bam / sam格式说明
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了bam / sam格式说明相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A在SAM输出的结果中每一行都包括十二项通过 Tab分隔(\\t) ,缺失值使用’*\'或者’0’代替,从左到右分别是:
1 QNAME , 序列的名字 (Read的名字)
2 FLAG , 概括出一个合适的标记,各个数字分别代表:
如果flag值是0,那么说明测序为单端测序且这条read是primary line,一般是该read的最佳比对。这里说一下secondary alignment和supplementary alignment的区别,secondary alignment代表的是该条read比对到多个位置,该条记录为次优比对,在双端测序中,代表hardclip,而supplementary alignment标记为该条比对记录为该read的补充比对记录,关于补充比对记录其实就是嵌合比对,这个常见于三代测序结果中,因为三代测序的reads很长,在比对的时候,遇到大片段的缺失,基因融合或者转座(translocation)时,结果的bam文件中就会出现多条记录,这些记录是相互的补充,有可能只是这条read的一部分,我在二代测序的结果中很容易找到很多的hardclip记录,但是却没有找到supplementary alignment的记录,在三代的比对结果中就比较多了,以下是命令和一个截图:
假如说标记为以上列举出的数目,就可以直接推断出匹配的情况。假如说标记不是以上列举出的数字,比如说83=(64+16+2+1),就是这几种情况值和。
注意看cigar值那一列,就是红框的那一列,都是带有Hardclip的
在三代测序的比对结果中常见2048的supplementary alignment。使用samtools view -f/-F参数可以获取包含/不包含指定flag的内容的条目。
flag的64和128为在(Paired-end sequencing)双端测序中的read1和read2,而flag为16和32则代表双端测序中一条read反向互补,即代表比对到了负链上。
3 RNAME ,参考序列的名字(染色体,contig)
4 POS ,在参考序列上的位置(染色体/contig上的位置)
5 MAPQ , mapping qulity 越高则位点越独特
比对有时并不能完全确定一个短的序列来自参考序列的哪个位置,特别是对那些比较简单的序列。但是会给出一个值来显示这段序列来自某个位点的概率值,这个值就是mapping qulity。Mapping qulity的计算方法是:Q=-10log10p,Q是一个非负值,p是这个序列不来自这个位点的估计值。
假如说一条序列在某个参考序列上找到了两个位点,但是其中一个位点的Q明显大于另一个位点的Q值,这条序列来源于前一个位点的可能性就比较大。Q值的差距越大,这独特性越高。
6 CIGAR ,代表比对结果的CIGAR字符串,如37M1D2M1I,这段字符的意思是37个匹配,1个参考序列上的删除,2个匹配,1个参考序列上的插入。M代表的是alignment match(可以是错配)
Cigar值中的=为完全匹配,X为不完全匹配,M为最优比对,从biostar上看到的一种解释方法如下:
7 RNEXT , mate 序列所在参考序列的名称; 下一个片段比对上的参考序列的编号,没有另外的片段,这里是’*‘,同一个片段,用’=‘;
8 PNEXT , mate 序列在参考序列上的位置;下一个片段比对上的位置,如果不可用,此处为0;
9 TLEN ,估计出的片段的长度,当mate 序列位于本序列上游时该值为负值。Template的长度,最左边得为正,最右边的为负,中间的不用定义正负,不分区段(single-segment)的比对上,或者不可用时,此处为0。另一个解释为:TLEN模板长度,如果reads对在同一条参考序列上,则模板长度为第4列减去第8列加上cigar值中的Match碱基数目。
10 SEQ ,read的序列;序列片段的序列信息,如果不存储此类信息,此处为’*‘,注意CIGAR中M/I/S/=/X对应数字的和要等于序列长度;
11 QUAL ,ASCII码格式的序列质量,格式同FASTQ一样。这个指的是碱基质量值,它的算法如下:
这里p指得是碱基判断错误的概率,英文:base-calling error probabilities ,这里在加33之前的值叫Pred quality score
之所以要加33是为了对应ascii码中的可见字符,如果一个碱基的质量为0,那么对应的就是ascii码中的33,也就是!
12 可选的字段(field)
示例:
Template: A DNA/RNA sequence part of which is sequenced on a sequencing machine or assembled from
raw sequences.
Segment: A contiguous sequence or subsequence.
Read: A raw sequence that comes off a sequencing machine. A read may consist of multiple segments. For
sequencing data, reads are indexed by the order in which they are sequenced
Linear alignment: An alignment of a read to a single reference sequence that may include insertions,
deletions, skips and clipping, but may not include direction changes (i.e., one portion of the alignment
on forward strand and another portion of alignment on reverse strand). A linear alignment can be
represented in a single SAM record.
