mybatis执行流程源码分析
Posted 客官不爱喝酒
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mybatis执行流程源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.简介
MyBatis是目前非常流行的ORM框架,它的功能很强大,然而其实现却比较简单、优雅。本文主要讲述MyBatis的架构设计思路。
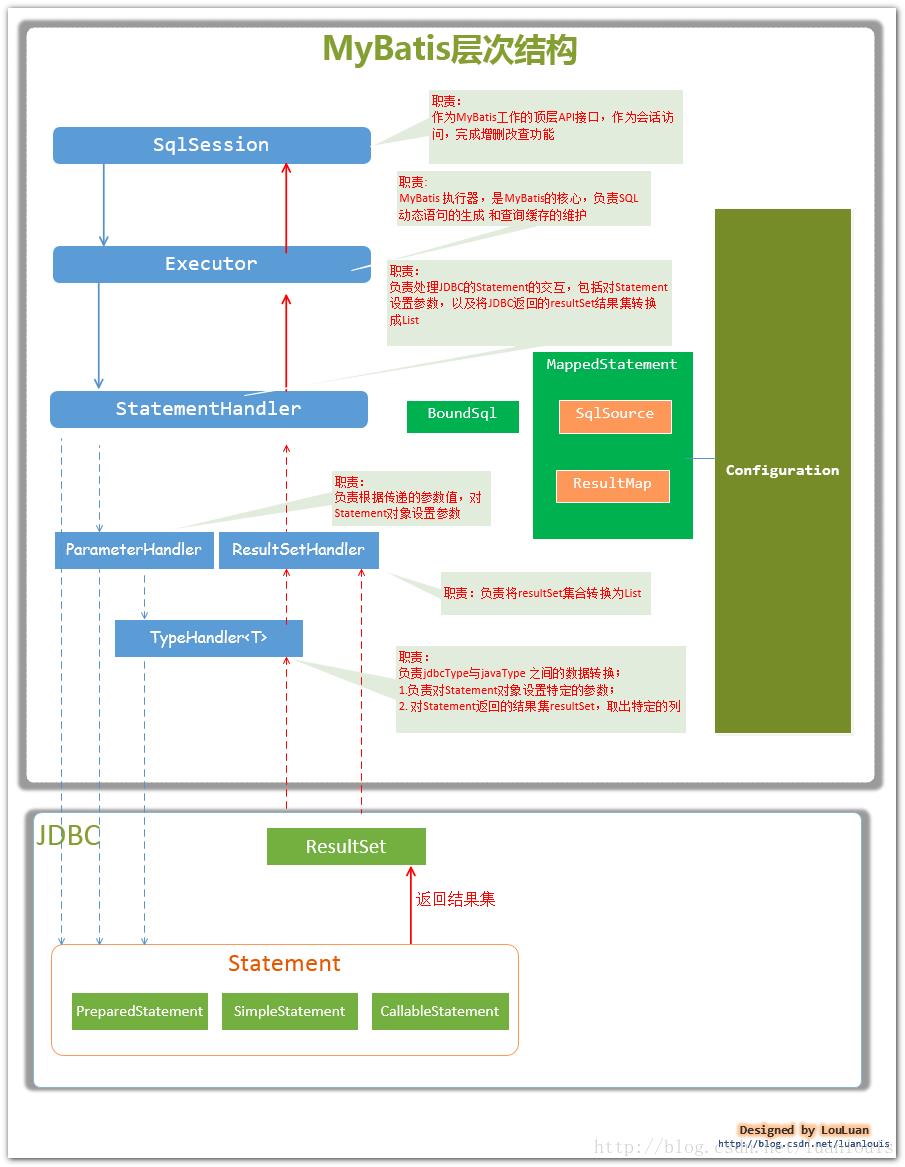
2.mybatis框架设计架构
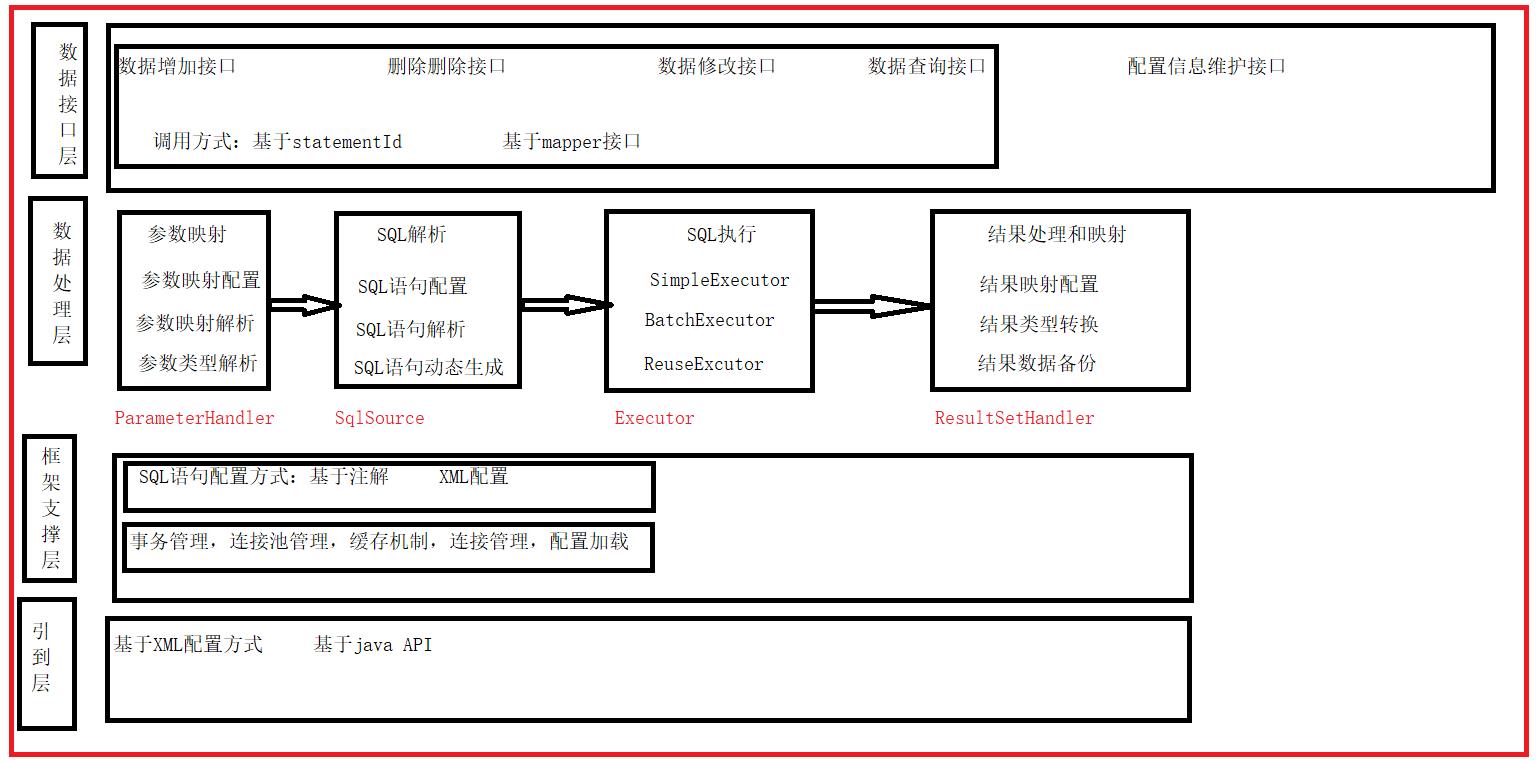
接口层与数据库交互的方式:
1.mybatis提供的传统API的方式,通过SqlSession对象进行调用
2.使用mapper接口,使用xml的方式配置sql
这是传统的传递Statement Id 和查询参数给 SqlSession 对象,使用 SqlSession对象完成和数据库的交互;MyBatis 提供了非常方便和简单的API,供用户实现对数据库的增删改查数据操作,以及对数据库连接信息和MyBatis 自身配置信息的维护操作。
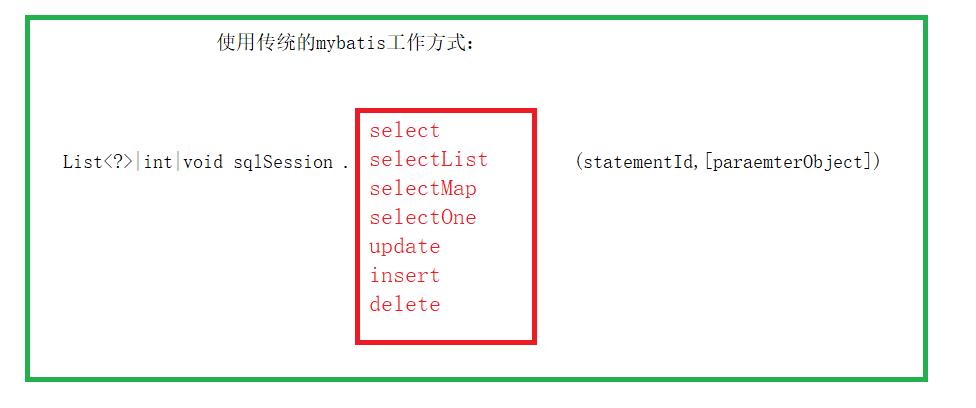
上述使用MyBatis 的方法,是创建一个和数据库打交道的SqlSession对象,然后根据Statement Id 和参数来操作数据库,这种方式固然很简单和实用,但是它不符合面向对象语言的概念和面向接口编程的编程习惯。由于面向接口的编程是面向对象的大趋势,MyBatis 为了适应这一趋势,增加了第二种使用MyBatis 支持接口(Interface)调用方式。
2.定义mapper接口的方式
MyBatis 将配置文件中的每一个 节点抽象为一个 Mapper 接口,而这个接口中声明的方法和跟 节点中的<select|update|delete|insert> 节点项对应,即<select|update|delete|insert> 节点的id值为Mapper 接口中的方法名称,parameterType 值表示Mapper 对应方法的入参类型,而resultMap 值则对应了Mapper 接口表示的返回值类型或者返回结果集的元素类型。
mapper接口和mapper.xml的关系
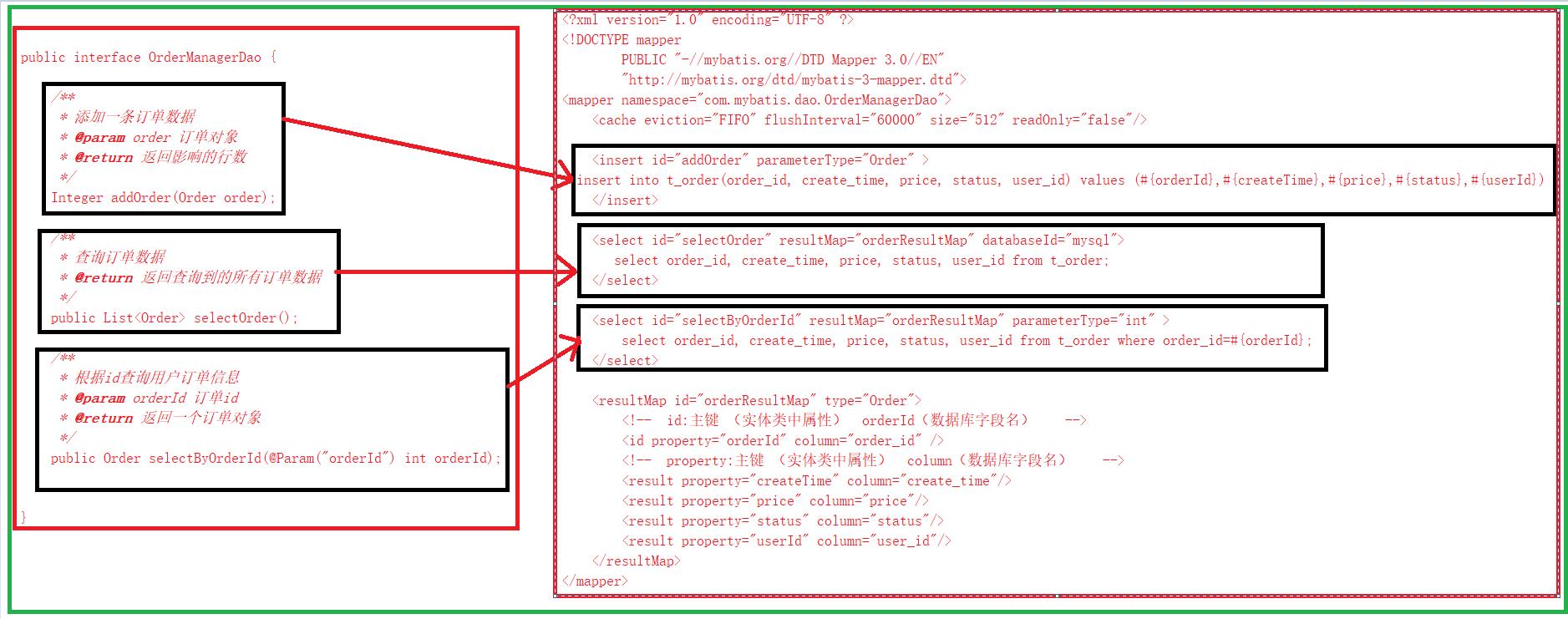
根据MyBatis 的配置规范配置好后,通过SqlSession.getMapper(XXXMapper.class) 方法,MyBatis 会根据相应的接口声明的方法信息,通过动态代理机制生成一个Mapper 实例,我们使用Mapper 接口的某一个方法时,MyBatis 会根据这个方法的方法名和参数类型,确定Statement Id,底层还是通过SqlSession.select(“statementId”,parameterObject);或者SqlSession.update(“statementId”,parameterObject); 等等来实现对数据库的操作。
