1.安装mininet
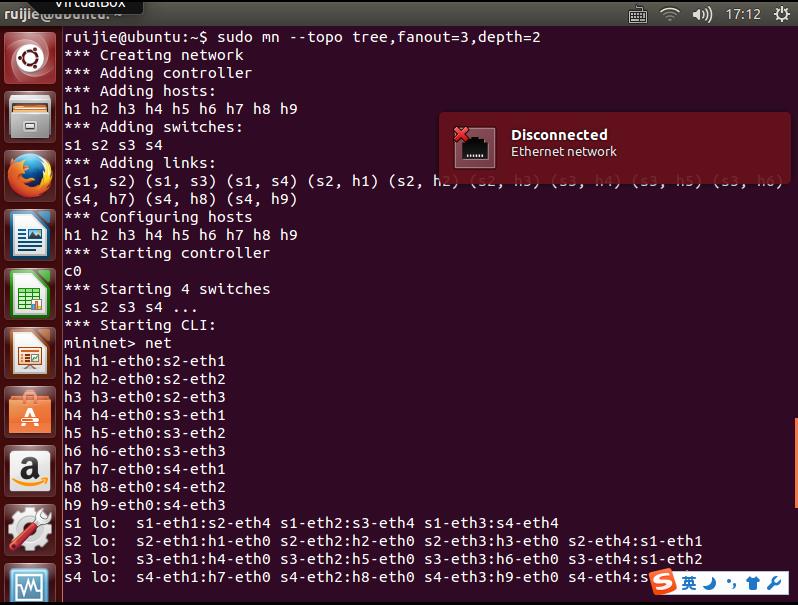
2.用字符命令生成拓扑,并测试连通性
截图:

3.用可视化界面生成拓扑,并测试连通性


4.用Python脚本生成一个Fat-tree型的拓扑


- python代码
#!/usr/bin/python
"""Custom topology example
Adding the \'topos\' dict with a key/value pair to generate our newly defined
topology enables one to pass in \'--topo=mytopo\' from the command line.
"""
from mininet.topo import Topo
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.node import RemoteController,CPULimitedHost
from mininet.link import TCLink
from mininet.util import dumpNodeConnections
class MyTopo( Topo ):
"Simple topology example."
def __init__( self ):
"Create custom topo."
# Initialize topology
Topo.__init__( self )
L1 = 2
L2 = L1 * 2
L3 = L2
c = []
a = []
e = []
# add core ovs
for i in range( L1 ):
sw = self.addSwitch( \'c{}\'.format( i + 1 ) )
c.append( sw )
# add aggregation ovs
for i in range( L2 ):
sw = self.addSwitch( \'a{}\'.format( L1 + i + 1 ) )
a.append( sw )
# add edge ovs
for i in range( L3 ):
sw = self.addSwitch( \'e{}\'.format( L1 + L2 + i + 1 ) )
e.append( sw )
# add links between core and aggregation ovs
for i in range( L1 ):
sw1 = c[i]
for sw2 in a[i/2::L1/2]:
# self.addLink(sw2, sw1, bw=10, delay=\'5ms\', loss=10, max_queue_size=1000, use_htb=True)
self.addLink( sw2, sw1 )
# add links between aggregation and edge ovs
for i in range( 0, L2, 2 ):
for sw1 in a[i:i+2]:
for sw2 in e[i:i+2]:
self.addLink( sw2, sw1 )
#add hosts and its links with edge ovs
count = 1
for sw1 in e:
for i in range(2):
host = self.addHost( \'h{}\'.format( count ) )
self.addLink( sw1, host )
count += 1
topos = { \'mytopo\': ( lambda: MyTopo() ) }