第九章 原子性
Posted 爨爨爨好
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第九章 原子性相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
▶ 本章介绍了原子操作,给出了基于原子操作的直方图计算的例子。
● 章节代码
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include "cuda_runtime.h" 3 #include "device_launch_parameters.h" 4 #include "D:\\Code\\CUDA\\book\\common\\book.h" 5 6 #define SIZE (100*1024*1024) 7 #define USE_SHARE_MEMORY true 8 9 __global__ void histo_kernel(unsigned char *buffer, long size, unsigned int *histo) 10 { 11 int i = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x; 12 13 #if USE_SHARE_MEMORY 14 __shared__ unsigned int temp[256]; 15 temp[threadIdx.x] = 0; 16 __syncthreads(); 17 18 while (i < size) 19 { 20 atomicAdd(&temp[buffer[i]], 1); 21 i += blockDim.x * gridDim.x; 22 } 23 __syncthreads(); 24 atomicAdd(&(histo[threadIdx.x]), temp[threadIdx.x]); 25 #else 26 while (i < size) 27 { 28 atomicAdd(&histo[buffer[i]], 1); 29 i += blockDim.x * gridDim.x;; 30 } 31 #endif 32 return; 33 } 34 35 int main(void) 36 { 37 int i; 38 unsigned char *buffer = (unsigned char*)big_random_block(SIZE);// 内置的生成随机字符数组的函数 39 40 cudaEvent_t start, stop; 41 cudaEventCreate(&start); 42 cudaEventCreate(&stop); 43 cudaEventRecord(start, 0); 44 45 unsigned char *dev_buffer; 46 unsigned int *dev_histo; 47 cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_buffer, SIZE); 48 cudaMemcpy(dev_buffer, buffer, SIZE, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 49 50 cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_histo, 256 * sizeof(int)); 51 cudaMemset(dev_histo, 0, 256 * sizeof(int)); 52 53 cudaDeviceProp prop; 54 cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, 0); 55 int blocks = prop.multiProcessorCount;// 书:实验表明使用MPS的两倍计算效率最高 56 histo_kernel << <blocks * 2, 256 >> >(dev_buffer, SIZE, dev_histo); 57 58 unsigned int histo[256]; 59 cudaMemcpy(histo, dev_histo, 256 * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); 60 61 cudaEventRecord(stop, 0); 62 cudaEventSynchronize(stop); 63 float elapsedTime; 64 cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsedTime, start, stop); 65 printf("Time to generate: %3.1f ms\\n", elapsedTime); 66 67 long histoCount = 0; 68 for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) 69 histoCount += histo[i]; 70 printf("Histogram Sum: %ld\\n", histoCount); 71 72 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)// 验证结果 73 histo[buffer[i]]--; 74 for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) 75 { 76 if (histo[i] != 0) 77 printf("Failure at hist[%d] == %d\\n", i,histo[i]); 78 } 79 if (i == 256) 80 printf("\\n\\tSucceeded!\\n"); 81 82 cudaFree(dev_histo); 83 cudaFree(dev_buffer); 84 free(buffer); 85 cudaEventDestroy(start); 86 cudaEventDestroy(stop); 87 88 getchar(); 89 return 0; 90 }
● 使用全局内存时,只要在每次线程尝试 +1 时使用原子加法即可;使用共享内存时算法分两步,线程先用原子加法往各线程块的共享内存中写入,同步以后,再用原子加法把各共享内存的结果往全局内存中写入。减缓了全局内存的写入冲突。
● 代码使用了两倍数量的MPS作为线程块数量,认为这样计算效率最高。在 GTX1070 上 prop.multiProcesser 为 16,程序默认使用 32 个线程块进行计算,我另用 1 到 256 个线程块依次测试,结果如下。
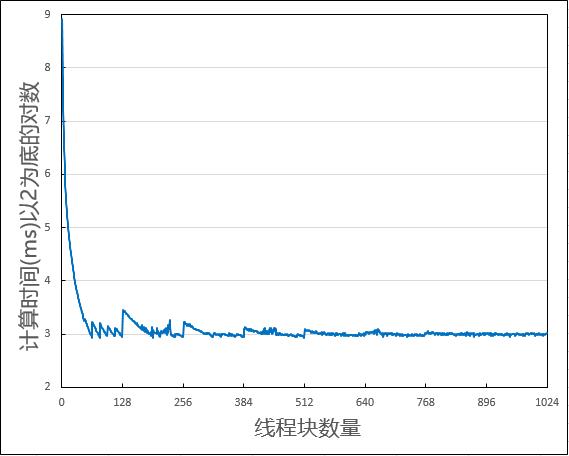
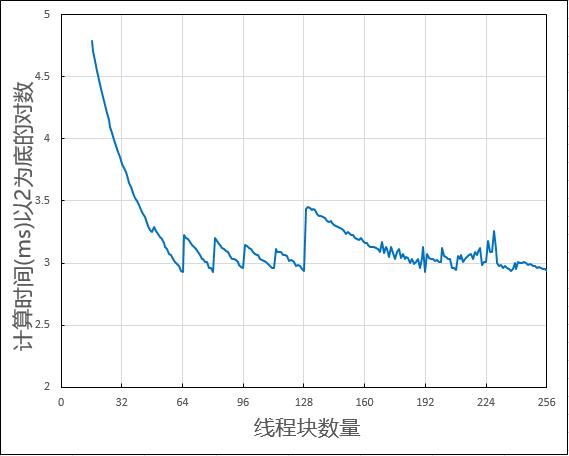
● big_random_block()定义于book.h中
1 void* big_random_block(int size) 2 { 3 unsigned char *data = (unsigned char*)malloc(size); 4 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 5 data[i] = rand(); 6 return data; 7 }
以上是关于第九章 原子性的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章