MyBatis 引用Mapper 接口这种调用方式,纯粹是为了满足面向接口编程的需要。(其实还有一个原因是在于,面向接口的编程,使得用户在接口上可以使用注解来配置SQL语句,这样就可以脱离XML配置文件,实现“0配置”)。
MyBatis框架主要完成的是以下2件事情:
1.根据JDBC规范建立与数据库的连接。
2.通过反射打通Java对象与数据库参数交互之间相互转换的关系
mybatis主要的类:
| 主要类 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| Configuration | MyBatis所有的配置信息都维持在Configuration对象之中。 |
| SqlSession | 作为MyBatis工作的主要顶层API,表示和数据库交互的会话,完成必要数据库增删改查功能 |
| Executor | MyBatis执行器,是MyBatis 调度的核心,负责SQL语句的生成和查询缓存的维护 |
| StatementHandler | 封装了JDBC Statement操作,负责对JDBC statement 的操作,如设置参数、将Statement结果集转换成List集合。 |
| ParameterHandler | 负责对用户传递的参数转换成JDBC Statement 所需要的参数,ResultSetHandler 负责将JDBC返回的ResultSet结果集对象转换成List类型的集合; |
| TypeHandler | 负责java数据类型和jdbc数据类型之间的映射和转换 |
| MappedStatement | MappedStatement维护了一条(select,update,delete,inserinto)节点的封装 |
| SqlSource | 负责根据用户传递的parameterObject,动态地生成SQL语句,将信息封装到BoundSql对象中,并返回 |
| BoundSql | 表示动态生成的SQL语句以及相应的参数信息 |
以上几个类在SQL操作中都会涉及,在SQL操作中重点关注下SQL参数什么时候写入和结果集怎么转换为Java对象,这两个过程正好对应的类是PreparedStatementHandler和ResultSetHandler类。
3.sqlSessionFactory的初始化过程
sqlSessionFactory最重要的就是解析我们的配置文件,以及解析我们的SQL,将这些信息封装到Configuration对象中,以便于供我们的SqlSession对象进行使用,因为SqlSession对象在执行SQL的过程中也会使用到我们的Configuration对象;
//读取mybatis.xml配置文件
String config = "mybatis.xml";
//将配置文件加入到流中
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
//创建factory对象(我们需要分析的就是这一段代码)
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
