关于bitset
Posted zubizakeli
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了关于bitset相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我们先来看一道题:
- 给你一个长度为n的数列(n <= 1e5)
- 3 种操作
- 查询某区间内不同种类数的个数(在 %2018 意义下)
- 将某区间内所有数变为k
- 将某区间内所有数+k
SOL :
- 维护区间?线段树?
- 线段树能维护什么? 和? 最值? 或? 对!就是或!
- 我们先建一棵线段树,假设每个节点维护的信息是一个2018位的二进制数a
- 那么叶子节点的a中只有一位是1
- 非叶子节点的a就是其左右子树取或后的结果 (想想为什么?)
那怎么维护这个2018位的二进制数呢?
一个很显然的方法是开一个bool数组储存每一位是1或者0,然后比较的时候再一位一位比较。
但其实STL中就有这么一个数据结构,叫bitset。
如 bitset<2018>hh,gg ; 表示的就是定义两个2018位的二进制数。 取或的话就 : hh = hh | gg ;。 统计其中有多少位是1的话就调用 hh.count() ; 。 (当然程序内部具体怎么实现的我也不知道,我只是类比一下,方便理解)。
而且它还能当做数组来对每一位修改。如 hh[i] = 1 ;
如果要把某区间内的值全部修改为k的话,只要把完全在区间内的节点都清零,然后对其中固定一位进行修改,再向上pushup即可。
如果要把某区间内的值全部加上k的话,只要把区间内的节点的bitset向左移动k位,同时处理一下最左边的k位移到最右边即可。
给出一道只有查询操作的例题:

(对于100%的数据,N <= 50000,M <= 200000。)
首先说明这道题正解不是线段树+bitset。(因为显然会炸空间对吧,而且就算离散化之后也会炸)。但我们用 离散化 + bitset 的话还是可以拿到50分的。
(给出这道题的目的是为了练习bitset,而不是A掉这道题)。
下面给出50分代码:
// 线段树 + bitset + 离散化 ( 还是过不了,因为这题卡空间 ) #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<bitset> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> using namespace std; const int N = 10000 + 10 ; // 不开5e5是因为开大了会炸空间,导致爆零.. inline int read() { int k = 0 , f = 1 ; char c = getchar() ; for( ; !isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) if(c == \'-\') f = -1 ; for( ; isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) k = k*10 + c-\'0\' ; return k*f ; } struct Node { bitset<N> w ; Node *ls, *rs; }pool[N<<1] ; int n,m ; int a,b ; bitset<N> ans; struct node { int val,p ; }hh[N] ; int gg[N] ; Node *newNode() { static int cnt = 0 ; return &pool[++cnt] ; } inline void pushup(Node *cur) { cur->w = cur->ls->w | cur->rs->w ; } Node *build(int l,int r) { Node *cur = newNode() ; cur->w.reset() ; if(l < r) { int mid = (l+r)>>1 ; cur->ls = build(l,mid) ; cur->rs = build(mid+1,r) ; pushup(cur) ; } else cur->w[gg[l]] = 1 ; return cur ; } void query(Node *cur,int l,int r) { if(l >= a && r <= b) { ans |= cur->w ; return ; } int mid = (l+r)>>1 ; if(a <= mid) query(cur->ls,l,mid) ; if(b > mid) query(cur->rs,mid+1,r) ; } inline bool cmp(node s,node t) { return s.val < t.val ; } inline void pre_pare() { sort(hh+1,hh+n+1,cmp) ; int pp ; int now = 1 ; gg[hh[1].p] = 1 ; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) { pp = hh[i].p ; if(hh[i].val == hh[i-1].val) gg[pp] = now ; else gg[pp] = ++now ; } } int main() { n = read() ; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { hh[i].val = read() ; hh[i].p = i ; } pre_pare() ; Node *root = build(1,n) ; m = read() ; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { a = read() ; b = read() ; ans.reset() ; query(root,1,n) ; printf("%d\\n",ans.count()) ; } return 0 ; }
(PS:离散化也是很重要的技巧,建议还没学的同学顺便学一下)。
最后附上bitset完整用法介绍
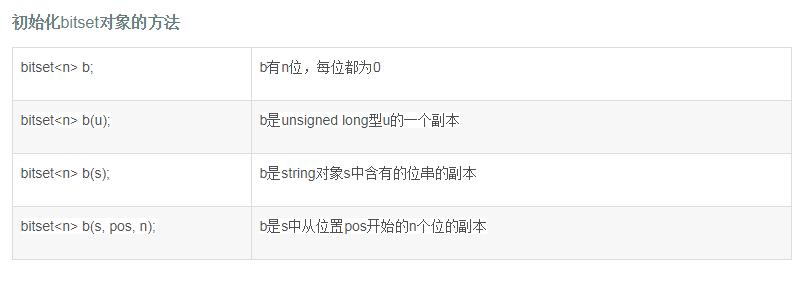

(具体用法图截自:http://blog.csdn.net/hallmeow/article/details/76162536)。
以上是关于关于bitset的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章