SparseArray源码浅析
Posted zhujm320
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SparseArray源码浅析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
介绍
SparseArray是android特有的轻量级数据结构,类似于hashmap以键值对的方式进行存储,但是key类型为int,key-value分别采用数组进行存储,采用二分法进行查询,具有很高的查询效率(时间复杂度O(logn)),但是插入和删除效率比较低(需要移动数组), 不适合大量数据的情况。
图示
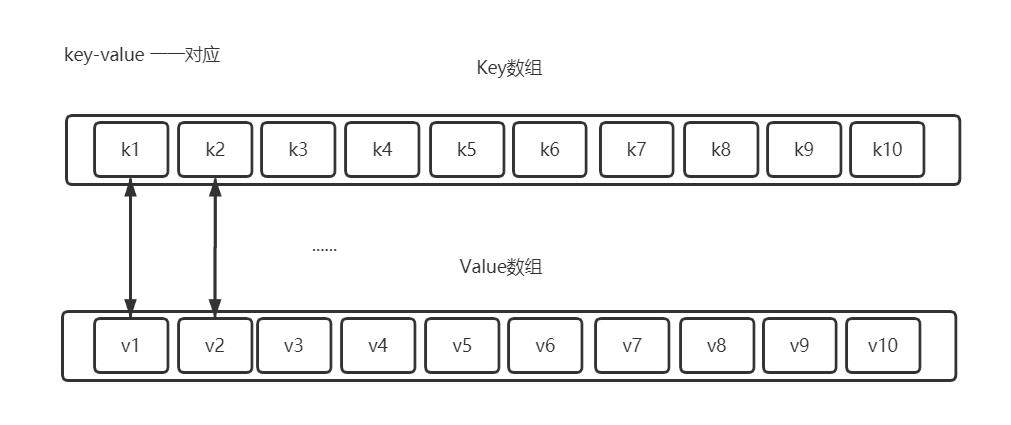
从上图中可以看出,key-value分别存储在Key数据和Value数组中,它们有者共同的索引。插入,删除,查询操作,遍历key数组通过二分查找法,找到key对应的index,那么value的位置在value数组下标为index地方。
属性介绍
//数组中元素删除标记(假删除)
private static final Object DELETED = new Object();
//是否进行回收的标记, 删除元素后, mGarbage=true
private boolean mGarbage = false;
//保存key的数组
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = 28) // Use keyAt(int)
private int[] mKeys;
//保存value的数组
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = 28) // Use valueAt(int), setValueAt(int, E)
private Object[] mValues;
//容器大小
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = 28) // Use size()
private int mSize;方法介绍
构造方法
public SparseArray() {
this(10);
}
public SparseArray(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity == 0) {
mKeys = EmptyArray.INT;
mValues = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
mValues = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedObjectArray(initialCapacity);
mKeys = new int[mValues.length];
}
mSize = 0;
}构造函数,初始化key和value数组,默认构造函数初始化key和value数组大小为10
克隆操作
public SparseArray<E> clone() {
SparseArray<E> clone = null;
try {
clone = (SparseArray<E>) super.clone();
clone.mKeys = mKeys.clone();
clone.mValues = mValues.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException cnse) {
/* ignore */
}
return clone;
}是否包含特定的key
public boolean contains(int key) {
return indexOfKey(key) >= 0;
}
/*
* 如果在该操作之前有进行删除操作,就进行一次垃圾回收
*/
public int indexOfKey(int key) {
if (mGarbage) {
gc();
}
return ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}
/*
* 通过二分法找到key对应的索引
*/
static int binarySearch(int[] array, int size, int value) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = size - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
final int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
final int midVal = array[mid];
if (midVal < value) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else if (midVal > value) {
hi = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid; // value found
}
}
return ~lo; // value not present
}通过value查找index
public int indexOfValueByValue(E value) {
if (mGarbage) {
gc();
}
for (int i = 0; i < mSize; i++) {
if (value == null) {
if (mValues[i] == null) {
return i;
}
} else {
if (value.equals(mValues[i])) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}清空所有的元素
public void clear() {
int n = mSize;
Object[] values = mValues;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
values[i] = null;
}
mSize = 0;
mGarbage = false;
}追加元素
public void append(int key, E value) {
if (mSize != 0 && key <= mKeys[mSize - 1]) {
put(key, value);
return;
}
//说明有垃圾, 需要进行垃圾回收
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
gc();
}
//空间不够,需要进行扩容,并将数组进行移位
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.append(mKeys, mSize, key);
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.append(mValues, mSize, value);
mSize++;
}
/*
* 插入元素
*/
public void put(int key, E value) {
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
mValues[i] = value;
} else {
i = ~i;
if (i < mSize && mValues[i] == DELETED) {
mKeys[i] = key;
mValues[i] = value;
return;
}
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
gc();
// Search again because indices may have changed.
