基于hadoop2.7集群的Spark2.0,Sqoop1.4.6,Mahout0.12.2完全分布式安装
Posted 搜索与推荐Wiki
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于hadoop2.7集群的Spark2.0,Sqoop1.4.6,Mahout0.12.2完全分布式安装相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
写在前边的话
hadoop2.7完全分布式安装请参考:点击阅读,继任该篇博客之后,诞生了下面的这一篇博客
基本环境:
CentOS 6.5,Hadoop 2.7,Java 1.7
Hive 2.0.0,Zookeeper 3.4.8, Hbase 1.2.2
预安装
Scala 2.11
Spark 2.0
Sqoop 1.4.6
Mahout 0.12.2
一:安装 Scala 2.11.X
下载:点击进入下载 (我使用的是Scala 2.11.8)
1:解压到指定目录,并重命名文件夹
sudo tar -zxvf /home/master/下载/scala-2.11.8.tar.gz -C /opt/
sudo mv scala-2.11.8/ /opt/scala
2:修改环境变量
sudo vim /etc/profile 加入如下代码:
#scala
export SCALA_HOME=/opt/scala
export PATH=$PATH:$SCALA_HOME/bin3:每台机器上都部署scala
执行 sudo scp -r /opt/scala/ slave1:/opt/scala
sudo scp -r /opt/scala/ slave2:/opt/scala
分别在各个节点上修改环境变量即可
4:运行scala
终端直接输入scala即可
二:安装 Spark 2.0
下载:点击进入下载 (这里建议不要安装最新版Spark,具体看评论)
1:解压到指定目录,并重命名文件夹
[master@master1 opt]$ sudo tar -zxvf /home/master/下载/spark-2.0.0-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz -C .
[master@master1 opt]$ sudo mv spark-2.0.0-bin-hadoop2.7/ spark
2:配置环境变量
sudo vim /etc/profile ,加入
#spark home
export SPARK_HOME=/opt/spark
export PATH=$SPARK_HOME/bin:$PATH 3:配置spark-env.sh
复制 :sudo cp spark-env.sh.template spark-env.sh
加入以下:
export SCALA_HOME=/opt/scala
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/java
export SPARK_MASTER_IP=192.168.48.130
export SPARK_WORKER_MEMORY=1g
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop4:将 slaves.template 拷贝到 slaves, 编辑内容为
master1
