data_root = 'kitti_tiny/'
cfg.data.test.ann_file = 'train.txt' # 训练集索引
cfg.data.test.img_prefix = 'training/image_2' # 图片文件夹
# 训练
cfg.data.train.type = 'KittiTinyDataset'
cfg.data.train.data_root = 'kitti_tiny/'
cfg.data.train.ann_file = 'train.txt'
cfg.data.train.img_prefix = 'training/image_2'
# 验证
cfg.data.val.type = 'KittiTinyDataset'
cfg.data.val.data_root = 'kitti_tiny/'
cfg.data.val.ann_file = 'val.txt'
cfg.data.val.img_prefix = 'training/image_2'
cfg.data.workers_per_gpu = 0 # 设置workers数量
cfg.model.roi_head.bbox_head.num_classes = 3
# 加载预训练权重
cfg.load_from = 'checkpoints/faster_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain_3x_coco_20210526_095054-1f77628b.pth'
# 输出模型/训练日志保存路径
cfg.work_dir = './tutorial_exps'
# 原始的预训练学习率0.02是在八卡GPU训练时设置的,只有单卡环境则需除以8
cfg.optimizer.lr = 0.02 / 8
cfg.lr_config.warmup = None
cfg.log_config.interval = 10
# 评估指标
cfg.evaluation.metric = 'mAP'
# 每12个epoch进行一次eval
cfg.evaluation.interval = 12
# 每12个epoch保存模型
cfg.checkpoint_config.interval = 12
# 设置随机种子/gpuid
cfg.seed = 0
set_random_seed(0, deterministic=False)
cfg.gpu_ids = range(1)
# 使用tensorboard
cfg.log_config.hooks = [
dict(type='TextLoggerHook'),
dict(type='TensorboardLoggerHook')]
# 构建数据集
datasets = [build_dataset(cfg.data.train)]
# 构建检测器
model = build_detector(cfg.model)
# 模型类别
model.CLASSES = datasets[0].CLASSES
# 创建输出路径,如果存在就跳过,不存在则创建文件夹
mmcv.mkdir_or_exist(osp.abspath(cfg.work_dir))
# 开始训练
train_detector(model, datasets, cfg, distributed=False, validate=True)
这里需要注意原始代码因为版本问题,可能存在两个问题[2]。
-
IOError
这个原因是windows对多线程支持欠佳,因此需要将workers数量设为0.
cfg.data.workers_per_gpu = 0 -
RuntimeError
将np.long改成np.int64
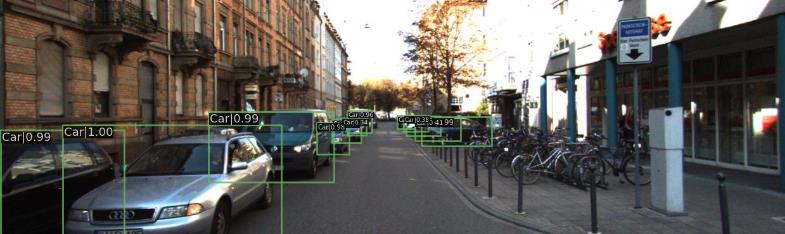
运行完之后,导入之前的模型进行检测,相关代码和第二个示例类似,检测效果。
扩展学习
MMDetection的使用体验下来难度不高,后续将探索更多示例进行学习。
这里看到一篇讲解比较细致的教程,对于MMCV机理作了比较详细的解析。
MMDetection框架入门教程(完全版):https://blog.csdn.net/qq_16137569/article/details/121316235
References
[1]https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Jb4y1r7ir?p=1&vd_source=9fef0d77bd45dc7fe5635b8e5496e032
[2]https://wenku.baidu.com/view/f6e8466a28160b4e767f5acfa1c7aa00b52a9d8e.html
以上是关于目标检测MMDetection的安装与基础使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
自动驾驶感知算法实战5——MMdetection3d环境搭建使用MMdetection3d做3D目标检测训练自己的数据集测试可视化,以及常见的错误
自动驾驶感知算法实战5——MMdetection3d环境搭建使用MMdetection3d做3D目标检测训练自己的数据集测试可视化,以及常见的错误