为树莓派3B添加LCD1602液晶屏
Posted 郑志强Aloha
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了为树莓派3B添加LCD1602液晶屏相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
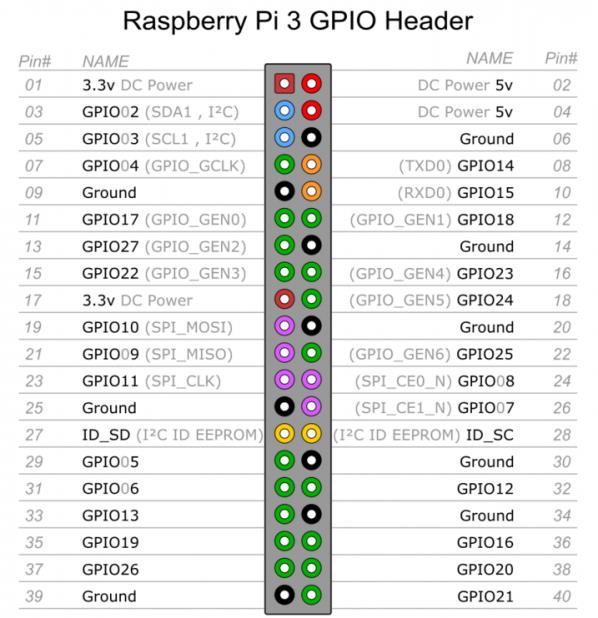
树莓派3B针脚说明
LCD1602接线说明
VSS,接地
VDD,接5V电源
VO,液晶对比度调节,接电位器中间的引脚,电位器两边的引脚分别接5V和接地。
RS,寄存器选择,接GPIO14
RW,读写选择,接地,表示写模式
EN,使能信号,接GPIO15
D0,数据位0,4位工作模式下不用,不接
D1,数据位1,4位工作模式下不用,不接
D2,数据位2,4位工作模式下不用,不接
D3,数据位3,4位工作模式下不用,不接
D4,数据位4,接GPIO17
D5,数据位5,接GPIO18
D6,数据位6,接GPIO27
D7,数据位7,接GPIO22
A,液晶屏背光+,接5V
K,液晶屏背光-,接地
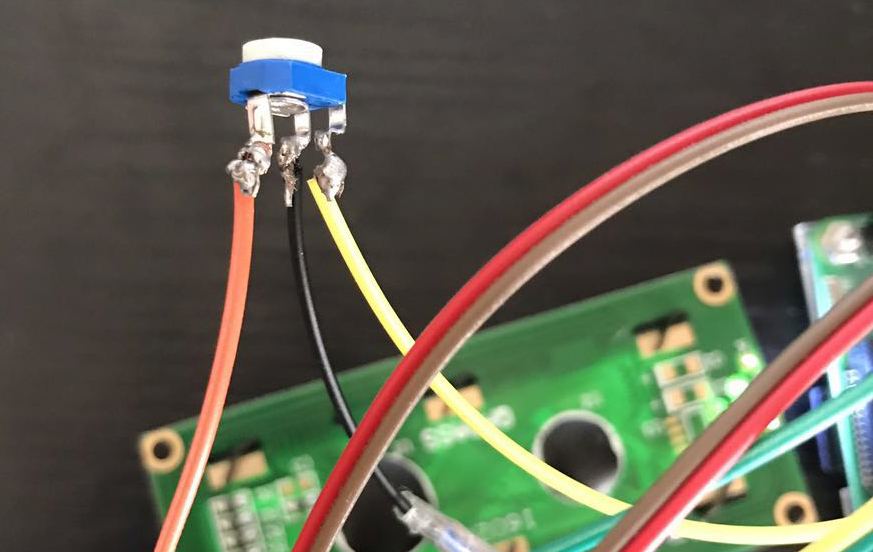
调整电位器
因为缺少1个5V的线,直接破皮拧一根进去就行,电位器调整到屏幕显示正常的对比度即可,第一次玩烙铁,焊的略丑…
lcd1602.py
#!/usr/bin/python
#
# based on code from lrvick and LiquidCrystal
# lrvic - https://github.com/lrvick/raspi-hd44780/blob/master/hd44780.py
# LiquidCrystal - https://github.com/arduino/Arduino/blob/master/libraries/LiquidCrystal/LiquidCrystal.cpp
#
from time import sleep
class lcd1602:
# commands
LCD_CLEARDISPLAY = 0x01
LCD_RETURNHOME = 0x02
LCD_ENTRYMODESET = 0x04
LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL = 0x08
LCD_CURSORSHIFT = 0x10
LCD_FUNCTIONSET = 0x20
LCD_SETCGRAMADDR = 0x40
LCD_SETDDRAMADDR = 0x80
# flags for display entry mode
LCD_ENTRYRIGHT = 0x00
LCD_ENTRYLEFT = 0x02
LCD_ENTRYSHIFTINCREMENT = 0x01
LCD_ENTRYSHIFTDECREMENT = 0x00
# flags for display on/off control
LCD_DISPLAYON = 0x04
LCD_DISPLAYOFF = 0x00
LCD_CURSORON = 0x02
LCD_CURSOROFF = 0x00
LCD_BLINKON = 0x01
LCD_BLINKOFF = 0x00
# flags for display/cursor shift
LCD_DISPLAYMOVE = 0x08
LCD_CURSORMOVE = 0x00
# flags for display/cursor shift
LCD_DISPLAYMOVE = 0x08
LCD_CURSORMOVE = 0x00
LCD_MOVERIGHT = 0x04
LCD_MOVELEFT = 0x00
# flags for function set
LCD_8BITMODE = 0x10
LCD_4BITMODE = 0x00
LCD_2LINE = 0x08
LCD_1LINE = 0x00
LCD_5x10DOTS = 0x04
LCD_5x8DOTS = 0x00
def __init__(self, pin_rs=14, pin_e=15, pins_db=[17, 18, 27, 22], GPIO = None):
# Emulate the old behavior of using RPi.GPIO if we haven\'t been given
# an explicit GPIO interface to use
if not GPIO:
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
self.GPIO = GPIO
self.pin_rs = pin_rs
self.pin_e = pin_e
self.pins_db = pins_db
self.GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
self.GPIO.setwarnings(False)
self.GPIO.setup(self.pin_e, GPIO.OUT)
self.GPIO.setup(self.pin_rs, GPIO.OUT)
for pin in self.pins_db:
self.GPIO.setup(pin, GPIO.OUT)
self.write4bits(0x33) # initialization
self.write4bits(0x32) # initialization
self.write4bits(0x28) # 2 line 5x7 matrix
self.write4bits(0x0C) # turn cursor off 0x0E to enable cursor
self.write4bits(0x06) # shift cursor right
self.displaycontrol = self.LCD_DISPLAYON | self.LCD_CURSOROFF | self.LCD_BLINKOFF
self.displayfunction = self.LCD_4BITMODE | self.LCD_1LINE | self.LCD_5x8DOTS
self.displayfunction |= self.LCD_2LINE
""" Initialize to default text direction (for romance languages) """
self.displaymode = self.LCD_ENTRYLEFT | self.LCD_ENTRYSHIFTDECREMENT
self.write4bits(self.LCD_ENTRYMODESET | self.displaymode) # set the entry mode