slave1
slave2
5:将spark目录拷贝到各个节点
sudo scp -r /opt/spark/ slave1:/opt/spark
sudo scp -r /opt/spark/ slave2:/opt/spark
并修改各个节点的环境变量
6:启动 spark
启动master: sbin/start-master.sh
启动salve: sbin/start-slaves.sh
如遇到权限不足问题,直接给每台机器上的spark目录赋予 777 的权限即可
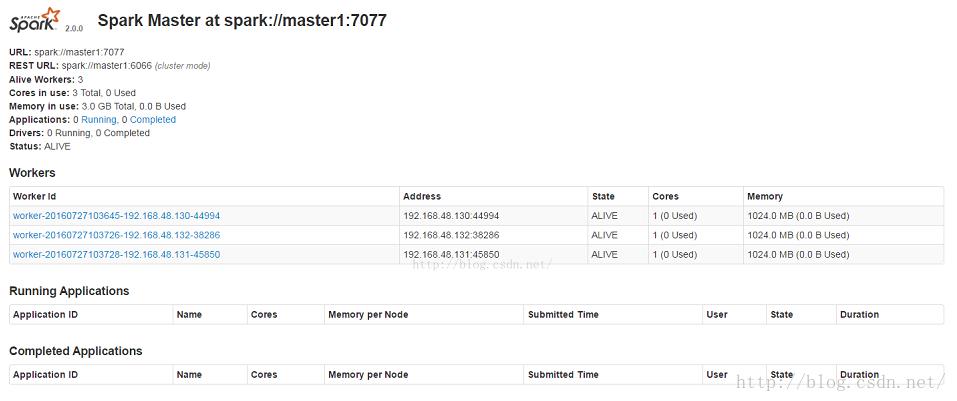
7:web界面
http://192.168.48.130:8080/
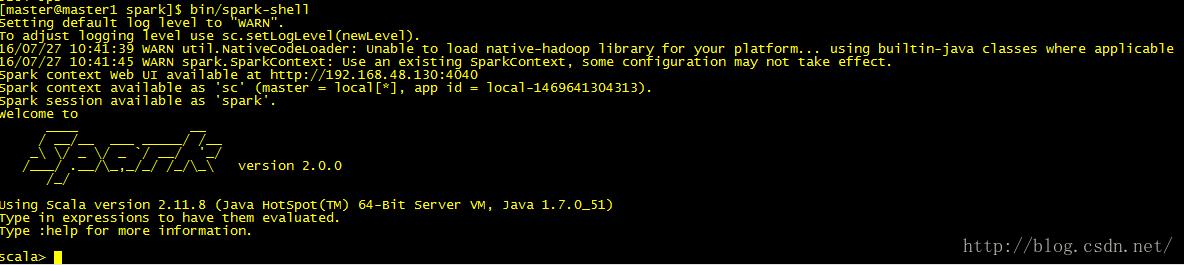
8:shell 界面
bin/spark-shell
三:安装 Sqoop 1.4.6
下载:点击进入下载
1:解压到指定目录,并重命名
sudo tar -zxvf /home/master/下载/sqoop-1.4.6.tar.gz -C
sudo mv sqoop-1.99.6/ sqoop
2:配置环境变量
sudo vim /etc/profile
#sqoop
export SQOOP_HOME=/opt/sqoop
export PATH = $SQOOP_HOME/bin:$PATH 保存生效:source /etc/profile3:复制mysql-jdbc 包到sqoop/lib目录下
sudo cp /home/master/下载/mysql-connector-java-5.1.39-bin.jar /opt/sqoop/lib/
4:修改bin/configure-sqoop文件
此时如果没有启用hbase,zookeeper等组件,将相应的信息注释,如果启用了,就pass,直接进入下一步
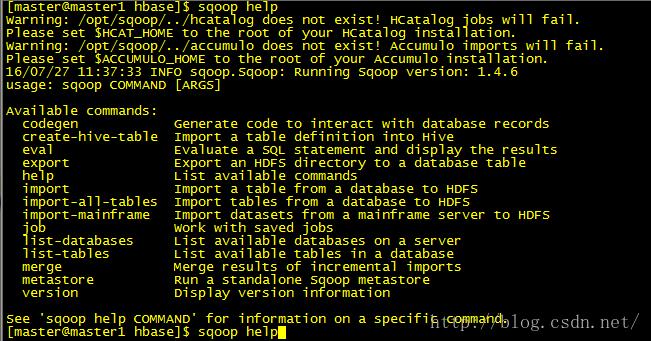
5:sqoop help 查看帮助
四:安装 Mahout 0.12.2
下载:点击进入下载
1:解压到指定目录,并重命名
注意路径问题
[master@master1 opt]$ sudo tar -zxvf /home/master/桌面/apache-mahout-distribution-0.12.0.tar.gz -C .
[master@master1 opt]$ sudo mv apache-mahout-distribution-0.12.0/ mahout2:配置环境变量
sudo vim /etc/profile ,加入以下内容:
<span style="font-size:14px;">#mahout home
export MAHOUT_HOME=/opt/mahout
export PATH=$MAHOUT_HOME/bin:$PATH
</span>3:启动mahout
进入mahout安装目录,执行:bin/mahout
[master@master1 mahout]$ bin/mahout
Running on hadoop, using /opt/hadoop/bin/hadoop and HADOOP_CONF_DIR=
MAHOUT-JOB: /opt/mahout/mahout-examples-0.12.0-job.jar
An example program must be given as the first argument.
