JS基础 类
Posted wgchen~
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JS基础 类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
阅读目录
基础知识
为了和其他语言继承形态一致,JS提供了class 关键词用于模拟传统的class ,但底层实现机制依然是原型继承。
class 只是语法糖为了让类的声明与继承更加简洁清晰。
声明定义
可以使用类声明和赋值表达式定义类,推荐使用类声明来定义类。
//类声明
class User
console.log(new User());

let Article = class
;
console.log(new Article());
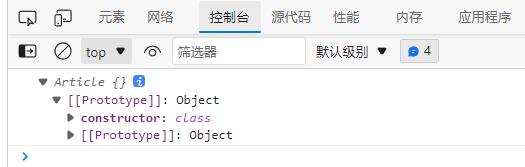
类方法间不需要逗号
class User
show()
get()
console.log("get method");
const hd = new User();
hd.get(); // get method
构造函数
使用 constructor 构造函数传递参数,下例中 show 为构造函数方法,getName为原型方法。
constructor 会在 new 时自动执行
class User
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
this.show = function() ;
getName()
return this.name;
const xj = new User("wgchen");
console.log(xj); // User name: 'wgchen', show: ƒ
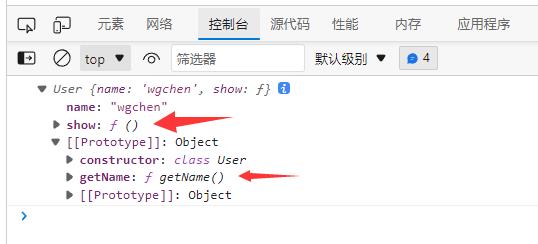
构造函数用于传递对象的初始参数,但不是必须定义的,如果不设置系统会设置如下类型
- 子构造器中调用完 super 后才可以使用 this
- 至于 super 的概念会在后面讲到
constructor(...args)
super(...args);
原理分析
类其实是函数
class User
console.log(typeof User); //function
constructor 用于定义函数代码,下面是与普通函数的对比,结构是一致的

class User
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
show()
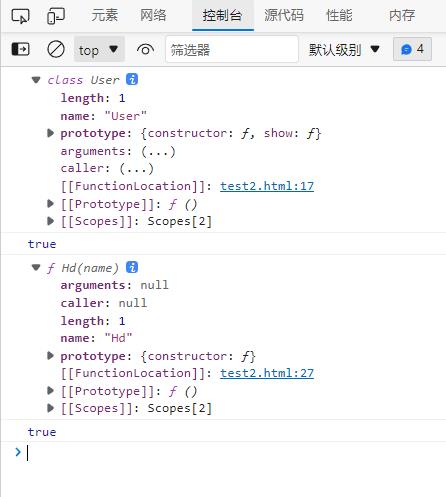
console.dir(User);
console.log(User == User.prototype.constructor); //true
//下面是对比的普通函数
function Hd(name)
this.name = name;
console.dir(Hd);
console.log(Hd == Hd.prototype.constructor); //true
在类中定义的方法也保存在函数原型中
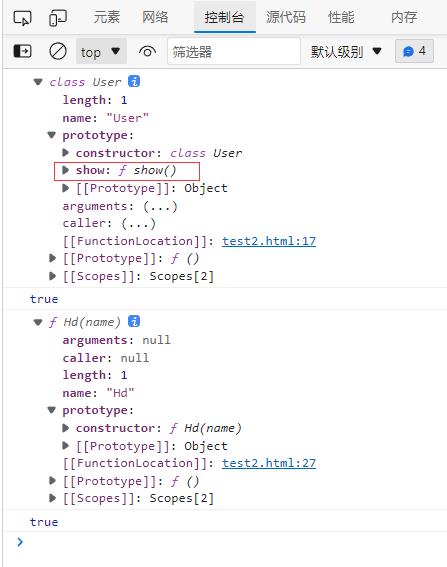
class User
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
show()
console.dir(User);
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyNames(User.prototype));
//["constructor", "show"]

所以下面定义的类
class User
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
show()
console.log(this.name);
与下面使用函数的定义是一致的
function User(name)
this.name = name;
Hd.prototype.show = function()
console.log(this.name);
;
属性定义
在 class 中定义的属性为每个 new 出的对象独立创建,下面定义了 site 与 name 两个对象属性。
class User
site = "wgchen";
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
show()
console.log(this.site + ":" + this.name); // wgchen:willem
let hd = new User("willem");
hd.show();
函数差异
class 是使用函数声明类的语法糖,但也有些区别
class 中定义的方法不能枚举
class User
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
show()
console.log(this.name);
let xj = new User("wgchen");
//不会枚举出show属性
for (const key in xj)
console.log(key);
function Hd(name)
this.name = name;
Hd.prototype.show = function()
console.log(this.name);
;
let obj = new Hd("willem");
for (const key in obj)
console.log(key);

严格模式
class 默认使用 strict 严格模式执行
class User
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
show()
function test()
//严格模式下输出 undefined
console.log(this);
test();
let xj = new User("wgchen");
xj.show();
function Hd(name)
this.name = name;
Hd.prototype.show = function()
function test()
//非严格模式输出 Window
console.log(this);
test();
;
let obj = new Hd("willem");
obj.show();

静态访问
静态属性
静态属性即为类设置属性,而不是为生成的对象设置,下面是原理实现
function User()
User.site = "wgchen";
console.dir(User);
const hd = new User();
console.log(hd.site); //undefiend
console.log(User.site); //wgchen

