Trie树解析
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Trie树解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
理论解释
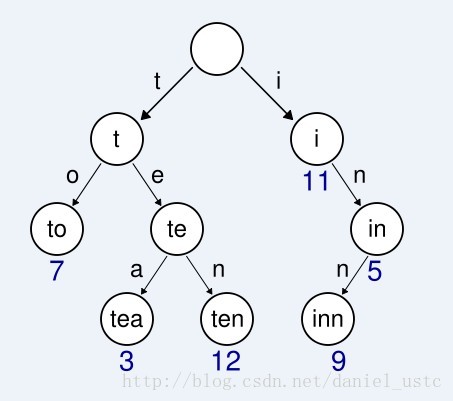
Trie树,当然是一种树形结构,树的节点(除了根节点)上都保存了一个字符,叶子节点会多一个标志,标志当前节点为叶子节点,我下面实现的方案是给结构体加了count属性,如果为叶子节点,count属性大于0。
用处
Trie树每个节点上保存了一个字符,常用来保存字符串,排序字符串,搜索字符串,下面代码实现就是搜索一个字符串在另外一个字符串的位置,如果没找到,则为-1,如果找到了,则返回了主字符串的位置。当然让我去研究Trie树的动力是aho-corasick算法。此算法后面也会出个博客,此算法的场景后续会提到,读那算法之前一定要先将这篇文章都弄明白。
代码实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_CHILD 26
typedef struct tree
{
int count;
struct tree *child[MAX_CHILD];
} Tree_node, *Trie_node;
Trie_node createNode()
{
Trie_node n;
n = (Trie_node) malloc(sizeof(Tree_node));
memset(n, 0, sizeof(Tree_node));
return n;
}
int insertNode(Trie_node root, char *str)
{
Trie_node temp, new_node;
temp = root;
char *p = str;
int child_index;
while(*p != '\0')
{
child_index = *p - 'a';
if(temp->child[child_index] != NULL)
{
temp = temp->child[child_index];
}
else
{
new_node = createNode();
temp->child[child_index] = new_node;
temp = temp->child[child_index];
}
p++;
}
temp->count++;
return 1;
}
int strpos(Trie_node root, char *handle_str)
{
char *p = handle_str;
Trie_node temp;
temp = root;
int pos = -1;
int key = 0;
int child_index;
int start_key = 0;
while(p[key] != '\0')
{
child_index = p[key] - 'a';
if(temp->child[child_index] != NULL)
{
if(start_key == 0)
{
start_key = key;
}
temp = temp->child[child_index];
}
else if(start_key > 0)
{
start_key = 0;
temp = root;
}
key++;
if(temp->count > 0)
{
pos = start_key;
break;
}
}
return pos;
}
void destroyTrie(Trie_node root)
{
Trie_node temp;
temp = root;
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_CHILD; i++)
{
if(temp->child[i])
{
destroyTrie(temp->child[i]);
}
}
free(root);
}
int main()
{
Trie_node root;
root = createNode();
char *posstr = "esd";
insertNode(root, posstr);
char *handle_str = "afeweasddesd";
int tpos = strpos(root, handle_str);
printf("find string pos is %d\n", tpos);
destroyTrie(root);
return 0;
}我用最原始的方法来实现strpos方法:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int strpos(char *handle, char *pos)
{
int m, n;
int r = -1;
for(int i = 0; handle[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
m = i;
n = 1;
for(int j = 0; pos[j] != '\0'; j++)
{
if(handle[m] != pos[j])
{
n = 0;
break;
}
m++;
}
if(n == 1)
{
r = i;
break;
}
}
return r;
}
int main()
{
char s[10] = "afk asdef";
char pos[5] = "afk";
int r = strpos(s, pos);
printf("%d\n", r);
return 0;
}相比Trie树实现strpos方法,原始方法代码很简单,就2个循环,但时间复杂度明显是n的平方。性能明显不如Trie树。
以上是关于Trie树解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章