周震教授「编辑精选」| 机器学习赋能材料创新
Posted RSC英国皇家化学会
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了周震教授「编辑精选」| 机器学习赋能材料创新相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
英国皇家化学会出版的两本材料科学期刊 Journal of Materials Chemistry A 和 Materials Advances 的副主编周震教授(南开大学/郑州大学)近日收集整理了发表在两本刊上的部分精彩论文,汇总成一期专辑 Machine Learning for Materials Innovation(机器学习赋能材料创新)。

南开大学
郑州大学

随着高性能计算和实验技术的发展,高通量材料设计 (high-throughput materials design) 已成为现实,材料大数据 (big materials data) 的时代也正向我们走来。通过对材料大数据的高效分析找出隐藏的规则,然后利用这些规则开展材料的理性设计,就有机会实现材料领域的突破性创新。
机器学习方兴未艾,对许多科学领域——尤其是材料科学——都产生了很大的影响。通常而言,描述符(或特性)与所需信息之间的关系是非常复杂且非线性的。因此,仅依靠物理洞察力和原理很难发现统计规律。通过机器学习技术可以开发出灵活的模型,并通过输入数据对其进行训练,从而使其能基于不同的算法预测出所需的信息。如今,随着机器学习工具包、算法过程和材料数据库的发展,机器学习在材料科学中得到了广泛应用。
本专辑汇集了与机器学习相关的近期研究论文与综述,突出机器学习在材料创新方面的最新进展。
来自中国作者的论文
部分通讯作者来自中国的论文:
Predicting the performance of polyvinylidene fluoride, polyethersulfone and polysulfone filtration membranes using machine learning
Tingli Liu, Lunyang Liu, Fengchao Cui, Fang Ding, Qifeng Zhang and Yunqi Li
We built machine learning-based models to predict the performance of filtration membranes, and integrated them into homemade standalone software (polySML).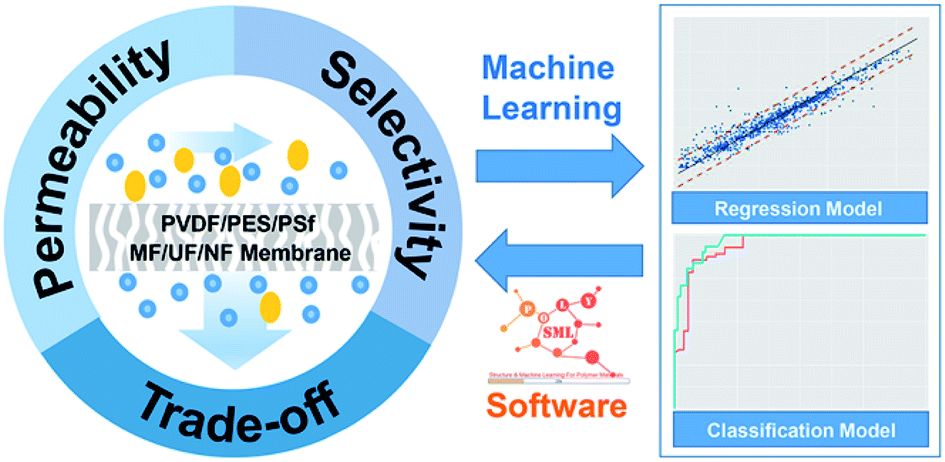 通讯作者 :刘伦洋(中科院长春应化所)、李云琦(中科院长春应化所)
通讯作者 :刘伦洋(中科院长春应化所)、李云琦(中科院长春应化所)J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020,8, 21862-21871
http://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA07607D
Rational design of transition metal single-atom electrocatalysts: a simulation-based, machine learning-accelerated study
Lianping Wu, Tian Guo and Teng Li