在 class 中为属性添加 static 关键字即声明为静态属性
可以把为所有对象使用的值定义为静态属性
class Request
static HOST = "https://wgchen.blog.csdn.net";
query(api)
return Request.HOST + "/" + api;
let request = new Request();
静态方法
指通过类访问不能使用对象访问的方法,比如系统的 Math.round() 就是静态方法。
一般来讲方法不需要对象属性参与计算就可以定义为静态方法
下面是静态方法实现原理
function User()
this.show = function()
return "this is a object function";
;
User.show = function()
return "welcome to wgchen blog";
;
const xj = new User();
console.dir(xj.show()); //this is a object function
console.dir(User.show()); //welcome to wgchen blog
在 class 内声明的方法前使用 static 定义的方法即是静态方法
class User
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
static create(name)
return new User(name);
const xj = User.create("wgchen");
console.log(xj); // User name: 'wgchen'
下面使用静态方法在课程类中的使用
const data = [
name: "js", price: 100 ,
name: "mysql", price: 212 ,
name: "vue.js", price: 98
];
class Lesson
constructor(data)
this.model = data;
get fprice()
return this.model.price;
get fname()
return this.model.name;
//批量生成对象
static createBatch(data)
return data.map(item => new Lesson(item));
//最贵的课程
static MaxPrice(collection)
return collection.sort((a, b) => b.fprice - a.fprice)[0];
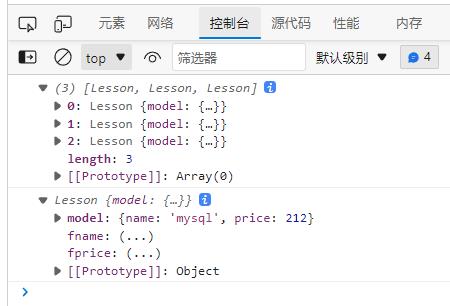
const lessons = Lesson.createBatch(data);
console.log(lessons);
console.log(Lesson.MaxPrice(lessons));
访问器
使用访问器可以对对象的属性进行访问控制,下面是使用访问器对私有属性进行管理。
语法介绍
- 使用访问器可以管控属性,有效的防止属性随意修改
- 访问器就是在函数前加上 get/set 修饰,操作属性时不需要加函数的扩号,直接用函数名
class User
constructor(name)
this.data = name ;
get name()
return this.data.name;
set name(value)
if (value.trim() == "") throw new Error("invalid params");
this.data.name = value;
let hd = new User("willem");
hd.name = "wgchen";
console.log(hd.name); // wgchen
访问控制
设置对象的私有属性有多种方式,包括后面章节介绍的模块封装。
public
public 指不受保护的属性,在类的内部与外部都可以访问到
class User
url = "blog";
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
let hd = new User("wgchen");
console.log(hd.name, hd.url); // wgchen blog
protected
protected 是受保护的属性修释,不允许外部直接操作,但可以继承后在类内部访问,有以下几种方式定义。
命名保护
将属性定义为以 _ 开始,来告诉使用者这是一个私有属性,请不要在外部使用。
- 外部修改私有属性时可以使用访问器 set 操作
- 但这只是提示,就像吸烟时烟盒上的吸烟有害健康,但还是可以抽的
class Article
_host = "https://wgchen.blog.csdn.net";
set host(url)
if (!/^https:\\/\\//i.test(url))
throw new Error("网址错误");
this._host = url;
lists()
return `$this._host/article`;
let article = new Article();
console.log(article.lists()); // https://wgchen.blog.csdn.net/article
article.host = "https://localhost";
console.log(article.lists()); // https://localhost/article
属性保护
保护属性并使用访问器控制
const protecteds = Symbol("protected");
class User
constructor(name)
this[protecteds] = name ;
get name()
return this[protecteds].name;
set name(value)
if (value.trim() == "") throw new Error("invalid params");
this[protecteds].name = value;
let hd = new User("wgchen");
hd.name = "willem";
console.log(hd.name);
console.log(Object.keys(hd));
</script>

详解继承
属性继承
属性继承的原型如下
function User(name)
this.name = name;
function Admin(name)
User.call(this, name);
let hd = new Admin("willem");
console.log(hd);

这就解释了为什么在子类构造函数中要先执行 super
class User
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
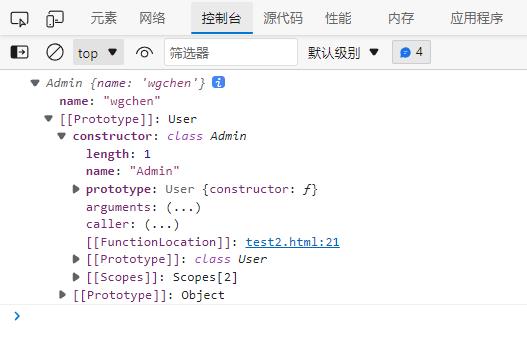
class Admin extends User
constructor(name)
super(name);
let hd = new Admin("wgchen");
console.log(hd);
继承原理
class 继承内部使用原型继承

class User
show()
console.log("user.show");
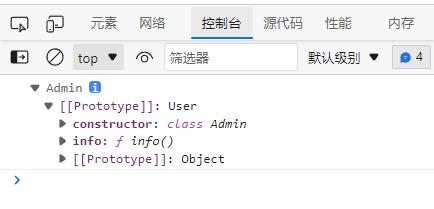
class Admin extends User
info()
this.show();
let hd = new Admin();
console.dir(hd);
方法继承
原生的继承主要是操作原型链,实现起来比较麻烦,使用 class 就要简单的多了。
- 继承时必须在子类构造函数中调用 super() 执行父类构造函数
- super.show() 执行父类方法
下面是子类继承了父类的方法 show
class Person
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
show()
return `wgchen会员: $this.name`;
以上是关于JS基础 类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章