hdu 2256 Problem of Precision
Posted starry
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了hdu 2256 Problem of Precision相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Problem of Precision
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1695 Accepted Submission(s): 1047
Problem Description
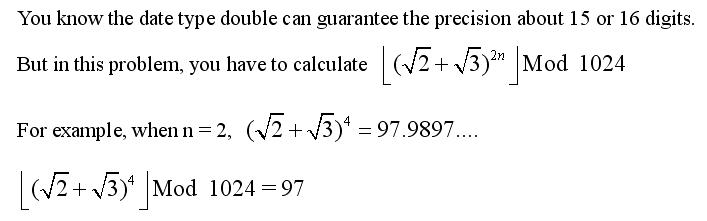
Input
The
first line of input gives the number of cases, T. T test cases follow,
each on a separate line. Each test case contains one positive integer n.
(1 <= n <= 10^9)
Output
For each input case, you should output the answer in one line.
Sample Input
3
1
2
5
Sample Output
9
97
841
(√2+√3)2n = (5+2√6)n = xn + yn√6 , 即xn + yn√6 = (xn-1 + yn-1√6)*(5+2√6) = (5xn-1+12yn-1)+(5√6yn-1+2√6xn-1)

由于有根号,浮点求模有误差
同理可得(5+2√6)n + (5-2√6)n = 2Xn
(5-2√6)n < 1
所以(5+2√6)n = 2Xn-1
(5+26‾√)n+(5−26‾√)n=2A
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h>
2 using namespace std;
3 const int mod = 1024;
4 typedef vector<int> vec;
5 typedef vector<vec> mat;
6
7 mat mul(mat &A, mat &B) {
8 mat C(A.size(), vec(B[0].size()));
9 for(int i = 0; i < A.size(); i ++) {
10 for(int j = 0; j < B[0].size(); j ++) {
11 for(int k = 0; k < B.size(); k ++) {
12 C[i][j] = (C[i][j] + A[i][k]*B[k][j]);
13 }
14 C[i][j] %= mod;
15 }
16 }
17 return C;
18 }
19
20 mat pow(mat A, int n) {
21 mat B(A.size(), vec(A[0].size()));
22 for(int i = 0; i < B.size(); i ++) B[i][i] = 1;
23 while(n) {
24 if(n&1) B = mul(A, B);
25 A = mul(A, A);
26 n >>= 1;
27 }
28 return B;
29 }
30
31 int main() {
32 int t, n;
33 cin >> t;
34 while(t--) {
35 cin >> n;
36 mat A(2, vec(2));
37 A[0][0] = 5; A[0][1] = 12;
38 A[1][0] = 2; A[1][1] = 5;
39 A = pow(A, n-1);
40 // cout << A[0][0]*5+A[0][1]*2 << ‘ ‘ << A[1][0]*5+A[1][1]*2 << endl;
41 int ans = (A[0][0]*5+A[0][1]*2)*2-1;
42 cout << ans%mod << endl;
43 }
44 return 0;
45 }
以上是关于hdu 2256 Problem of Precision的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
HDU2256-Problem of Precision(矩阵构造+高速幂)
hdu-2256 Problem of Precision---矩阵快速幂+数学技巧
HDU 2256 Problem of Precision 数论矩阵快速幂