With maximum atom-utilization efficiency, single atom catalysts (SACs) are surging as a new research frontier in catalysis science.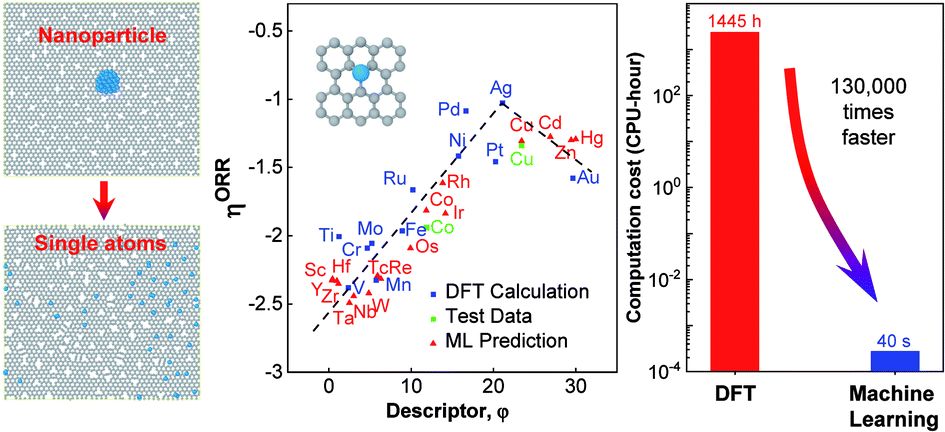 通讯作者 :李腾(马里兰大学)
通讯作者 :李腾(马里兰大学)J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020,8, 19290-19299
http://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA06207C
Computational design of (100) alloy surfaces for the hydrogen evolution reaction
Hao Li, Shaopeng Xu, Min Wang, Ziheng Chen, Fengfeng Ji, Kewei Cheng, Zhengyang Gao, Zhao Ding and Weijie Yang
Based on the understandings of alloying effects in bimetallic (100) surfaces, we explored their four-fold active sites for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction.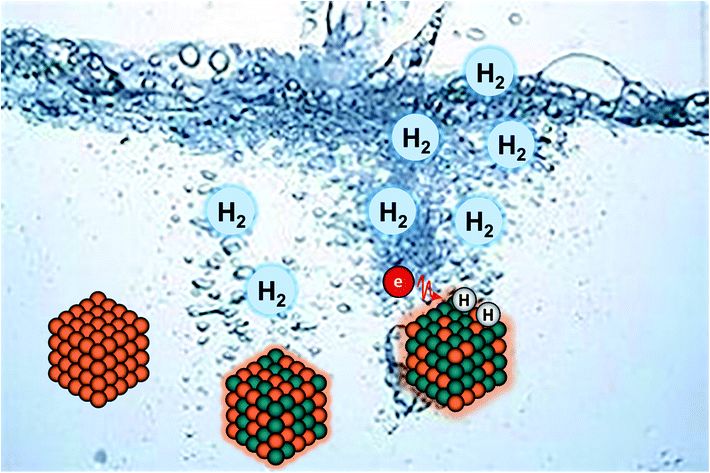 通讯作者 :杨维结(华北电力大学)
通讯作者 :杨维结(华北电力大学)J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020,8, 17987-17997
http://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA04615A
A machine learning scheme for the catalytic activity of alloys with intrinsic descriptors
Ze Yang, Wang Gao and Qing Jiang
We develop a universal design scheme based on the machine learning method and the intrinsic properties of substrates and adsorbates, allowing accurate prediction and rapid screening through a large phase space of alloys and multiple adsorbates.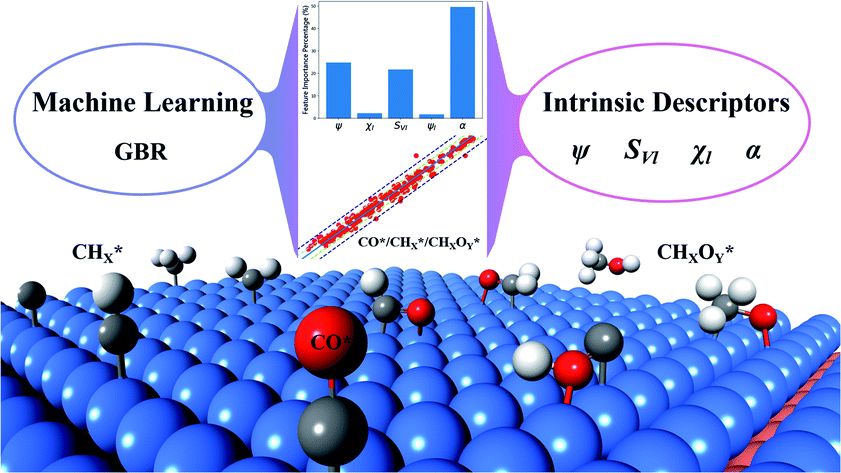 通讯作者 :高旺(吉林大学)、蒋青(吉林大学)
通讯作者 :高旺(吉林大学)、蒋青(吉林大学)J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020,8, 17507-17515
http://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA06203K
Directly predicting limiting potentials from easily obtainable physical properties of graphene-supported single-atom electrocatalysts by machine learning