Chimeric alignment: An alignment of a read that cannot be represented as a linear alignment. A chimeric
alignment is represented as a set of linear alignments that do not have large overlaps. Typically, one
of the linear alignments in a chimeric alignment is considered the “representative” alignment, and the
others are called “supplementary” and are distinguished by the supplementary alignment flag. All the
SAM records in a chimeric alignment have the same QNAME and the same values for 0x40 and 0x80
flags (see Section 1.4). The decision regarding which linear alignment is representative is arbitrary.
Read alignment: A linear alignment or a chimeric alignment that is the complete representation of the
alignment of the read.
Multiple mapping: The correct placement of a read may be ambiguous, e.g., due to repeats. In this case,
there may be multiple read alignments for the same read. One of these alignments is considered
primary. All the other alignments have the secondary alignment flag set in the SAM records that
represent them. All the SAM records have the same QNAME and the same values for 0x40 and 0x80
flags. Typically the alignment designated primary is the best alignment, but the decision may be
arbitrary.3
线性比对和嵌合比对:实际上,一条read的比对情况有时候会很复杂,例如一个read可能比对到多个位置,因为基因组非常庞大,存在很多的repeat区域,而二代测序的read一般比较短,在200bp以内,所以这种时候,可能在bam文件就会出现多条记录该read比对情况的记录,它们拥有相同的id,其中的一个较好的比对被认为是"典型的"比对结果,而其他的都被称为“补充的”比对结果。而且就算比对到同一个位置,还有可能有方向性问题,这是也会有两条记录存在,而没有方向问题,单一的最优比对的read就被叫做线性比对,具体表现在bam文件中将只有一条关于该read的比对记录(注意是read而不是paired reads)。
Phred scale: Given a probability 0 < p ≤ 1, the phred scale of p equals −10 log10 p, rounded to the closest
integer.
这个值是在二代测序文件中常常出现的Phred 值,这个值是对p值的一个log变换,可以更加直观的反应p值,Phred值越大,代表p值越小,例如Phred值为10,那么p值则为0.1;Phred为20时,p值为0.01 。
根据samtools的说明,1base的文件主要有 SAM,VCF,GFF,Wiggle文件,而0base的文件主要是BAM,BCF,BED这样的文件。
1-based coordinate system: A coordinate system where the first base of a sequence is one. In this coordinate
system, a region is specified by a closed interval. For example, the region between the 3rd
and the 7th bases inclusive is [3, 7]. The SAM, VCF, GFF and Wiggle formats are using the 1-based
coordinate system.
0-based coordinate system: A coordinate system where the first base of a sequence is zero. In this
coordinate system, a region is specified by a half-closed-half-open interval. For example, the region
between the 3rd and the 7th bases inclusive is [2, 7). The BAM, BCFv2, BED, and PSL formats are