self.clear()
def begin(self, cols, lines):
if (lines > 1):
self.numlines = lines
self.displayfunction |= self.LCD_2LINE
self.currline = 0
def home(self):
self.write4bits(self.LCD_RETURNHOME) # set cursor position to zero
self.delayMicroseconds(3000) # this command takes a long time!
def clear(self):
self.write4bits(self.LCD_CLEARDISPLAY) # command to clear display
self.delayMicroseconds(3000) # 3000 microsecond sleep, clearing the display takes a long time
def setCursor(self, col, row):
self.row_offsets = [ 0x00, 0x40, 0x14, 0x54 ]
if ( row > self.numlines ):
row = self.numlines - 1 # we count rows starting w/0
self.write4bits(self.LCD_SETDDRAMADDR | (col + self.row_offsets[row]))
def noDisplay(self):
""" Turn the display off (quickly) """
self.displaycontrol &= ~self.LCD_DISPLAYON
self.write4bits(self.LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL | self.displaycontrol)
def display(self):
""" Turn the display on (quickly) """
self.displaycontrol |= self.LCD_DISPLAYON
self.write4bits(self.LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL | self.displaycontrol)
def noCursor(self):
""" Turns the underline cursor on/off """
self.displaycontrol &= ~self.LCD_CURSORON
self.write4bits(self.LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL | self.displaycontrol)
def cursor(self):
""" Cursor On """
self.displaycontrol |= self.LCD_CURSORON
self.write4bits(self.LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL | self.displaycontrol)
def noBlink(self):
""" Turn on and off the blinking cursor """
self.displaycontrol &= ~self.LCD_BLINKON
self.write4bits(self.LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL | self.displaycontrol)
def noBlink(self):
""" Turn on and off the blinking cursor """
self.displaycontrol &= ~self.LCD_BLINKON
self.write4bits(self.LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL | self.displaycontrol)
def DisplayLeft(self):
""" These commands scroll the display without changing the RAM """
self.write4bits(self.LCD_CURSORSHIFT | self.LCD_DISPLAYMOVE | self.LCD_MOVELEFT)
def scrollDisplayRight(self):
""" These commands scroll the display without changing the RAM """
self.write4bits(self.LCD_CURSORSHIFT | self.LCD_DISPLAYMOVE | self.LCD_MOVERIGHT);
def leftToRight(self):
""" This is for text that flows Left to Right """
self.displaymode |= self.LCD_ENTRYLEFT
self.write4bits(self.LCD_ENTRYMODESET | self.displaymode);
def rightToLeft(self):
""" This is for text that flows Right to Left """
self.displaymode &= ~self.LCD_ENTRYLEFT
self.write4bits(self.LCD_ENTRYMODESET | self.displaymode)
def autoscroll(self):
""" This will \'right justify\' text from the cursor """
self.displaymode |= self.LCD_ENTRYSHIFTINCREMENT
self.write4bits(self.LCD_ENTRYMODESET | self.displaymode)
def noAutoscroll(self):
""" This will \'left justify\' text from the cursor """
self.displaymode &= ~self.LCD_ENTRYSHIFTINCREMENT