Shiru Lin, Haoxiang Xu, Yekun Wang, Xiao Cheng Zeng and Zhongfang Chen
The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), oxygen evolution reaction (OER), and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) are three critical reactions for energy-related applications, such as water electrolyzers and metal–air batteries.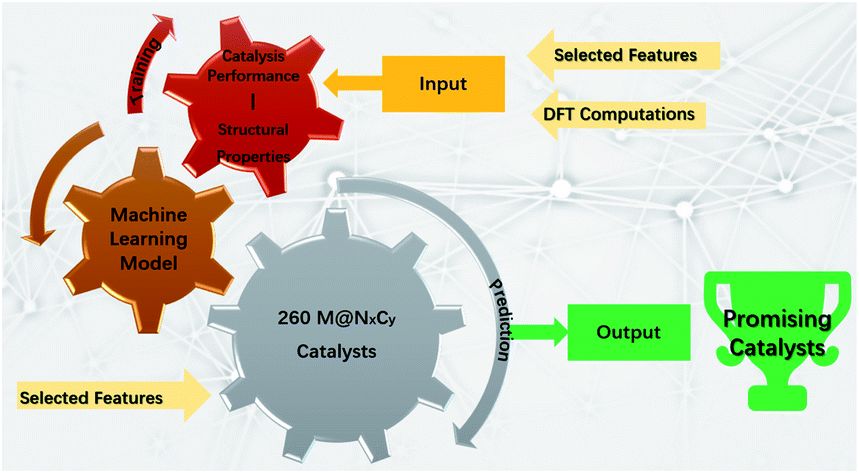 通讯作者 :陈中方(波多黎各大学)
通讯作者 :陈中方(波多黎各大学)J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020,8, 5663-5670
http://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA13404B
Machine-learning-assisted screening of pure-silica zeolites for effective removal of linear siloxanes and derivatives
Shiru Lin, Yekun Wang, Yinghe Zhao, Luis R. Pericchi, Arturo J. Hernández-Maldonado and Zhongfang Chen
By a two-step computational process, namely Grand Canonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) simulations and machine learning (ML), we screened 50 959 hypothetical pure-silica zeolites and identified 230 preeminent zeolites with excellent adsorption performances.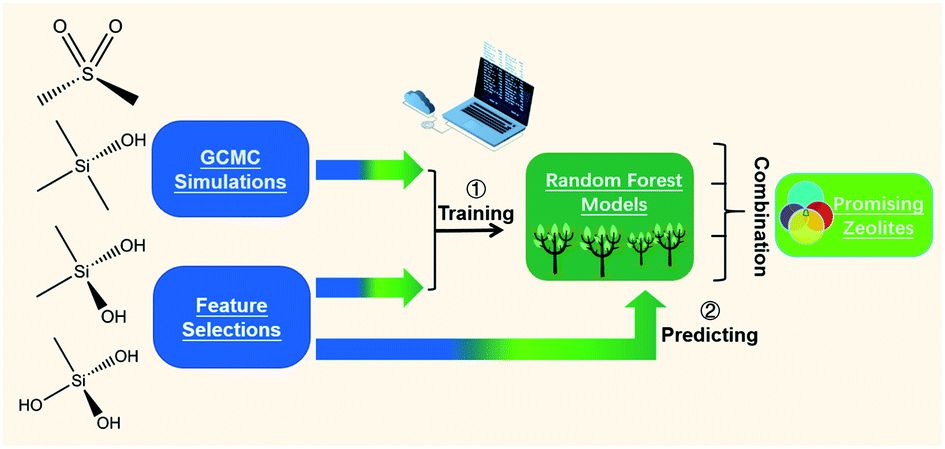 通讯作者 :Arturo J. Hernández-Maldonado(波多黎各大学)、陈中方(波多黎各大学)
通讯作者 :Arturo J. Hernández-Maldonado(波多黎各大学)、陈中方(波多黎各大学)J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020,8, 3228-3237
http://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA11909D
Large-scale evaluation of cascaded adsorption heat pumps based on metal/covalent–organic frameworks
Wei Li, Xiaoxiao Xia and Song Li
High-throughput computational screening of millions of cascaded adsorption heat pumps based on metal–organic frameworks and covalent–organic frameworks.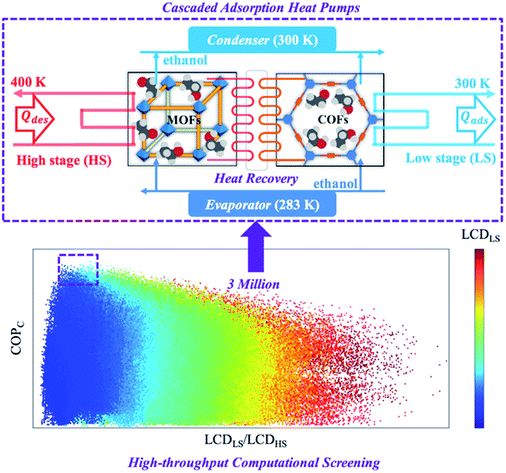