using the 0-based coordinate system.
找到一个bam文件并输入如下命令查看title信息
可以看到bam文件的header有如下几个部分组成
https://www.jianshu.com/p/c48c36affff7
https://samtools.github.io/hts-specs/SAMv1.pdf
https://genome.sph.umich.edu/wiki/SAM
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SAM_(file_format)
https://www.biostars.org/p/60765/
https://www.cnblogs.com/emanlee/p/4316581.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35696312/article/details/101760397
sam/bam格式
2.1)首先看一个比对事件:

ref是参考序列,Read r001/1和 r001/2组成read pair,r003是嵌合体(chimeric read) ,r004表示 split alignment事件
2.2)相应的sam格式是:
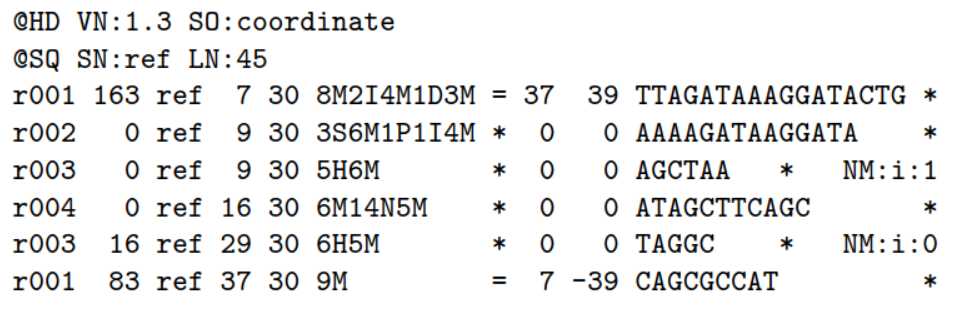
这11列内容的解释:
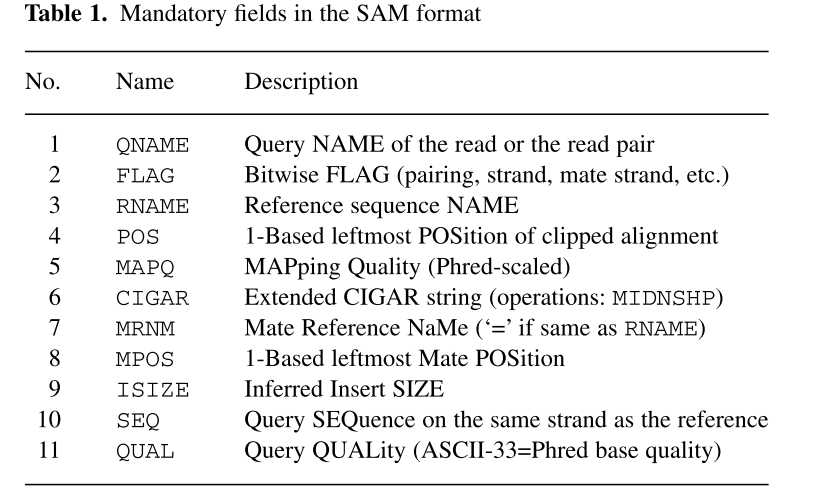
由此我们可以看到,SAM是由两部分组成:分为标头注释信息(header section)和比对结果(alignment section)。标头信息可有可无,都是以@开头,用不同的tag表示不同的信息,主要有:
-
@HD,说明符合标准的版本、对比序列的排列顺序(这里为coordinate)
-
@SQ,参考序列说明 (SN:ref,LN 是参考序列的长度)
-
@PG,使用的比对程序说明(这里没有给出)
-
比对结果部分(alignment section)每一行表示一个片段(segment)的比对信息,包括11个必须的字段(mandatory fields)和一个可选的字段,字段之间用tag分割。必须的字段有11个,顺序固定,根据字段定义,可以为’0‘或者’*‘,这11个字段是:
1)QNAME:比对片段的(template)的编号;
2)FLAG:位标识,template mapping情况的数字表示,每一个数字代表一种比对情况,这里的值是符合情况的数字相加总和;进一步学习可查看https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/explain-flags.html
3)RNAME:参考序列的编号,如果注释中对SQ-SN进行了定义,这里必须和其保持一致,另外对于没有mapping上的序列;
4)POS:比对上的位置,注意是从1开始计数,没有比对上,此处为0;
5)MAPQ:mappint的质量;
6)CIGAR:简要比对信息表达式(Compact Idiosyncratic Gapped Alignment Report),其以参考序列为基础,使用数字加字母表示比对结果,比如3S6M1P1I4M,前三个碱基被剪切去除了,然后6个比对上了,然后打开了一个缺口,有一个碱基插入,最后是4个比对上了,是按照顺序的;
7)RNEXT:下一个片段比对上的参考序列的编号,没有另外的片段,这里是’*‘,同一个片段,用’=‘;
8)PNEXT:下一个片段比对上的位置,如果不可用,此处为0;
9)TLEN:Template的长度,最左边得为正,最右边的为负,中间的不用定义正负,不分区段(single-segment)的比对上,或者不可用时,此处为0;
10)SEQ:序列片段的序列信息,如果不存储此类信息,此处为’*‘,注意CIGAR中M/I/S/=/X对应数字的和要等于序列长度;
11) QUAL:序列的质量信息,格式同FASTQ一样
1 read是pair中的一条(read表示本条read,mate表示pair中的另一条read)
2 pair一正一负完美的比对上
4 这条read没有比对上
8 mate没有比对上
16 这条read反向比对
32 mate反向比对
64 这条read是read1
128 这条read是read2
256 第二次比对
512 比对质量不合格
1024 read是PCR或光学副本产生
2048 辅助比对结果
M: match/mismatch
I :插入 insertion(和参考基因组相比)
D: 删除 deletion(和参考基因组相比)
N: 跳跃 skipped(和参考基因组相比)
S: 软剪切 soft clipping ,(表示unaligned)
H: 硬剪切 hard clipping (被剪切的序列不存在于序列中)
P: 填充 padding(表示参考基因组没有,而reads里面含有位点)
bam文件是Sam 文件的二进制压缩格式,保留了与sam 完成相同的内容信息。SAM/BAM 文件可以是未排序的,但是按照坐标(coodinate)排序可以线性的监控数据处理过程。samtools可以用来转化bam/sam文件,可以merg,sort aligment,可以去除duplicate,可以call snp及indels.
以上是关于bam / sam格式说明的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章