剑指Offer - 面试题28:对称的二叉树
Posted 林夕07
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了剑指Offer - 面试题28:对称的二叉树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目
请实现一个函数,用来判断一棵二叉树是不是对称的。如果一棵二叉树和它的镜像一样,那么它是对称的。例如,在下图中,只有第一颗二叉树是对称的。而另外俩颗不是。
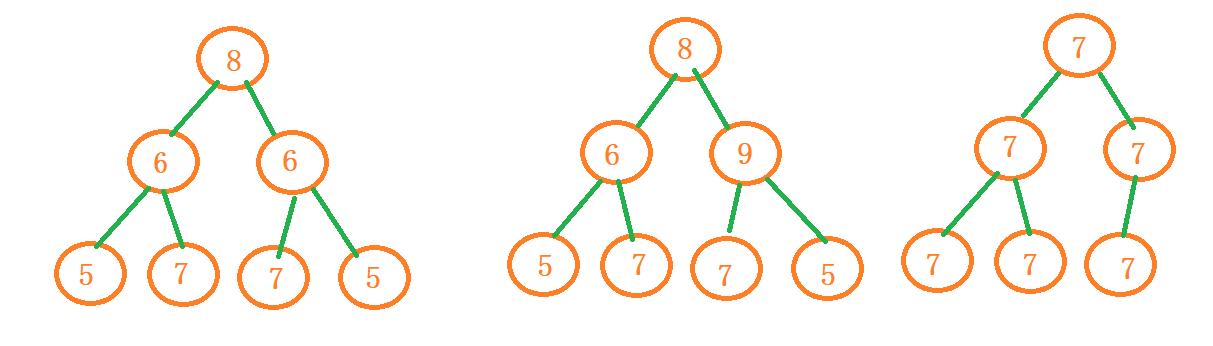
分析
对称遍历
对称的二叉树本质就是左右节点相同就好,所以我们可以用俩种对称的遍历方法将指向节点的指针存入容器中(如果放的是节点值的话,就如上图第三个二叉树,会造成混乱),然后一一对比,若有不同时就表示不是对称二叉树。
选取:根左右 和 根右左 做对比
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef int TElemType; //树结点的数据类型,目前暂定为整型
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
TElemType m_nValue;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft;//左孩子节点
BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight;//右孩子节点
};
void CreatTree(BinaryTreeNode** T)
{
TElemType elem;
cin >> elem;
if (elem != 999)
{
*T = new BinaryTreeNode();
if (NULL == T)
{
return;
}
(*T)->m_nValue = elem;
CreatTree(&((*T)->m_pLeft));
CreatTree(&((*T)->m_pRight));
}
else
{
*T = nullptr;
}
}
void RootRightLeft(BinaryTreeNode* root, vector<BinaryTreeNode*>& v)//前序遍历 根左右
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return;
}
v.push_back(root);
RootRightLeft(root->m_pLeft, v);
RootRightLeft(root->m_pRight, v);
}
void RootLeftRight(BinaryTreeNode* root, vector<BinaryTreeNode*>& v)// 根右左
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return;
}
v.push_back(root);
RootLeftRight(root->m_pRight, v);
RootLeftRight(root->m_pLeft, v);
}
bool Comparison(vector<BinaryTreeNode*>& v1, vector<BinaryTreeNode*>& v2)//对比俩容器
{
//参数出现异常
if (v1.size() < 0 || v2.size() < 0 || v1.size() != v2.size())
{
return false;
}
int size = v1.size();
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (v1.at(i) != v2.at(i))
{
return false;
}
}
cout << "size = " << size << endl;
return true;
}
bool isSymmetrical(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{
vector<BinaryTreeNode*> v1;//用于存放 根左右 的遍历结果
vector<BinaryTreeNode*> v2;//用于存放 根右左 的遍历结果
RootRightLeft(pRoot, v1);
RootLeftRight(pRoot, v2);
return Comparison(v1, v2);
}
int main()
{
BinaryTreeNode* root = nullptr;
cout << "请按照先序遍历规则输入节点值(输入999表示当前为空):" << endl;
CreatTree(&root);
bool ret = isSymmetrical(root);
if (ret == true)
{
cout << "该二叉树是对称二叉树" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "该二叉树不是对称二叉树" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
测试数据为题目的三个二叉树

递归法
我们还可以拿递归来实现,省掉了空间存储。
递归信息
- 当传入俩节点均为nullptr就返回true
- 当传入俩节点有一个nullptr就返回false;因为这是俩边已经不同了
- 当传入俩节点的值相同时就继续递归,反之直接false;不能有一次false
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef int TElemType; //树结点的数据类型,目前暂定为整型
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
TElemType m_nValue;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft;//左孩子节点
BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight;//右孩子节点
};
void CreatTree(BinaryTreeNode** T)
{
TElemType elem;
cin >> elem;
if (elem != 999)
{
*T = new BinaryTreeNode();
if (NULL == T)
{
return;
}
(*T)->m_nValue = elem;
CreatTree(&((*T)->m_pLeft));
CreatTree(&((*T)->m_pRight));
}
else
{
*T = nullptr;
}
}
bool Recursion(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot1, BinaryTreeNode* pRoot2)//递归
{
if (nullptr == pRoot1 && nullptr == pRoot2)//同时达底
{
return true;
}
if (nullptr == pRoot1 || nullptr == pRoot2)//有一边提前完
{
return false;
}
if (pRoot1->m_nValue != pRoot2->m_nValue)
{
return false;
}
//对比 proot1的左儿子和proot2的右儿子
//对比 proot2的左儿子和proot1的右儿子 都必须相等。
return Recursion(pRoot1->m_pLeft, pRoot2->m_pRight) &&
Recursion(pRoot1->m_pRight, pRoot2->m_pLeft);
}
bool isSymmetrical(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)//二叉树是否对称
{
return Recursion(pRoot, pRoot);
}
int main()
{
BinaryTreeNode* root = nullptr;
cout << "请按照先序遍历规则输入节点值(输入999表示当前为空):" << endl;
CreatTree(&root);
bool ret = isSymmetrical(root);
if (ret == true)
{
cout << "该二叉树是对称二叉树" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "该二叉树不是对称二叉树" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
测试数据
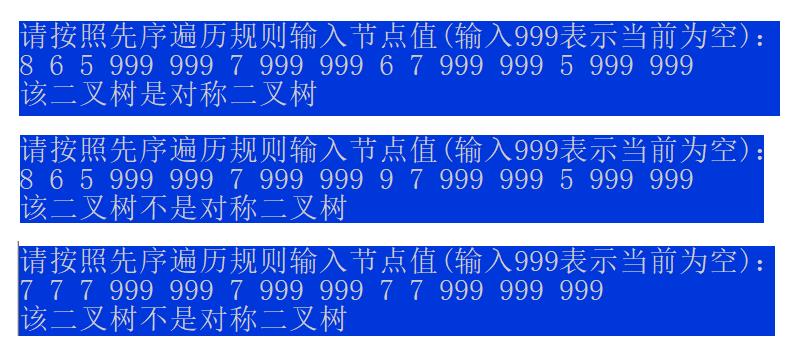
本章完!
以上是关于剑指Offer - 面试题28:对称的二叉树的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章