Valid program names are:
arff.vector: : Generate Vectors from an ARFF file or directory
baumwelch: : Baum-Welch algorithm for unsupervised HMM training
canopy: : Canopy clustering
cat: : Print a file or resource as the logistic regression models would see it
cleansvd: : Cleanup and verification of SVD output
clusterdump: : Dump cluster output to text
clusterpp: : Groups Clustering Output In Clusters
cmdump: : Dump confusion matrix in html or text formats
cvb: : LDA via Collapsed Variation Bayes (0th deriv. approx)
cvb0_local: : LDA via Collapsed Variation Bayes, in memory locally.
describe: : Describe the fields and target variable in a data set
evaluateFactorization: : compute RMSE and MAE of a rating matrix factorization against probes
fkmeans: : Fuzzy K-means clustering
hmmpredict: : Generate random sequence of observations by given HMM
itemsimilarity: : Compute the item-item-similarities for item-based collaborative filtering
kmeans: : K-means clustering
lucene.vector: : Generate Vectors from a Lucene index
matrixdump: : Dump matrix in CSV format
matrixmult: : Take the product of two matrices
parallelALS: : ALS-WR factorization of a rating matrix
qualcluster: : Runs clustering experiments and summarizes results in a CSV
recommendfactorized: : Compute recommendations using the factorization of a rating matrix
recommenditembased: : Compute recommendations using item-based collaborative filtering
regexconverter: : Convert text files on a per line basis based on regular expressions
resplit: : Splits a set of SequenceFiles into a number of equal splits
rowid: : Map SequenceFile<Text,VectorWritable> to SequenceFile<IntWritable,VectorWritable>, SequenceFile<IntWritable,Text>
rowsimilarity: : Compute the pairwise similarities of the rows of a matrix
runAdaptiveLogistic: : Score new production data using a probably trained and validated AdaptivelogisticRegression model
runlogistic: : Run a logistic regression model against CSV data
seq2encoded: : Encoded Sparse Vector generation from Text sequence files
seq2sparse: : Sparse Vector generation from Text sequence files
seqdirectory: : Generate sequence files (of Text) from a directory
seqdumper: : Generic Sequence File dumper
seqmailarchives: : Creates SequenceFile from a directory containing gzipped mail archives
seqwiki: : Wikipedia xml dump to sequence file
spectralkmeans: : Spectral k-means clustering
split: : Split Input data into test and train sets
splitDataset: : split a rating dataset into training and probe parts
ssvd: : Stochastic SVD
streamingkmeans: : Streaming k-means clustering
svd: : Lanczos Singular Value Decomposition
testnb: : Test the Vector-based Bayes classifier
trainAdaptiveLogistic: : Train an AdaptivelogisticRegression model
trainlogistic: : Train a logistic regression using stochastic gradient descent
trainnb: : Train the Vector-based Bayes classifier
transpose: : Take the transpose of a matrix
validateAdaptiveLogistic: : Validate an AdaptivelogisticRegression model against hold-out data set
vecdist: : Compute the distances between a set of Vectors (or Cluster or Canopy, they must fit in memory) and a list of Vectors
vectordump: : Dump vectors from a sequence file to text
viterbi: : Viterbi decoding of hidden states from given output states sequence五:额外补充
1:出现 sudo: command not found时
执行 export PATH=$PATH:/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin 即可
2:这里我们发现除了spark的分布式安装以外要把安装包拷贝到各个节点之外,sqoop和mahout并不需要,只需要在master主机上部署即可,我的理解是sqoop只是进行数据传输的,数据可以是HDFS上的,也可以是Hive,或者Hbase上的,而本身他们已经是分布式的了,所以这里自然不需要将其拷贝到各个节点,而mahout也一样吧,只要运行在分布式的平台上即可,其所依赖的数据也是在hdfs或者hive上,故也不需要将其拷贝到各个节点
3:那么问题来了,我们是否可以将sqoop或者mahout部署到slave节点上呢?答案是肯定的吧,因为每台机器之间是可以互相通过ssh访问的,sqoop使用时可以直接加上对应的IP地址即可,而mahout就可以直接使用了
大数据全新视频教程,博主亲自整理,点击查看
以上是关于基于hadoop2.7集群的Spark2.0,Sqoop1.4.6,Mahout0.12.2完全分布式安装的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
spark 2.0.0集群安装与hive on spark配置
CentOS7上Hadoop2.7.7集群部署hive3+Tez0.9.1