通讯作者 :李松(华中科技大学)
J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019,7, 25010-25019
http://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA09227G
Rationalizing the interphase stability of Li|doped-Li7La3Zr2O12via automated reaction screening and machine learning
Bo Liu, Jiong Yang, Hongliang Yang, Caichao Ye, Yuanqing Mao, Jiping Wang, Siqi Shi, Jihui Yang and Wenqing Zhang
Lithium metal batteries are a promising candidate for future high-energy-density energy storage.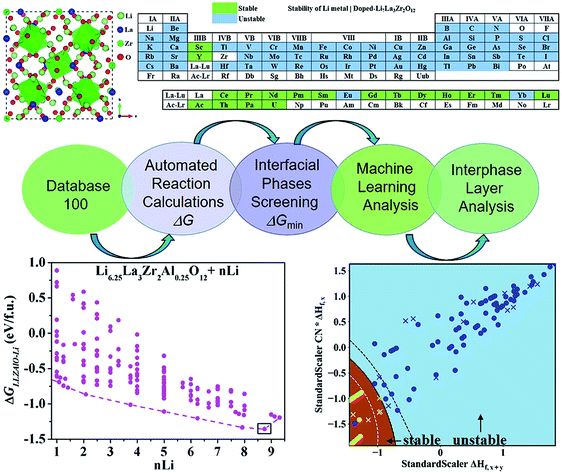
通讯作者 :杨炯(上海大学)、Jihui Yang(华盛顿大学)、张文清(南方科技大学)
J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019,7, 19961-19969
http://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA06748E
Designing promising molecules for organic solar cells via machine learning assisted virtual screening
Harikrishna Sahu, Feng Yang, Xiaobo Ye, Jing Ma, Weihai Fang and Haibo Ma
Rational design of new OPV molecules via virtual screening of candidate materials using high-performing machine learning models. 通讯作者 :马海波(南京大学)
通讯作者 :马海波(南京大学)J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019,7, 17480-17488
http://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA04097H
Rational design of hydrocarbon-based sulfonated copolymers for proton exchange membranes
Lunyang Liu, Wenduo Chen, Tingli Liu, Xiangxin Kong, Jifu Zheng and Yunqi Li
Developing novel hydrocarbon-based proton exchange membranes is at the Frontier of research on fuel cells, batteries and electrolysis, aiming to reach the demand for advanced performance in proton conductivity, fuel retardation, swelling, mechanical and thermal stability etc.
