视觉基础篇15 # 如何用极坐标系绘制有趣图案?
Posted 凯小默
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了视觉基础篇15 # 如何用极坐标系绘制有趣图案?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
说明
【跟月影学可视化】学习笔记。
极坐标示意图
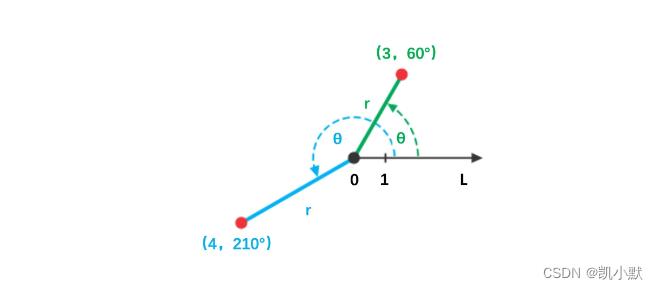
极坐标系使用相对极点的距离,以及与 x 轴正向的夹角来表示点的坐标,如(3,60°)。
直角坐标和极坐标相互转换
// 直角坐标影射为极坐标
function toPolar(x, y)
const r = Math.hypot(x, y);
const θ= Math.atan2(y, x);
return [r, θ];
// 极坐标映射为直角坐标
function fromPolar(r, θ)
const x = r * cos(θ);
const y = r * sin(θ);
return [x, y];
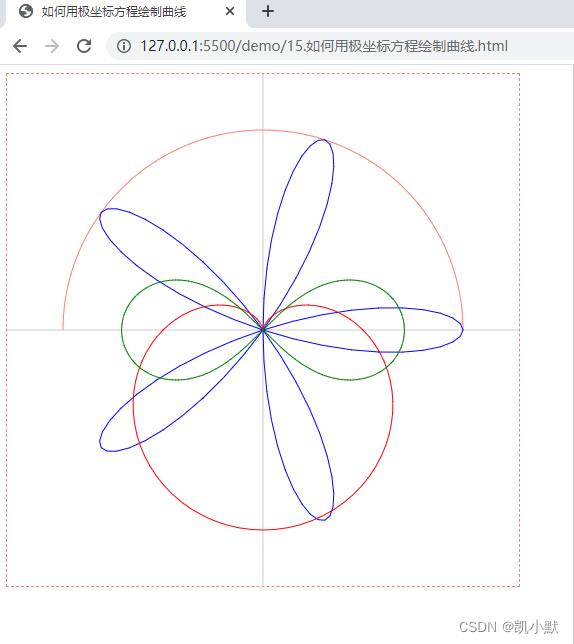
如何用极坐标方程绘制曲线
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>如何用极坐标方程绘制曲线</title>
<style>
canvas
border: 1px dashed salmon;
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script type="module">
import parametric from "./common/lib/parametric.js";
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
const width, height = canvas;
const w = 0.5 * width,
h = 0.5 * height;
ctx.translate(w, h);
ctx.scale(1, -1);
function drawAxis()
ctx.save();
ctx.strokeStyle = "#ccc";
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(-w, 0);
ctx.lineTo(w, 0);
ctx.stroke();
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(0, -h);
ctx.lineTo(0, h);
ctx.stroke();
ctx.restore();
drawAxis();
// fromPolar 作为 parametric 的参数是坐标映射函数,通过它可以将任意坐标映射为直角坐标
const fromPolar = (r, theta) =>
return [r * Math.cos(theta), r * Math.sin(theta)];
;
// 画一个半径为 200 的半圆
const arc = parametric(
(t) => 200,
(t) => t,
fromPolar
);
arc(0, Math.PI).draw(ctx);
// 玫瑰线
const rose = parametric(
(t, a, k) => a * Math.cos(k * t),
(t) => t,
fromPolar
);
rose(0, Math.PI, 100, 200, 5).draw(ctx, strokeStyle: "blue" );
// 心形线
const heart = parametric(
(t, a) => a - a * Math.sin(t),
(t) => t,
fromPolar
);
heart(0, 2 * Math.PI, 100, 100).draw(ctx, strokeStyle: "red" );
// 双纽线
const foliumRight = parametric(
(t, a) => Math.sqrt(2 * a ** 2 * Math.cos(2 * t)),
(t) => t,
fromPolar
);
const foliumLeft = parametric(
(t, a) => -Math.sqrt(2 * a ** 2 * Math.cos(2 * t)),
(t) => t,
fromPolar
);
foliumRight(-Math.PI / 4, Math.PI / 4, 100, 100).draw(ctx,
strokeStyle: "green",
);
foliumLeft(-Math.PI / 4, Math.PI / 4, 100, 100).draw(ctx,
strokeStyle: "green",
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
如何使用片元着色器与极坐标系绘制图案?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>如何使用片元着色器与极坐标系绘制图案</title>