1.new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in),最终返回的是一个他的实现类DefaultSqlSessionFactory,DefaultSqlSessionFactory中有一个重要的属性就是Configuration对象。
2.调用自己的build方法创建一个 XMLConfigBuilder(mybatis.xml配置文件解析器对象)=>parser
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
3.调用parser.parse()解析mybati.xml配置文件中的配置属性,返回Configuration对象,mybatis.xml配置文件中所有的节点信息都被解析,然后封装到Configuration对象中。
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// 拿到根节点对象
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
4.在XMLConfigBuilder类中调用parseConfiguration(XNode root)对配置文件中的每个配置标签进行逐一解析,并且赋默认值。然后封装到Configuration对象中,然后返回。
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
4.2我们看一个 settingsElement(settings);方法,其余的也是在这个类中,大家可以自行查看。
private void settingsElement(Properties props) {
configuration.setAutoMappingBehavior(AutoMappingBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingBehavior", "PARTIAL")));
configuration.setAutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior(AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior", "NONE")));
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
configuration.setProxyFactory((ProxyFactory) createInstance(props.getProperty("proxyFactory")));
configuration.setLazyLoadingEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadingEnabled"), false));
configuration.setAggressiveLazyLoading(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("aggressiveLazyLoading"), false));
configuration.setMultipleResultSetsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("multipleResultSetsEnabled"), true));
configuration.setUseColumnLabel(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useColumnLabel"), true));
configuration.setUseGeneratedKeys(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useGeneratedKeys"), false));
configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(ExecutorType.valueOf(props.getProperty("defaultExecutorType", "SIMPLE")));
configuration.setDefaultStatementTimeout(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultStatementTimeout"), null));
configuration.setDefaultFetchSize(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultFetchSize"), null));
configuration.setDefaultResultSetType(resolveResultSetType(props.getProperty("defaultResultSetType")));
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("mapUnderscoreToCamelCase"), false));
configuration.setSafeRowBoundsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeRowBoundsEnabled"), false));
configuration.setLocalCacheScope(LocalCacheScope.valueOf(props.getProperty("localCacheScope", "SESSION")));
configuration.setJdbcTypeForNull(JdbcType.valueOf(props.getProperty("jdbcTypeForNull", "OTHER")));
configuration.setLazyLoadTriggerMethods(stringSetValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadTriggerMethods"), "equals,clone,hashCode,toString"));
configuration.setSafeResultHandlerEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeResultHandlerEnabled"), true));
configuration.setDefaultScriptingLanguage(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultScriptingLanguage")));
configuration.setDefaultEnumTypeHandler(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultEnumTypeHandler")));
configuration.setCallSettersOnNulls(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("callSettersOnNulls"), false));
configuration.setUseActualParamName(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useActualParamName"), true));
configuration.setReturnInstanceForEmptyRow(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("returnInstanceForEmptyRow"), false));
configuration.setLogPrefix(props.getProperty("logPrefix"));
configuration.setConfigurationFactory(resolveClass(props.getProperty("configurationFactory")));
}
4.3:我们来看下 mapperElement(root.evalNode(“mappers”));这行代码的执行步骤
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
4.4 通过configurationElement(XNode context)方法解析mapper.xml文件中的所有标签,以及标签中配置的属性。
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
4.5 接下来我们看下解析增删改查是如何进行解析的,首先会将select标签中所有可配置的属性解析解析,如果没有配置,开始进行赋默认值。
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType以上是关于mybatis执行流程源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章