通讯作者 :李云琦(中科院长春应化所)
J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019,7, 11847-11857
http://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA00688E
Enhancing photovoltaic performance by tuning the domain sizes of a small-molecule acceptor by side-chain-engineered polymer donors
Yu-Che Lin, Yi-Ju Lu, Cheng-Si Tsao, Akinori Saeki, Jia-Xing Li, Chung-Hao Chen, Hao-Cheng Wang, Hsiu-Cheng Chen, Dong Meng, Kaung-Hsiung Wu, Yang Yang and Kung-Hwa Wei
This paper reports side-chain-engineered polymer donors and a small-molecule acceptor that are capable of simultaneous charge and energy transfer as the active layer for organic photovoltaics.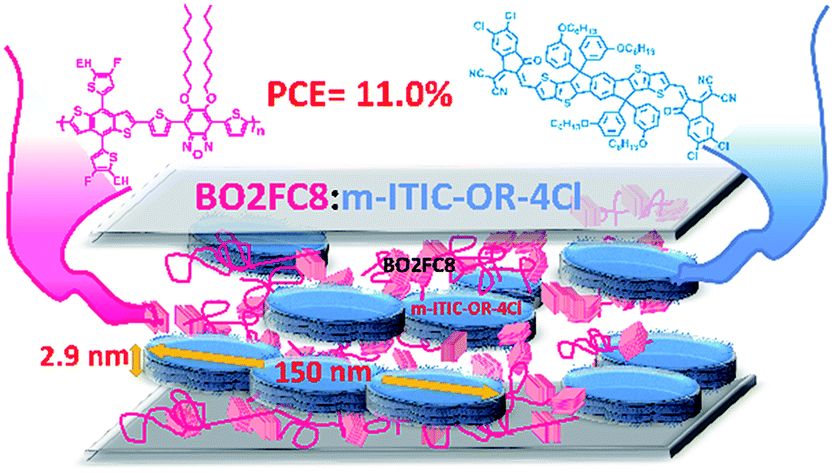 通讯作者 :韦光华(台湾阳明交通大学)
通讯作者 :韦光华(台湾阳明交通大学)J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019,7, 3072-3082
http://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA11059J
支持期刊


Journal of Materials Chemistry A
Publishing frequency: 48 issues per year
Time to first decision: 25 days **
Journal of Materials Chemistry A、B 和 C 报道材料化学各领域的高质量理论或实验研究工作。这三本期刊发表的论文侧重于报道对材料及其性质的新理解、材料的新应用以及材料合成的新方法。Journal of Materials Chemistry A、B 和 C 的区别在于所报道材料的不同预期用途。粗略的划分是,Journal of Materials Chemistry A 报道材料在能源和可持续性方面的应用,Journal of Materials Chemistry B 报道材料在生物学和医学方面的应用,Journal of Materials Chemistry C 报道材料在光学、磁学和电子设备方面的应用。


Materials Advances
该刊报道材料科学各领域的实验或理论研究成果,所发表的论文涵盖对材料的新认识以及材料的新应用、新特性和新合成方法。同时,该刊与英国皇家化学会现有的材料科学类期刊(Materials Horizons 及 Journal of Materials Chemistry A、B、C)相互依托并形成互补。作为一本金色开放获取的期刊,读者可以免费获取所发表论文的全文,同时从该刊发布起到 2022 年年中免收论文版面费。
点击文末“阅读原文”查看该专辑的全部论文。
以上是关于周震教授「编辑精选」| 机器学习赋能材料创新的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
5月截稿特刊 | 机器学习干细胞治疗网络安全电动汽车材料学和天文学等研究领域