<style>
canvas
border: 1px dashed salmon;
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main()
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
`;
// // 三瓣玫瑰线
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// vec2 polar(vec2 st)
// return vec2(length(st), atan(st.y, st.x));
//
// void main()
// vec2 st = vUv - vec2(0.5);
// st = polar(st);
// float d = 0.5 * cos(st.y * 3.0) - st.x;
// gl_FragColor.rgb = smoothstep(-0.01, 0.01, d) * vec3(1.0);
// gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
//
// `;
// // 不同瓣数的玫瑰线图案
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// uniform float u_k;
// vec2 polar(vec2 st)
// return vec2(length(st), atan(st.y, st.x));
//
// void main()
// vec2 st = vUv - vec2(0.5);
// st = polar(st);
// float d = 0.5 * cos(st.y * u_k) - st.x;
// gl_FragColor.rgb = smoothstep(-0.01, 0.01, d) * vec3(1.0);
// gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
//
// `;
// 花瓣线
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
uniform float u_k;
vec2 polar(vec2 st)
return vec2(length(st), atan(st.y, st.x));
void main()
vec2 st = vUv - vec2(0.5);
st = polar(st);
float d = 0.5 * abs(cos(st.y * u_k * 0.5)) - st.x;
gl_FragColor.rgb = smoothstep(-0.01, 0.01, d) * vec3(1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
`;
// // 葫芦图案
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// uniform float u_k;
// uniform float u_scale;
// uniform float u_offset;
// vec2 polar(vec2 st)
// return vec2(length(st), atan(st.y, st.x));
//
// void main()
// vec2 st = vUv - vec2(0.5);
// st = polar(st);
// float d = u_scale * 0.5 * abs(cos(st.y * u_k * 0.5)) - st.x + u_offset;
// gl_FragColor.rgb = smoothstep(-0.01, 0.01, d) * vec3(1.0);
// gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
//
// `;
// 花苞图案
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// uniform float u_k;
// uniform float u_scale;
// uniform float u_offset;
// vec2 polar(vec2 st)
// return vec2(length(st), atan(st.y, st.x));
//
// void main()
// vec2 st = vUv - vec2(0.5);
// st = polar(st);
// float d = smoothstep(-0.3, 1.0, u_scale * 0.5 * cos(st.y * u_k) + u_offset) - st.x;
// gl_FragColor.rgb = smoothstep(-0.01, 0.01, d) * vec3(1.0);
// gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
//
// `;