self.write4bits(self.LCD_ENTRYMODESET | self.displaymode)
def write4bits(self, bits, char_mode=False):
""" Send command to LCD """
self.delayMicroseconds(1000) # 1000 microsecond sleep
bits=bin(bits)[2:].zfill(8)
self.GPIO.output(self.pin_rs, char_mode)
for pin in self.pins_db:
self.GPIO.output(pin, False)
for i in range(4):
if bits[i] == "1":
self.GPIO.output(self.pins_db[::-1][i], True)
self.pulseEnable()
for pin in self.pins_db:
self.GPIO.output(pin, False)
for i in range(4,8):
if bits[i] == "1":
self.GPIO.output(self.pins_db[::-1][i-4], True)
self.pulseEnable()
def delayMicroseconds(self, microseconds):
seconds = microseconds / float(1000000) # divide microseconds by 1 million for seconds
sleep(seconds)
def pulseEnable(self):
self.GPIO.output(self.pin_e, False)
self.delayMicroseconds(1) # 1 microsecond pause - enable pulse must be > 450ns
self.GPIO.output(self.pin_e, True)
self.delayMicroseconds(1) # 1 microsecond pause - enable pulse must be > 450ns
self.GPIO.output(self.pin_e, False)
self.delayMicroseconds(1) # commands need > 37us to settle
def message(self, text):
""" Send string to LCD. Newline wraps to second line"""
for char in text:
if char == \'\\n\':
self.write4bits(0xC0) # next line
else:
self.write4bits(ord(char),True)
if __name__ == \'__main__\':
lcd = lcd1602()
lcd.clear()
lcd.message("hello world!")
|
1602.py
#!/usr/bin/python
from lcd1602 import *
from datetime import *
import commands
def get_cpu_temp():
tmp = open(\'/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp\')
cpu = tmp.read()
tmp.close()
return \'{:.2f}\'.format( float(cpu)/1000 ) + \' C\'
def get_gpu_temp():
tmp = commands.getoutput(\'vcgencmd measure_temp|awk -F= \\\'{print $2}\\\'\').replace(\'\\\'C\',\'\')
gpu = float(tmp)
return \'{:.2f}\'.format( gpu ) + \' C\'
def get_time_now():
return datetime.now().strftime(\' %H:%M:%S\\n %Y-%m-%d\')
def get_ip_info():
return commands.getoutput(\'ifconfig wlan0|grep inet|awk -Faddr: \\\'{print $2}\\\'|awk \\\'{print $1}\\\'\')
def get_mem_info():
total= commands.getoutput(\'free -m|grep Mem:|awk \\\'{print $2}\\\'\')
free = commands.getoutput(\'free -m|grep cache:|awk \\\'{print $4}\\\'\')
return \'MEM:\\n \' + free +\' / \'+ total +\' M\'
lcd = lcd1602()
lcd.clear()
if __name__ == \'__main__\':
while(1):
lcd.clear()
lcd.message( get_ip_info() )
sleep(5)
lcd.clear()
lcd.message( get_time_now() )
sleep(5)
lcd.clear()
lcd.message( get_mem_info() )
sleep(5)
lcd.clear()
lcd.message( \'CPU: \' + get_cpu_temp()+\'\\n\' )
lcd.message( \'GPU: \' + get_gpu_temp() )
sleep(5)
|
将以上两个文件保存在同一个目录下,运行1602.py即可打印信息到LCD上。
效果图
参考链接
http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaowuyi/p/4051238.html
https://www.6zou.net/tech/raspberry-pi-lcd1602-system-monitor.html
以上是关于为树莓派3B添加LCD1602液晶屏的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
记树莓派的一个项目_RGB1602的实际使用(续——使用日语/添加常用汉字)
《树莓派项目实战》第五节 使用Nokia 5110液晶屏显示Hello World
《树莓派项目实战》第五节 使用Nokia 5110液晶屏显示Hello World