i = ~ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mValues, mSize, i, value);
mSize++;
}
}查询
public E get(int key) {
return get(key, null);
}
public E get(int key, E valueIfKeyNotFound) {
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i < 0 || mValues[i] == DELETED) {
return valueIfKeyNotFound;
} else {
return (E) mValues[i];
}
}根据key查询value,基本思想也是遍历key数组找到key对应的index,然后从value数组中取出index对应的值
删除
public void delete(int key) {
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
if (mValues[i] != DELETED) {
mValues[i] = DELETED;
mGarbage = true;
}
}
}
/*
* 删除并返回value
*/
public E removeReturnOld(int key) {
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
if (mValues[i] != DELETED) {
final E old = (E) mValues[i];
mValues[i] = DELETED;
mGarbage = true;
return old;
}
}
return null;
}
/*
* 根据索引进行删除
*/
public void removeAt(int index) {
if (index >= mSize && UtilConfig.sThrowExceptionForUpperArrayOutOfBounds) {
// The array might be slightly bigger than mSize, in which case, indexing won't fail.
// Check if exception should be thrown outside of the critical path.
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
if (mValues[index] != DELETED) {
mValues[index] = DELETED;
mGarbage = true;
}
}
/*
* 删除一个范围的元素
*/
public void removeAtRange(int index, int size) {
final int end = Math.min(mSize, index + size);
for (int i = index; i < end; i++) {
removeAt(i);
}
}根据key删除对应的元素,注意这里是假删除,只是将需要删除的位置设置删除标记,同时设置垃圾回收标记。假删除的好处是进行了内存复用,避免重复申请内存。将垃圾回收,延迟到一下操作(如: 插入,计算大小)
垃圾回收
private void gc() {
// Log.e("SparseArray", "gc start with " + mSize);
int n = mSize;
int o = 0;
int[] keys = mKeys;
Object[] values = mValues;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Object val = values[i];
if (val != DELETED) {
if (i != o) {
keys[o] = keys[i];
values[o] = val;
values[i] = null;
}
o++;
}
}
mGarbage = false;
mSize = o;
// Log.e("SparseArray", "gc end with " + mSize);
}将value数组中值为DELETED的元素全部设置为null,以便进行垃圾回收
元素个数
public int size() {
if (mGarbage) {
gc();
}
return mSize;
}根据索引查询key
public int keyAt(int index) {
if (index >= mSize && UtilConfig.sThrowExceptionForUpperArrayOutOfBounds) {
// The array might be slightly bigger than mSize, in which case, indexing won't fail.
// Check if exception should be thrown outside of the critical path.
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
if (mGarbage) {
gc();
}
return mKeys[index];
}根据索引查询value
public E valueAt(int index) {
if (index >= mSize && UtilConfig.sThrowExceptionForUpperArrayOutOfBounds) {
// The array might be slightly bigger than mSize, in which case, indexing won't fail.
// Check if exception should be thrown outside of the critical path.
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
if (mGarbage) {
gc();
}
return (E) mValues[index];
}根据索引设置value
public void setValueAt(int index, E value) {
if (index >= mSize && UtilConfig.sThrowExceptionForUpperArrayOutOfBounds) {
// The array might be slightly bigger than mSize, in which case, indexing won't fail.
// Check if exception should be thrown outside of the critical path.
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
if (mGarbage) {
gc();
}
mValues[index] = value;
}根据key查询索引
public int indexOfKey(int key) {
if (mGarbage) {
gc();
}
return ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}根据value查询索引
public int indexOfValue(E value) {
if (mGarbage) {
gc();
}
for (int i = 0; i < mSize; i++) {
if (mValues[i] == value) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public int indexOfValueByValue(E value) {
if (mGarbage) {
gc();
}
for (int i = 0; i < mSize; i++) {
if (value == null) {
if (mValues[i] == null) {
return i;
}
} else {
if (value.equals(mValues[i])) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}toString实现
public String toString() {
if (size() <= 0) {
return "{}";
}
StringBuilder buffer = new StringBuilder(mSize * 28);
buffer.append('{');
for (int i=0; i<mSize; i++) {
if (i > 0) {
buffer.append(", ");
}
int key = keyAt(i);
buffer.append(key);
buffer.append('=');
Object value = valueAt(i);
if (value != this) {
buffer.append(value);
} else {
buffer.append("(this Map)");
}
}
buffer.append('}');
return buffer.toString();
}总结:
SparseArray作为轻量级key-value数据结构,适用于key为int的场景,避免了自动装箱的操作,在该场景下可以替代HashMap,进行内存优化。
以上是关于SparseArray源码浅析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章