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
// // 不同瓣数的玫瑰线图案
// renderer.uniforms.u_k = 2;
// setInterval(() =>
// renderer.uniforms.u_k += 2;
// , 200);
// 花瓣线
// renderer.uniforms.u_k = 3;
renderer.uniforms.u_k = 1.3; // 1.3 的情况下是苹果
// // 葫芦图案
// renderer.uniforms.u_k = 1.7;
// renderer.uniforms.u_scale = 0.5; // default 1.0
// renderer.uniforms.u_offset = 0.2; // default 0.0
// // 花苞图案
// renderer.uniforms.u_k = 5;
// renderer.uniforms.u_scale = 0.2; // default 1.0
// renderer.uniforms.u_offset = 0.2; // default 0.0
renderer.setMeshData([
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes:
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
,
cells: [
[0, 1, 2],
[2, 0, 3],
],
,
]);
renderer.render();
</script>
</body>
</html>

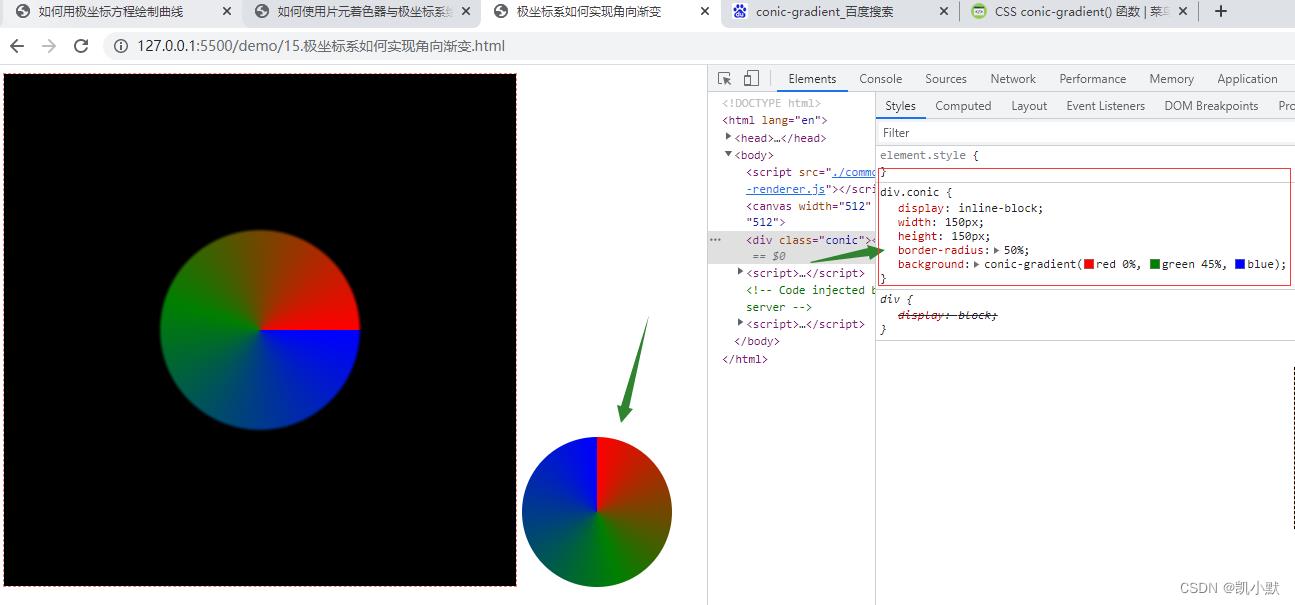
极坐标系如何实现角向渐变?
角向渐变(Conic Gradients)就是以图形中心为轴,顺时针地实现渐变效果。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>极坐标系如何实现角向渐变</title>
<style>
canvas
border: 1px dashed salmon;
div.conic
display: inline-block;
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: conic-gradient(red 0%, green 45%, blue);
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<div class="conic"></div>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main()
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
`;
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
vec2 polar(vec2 st)
return vec2(length(st), atan(st.y, st.x));
void main()
vec2 st = vUv - vec2(0.5);
st = polar(st);
float d = smoothstep(st.x, st.x + 0.01, 0.2);
// 将角度范围转换到0到2pi之间
if(st.y < 0.0) st.y += 6.28;
// 计算p的值,也就是相对角度,p取值0到1
float p = st.y / 6.28;
if(p < 0.45)
// p取0到0.45时从红色线性过渡到绿色
gl_FragColor.rgb = d * mix(vec3(1.0, 0, 0), vec3(0, 0.5, 0), p / 0.45);
else
// p超过0.45从绿色过渡到蓝色
gl_FragColor.rgb = d * mix(vec3(0, 0.5, 0), vec3(0, 0, 1.0), (p - 0.45) / (1.0 - 0.45));
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
renderer.setMeshData([
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes:
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
,
cells: [
[0, 1, 2],
[2, 0, 3],
],
,
]);
renderer.render();
</script>
</body>
</html>
极坐标如何绘制 HSV 色轮?
只需要将像素坐标转换为极坐标,再除以 2π,就能得到 HSV 的 H 值。然后用鼠标位置的 x、y 坐标来决定 S 和 V 的值。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv视觉基础篇11 # 图案生成:如何生成重复图案分形图案以及随机效果?
图形基础篇02 # 指令式绘图系统:如何用Canvas绘制层次关系图?