Logistic回归之基于最优化方法的最佳回归系数确定
Posted 我在看代码
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Logistic回归之基于最优化方法的最佳回归系数确定相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
之前学习Java的时候,用过一个IDE叫做EditPlus,虽然他敲代码的高亮等体验度不及eclipse,但是打开软件特别快捷,现在也用他读python特别方便。
训练算法::使用梯度上升找到最佳参数
之前看过吴恩达的视频的同学们,听得比较多的就是梯度下降算法,但是梯度上升算法和梯度下降算法本质是是一样的,只是梯度计算的时候加减号不一样罢了。
1 def loadDataSet(): 2 dataMat = []; labelMat = [] 3 fr = open(\'testSet.txt\') 4 for line in fr.readlines(): 5 lineArr = line.strip().split() 6 dataMat.append([1.0, float(lineArr[0]), float(lineArr[1])]) 7 labelMat.append(int(lineArr[2])) 8 return dataMat,labelMat 9 10 def sigmoid(inX): 11 return 1.0/(1+exp(-inX)) 12 13 def gradAscent(dataMatIn, classLabels): 14 dataMatrix = mat(dataMatIn) #convert to NumPy matrix 15 labelMat = mat(classLabels).transpose() #convert to NumPy matrix 16 m,n = shape(dataMatrix) 17 alpha = 0.001 18 maxCycles = 500 19 weights = ones((n,1)) 20 for k in range(maxCycles): #heavy on matrix operations 21 h = sigmoid(dataMatrix*weights) #matrix mult 22 error = (labelMat - h) #vector subtraction 23 weights = weights + alpha * dataMatrix.transpose()* error #matrix mult 24 return weights
第一个函数打开testSet。txt并逐行读取,每行前两个值分别是x1和x2,第三个值是对应的类别标签。为了方便计算,该函数还将x0的值设为1.0
第二个函数是sigmoid函数,x为0时,函数值为0.5,x增大时,函数值将不断增大逼近1。
第三个函数有两个参数,第一个是2维数组,每列代表不同的特征,每行代表每个训练样本。我们采用100个样本的简单数据集它包含两个特征x1,x2,再加上第0维特征x0,所以dataMatln里面存放的是100*3的矩阵。
分析数据:画出决策边界
1 def plotBestFit(weights): 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 dataMat,labelMat=loadDataSet() 4 dataArr = array(dataMat) 5 n = shape(dataArr)[0] 6 xcord1 = []; ycord1 = [] 7 xcord2 = []; ycord2 = [] 8 for i in range(n): 9 if int(labelMat[i])== 1: 10 xcord1.append(dataArr[i,1]); ycord1.append(dataArr[i,2]) 11 else: 12 xcord2.append(dataArr[i,1]); ycord2.append(dataArr[i,2]) 13 fig = plt.figure() 14 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 15 ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s=30, c=\'red\', marker=\'s\') 16 ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s=30, c=\'green\') 17 x = arange(-3.0, 3.0, 0.1) 18 y = (-weights[0]-weights[1]*x)/weights[2] 19 ax.plot(x, y) 20 plt.xlabel(\'X1\'); plt.ylabel(\'X2\'); 21 plt.show()
>>> from numpy import * >>> reload(logRegres) <module \'logRegres\' from \'D:\\Python27\\logRegres.pyc\'> >>> weights=logRegres.gradAscent(dataArr,labelMat) >>> logRegres.plotBestFit(weights.getA())
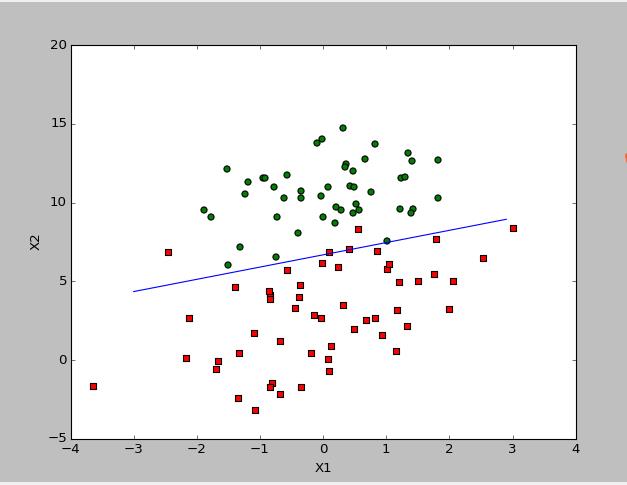
训练算法:随机梯度上升
梯度上升算法在每次更新回归系数时都需要遍历整个数据集。改进的方法是一次仅使用一个样本点来更新回归系数,该方法称为随机梯度上升算法。由于可以在样本到来时对分类器进行增量式更新,因而随机梯度上升算法是一个在线学习算法。与在线学习相对应,一次处理所有数据被称作是批处理。
1 def stocGradAscent0(dataMatrix, classLabels): 2 m,n = shape(dataMatrix) 3 alpha = 0.01 4 weights = ones(n) #initialize to all ones 5 for i in range(m): 6 h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[i]*weights)) 7 error = classLabels[i] - h 8 weights = weights + alpha * error * dataMatrix[i] 9 return weights
>>> from numpy import * >>> reload(logRegres) <module \'logRegres\' from \'D:\\Python27\\logRegres.pyc\'> >>> dataArr,labelMat=logRegres.loadDataSet() >>> weights=logRegres.stocGradAscent0(array(dataArr),labelMat) >>> logRegres.plotBestFit(weights)

改进的随机梯度上升算法
1 def stocGradAscent1(dataMatrix, classLabels, numIter=150): 2 m,n = shape(dataMatrix) 3 weights = ones(n) #initialize to all ones 4 for j in range(numIter): 5 dataIndex = range(m) 6 for i in range(m): 7 alpha = 4/(1.0+j+i)+0.0001 #apha decreases with iteration, does not 8 randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex)))#go to 0 because of the constant 9 h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[randIndex]*weights)) 10 error = classLabels[randIndex] - h 11 weights = weights + alpha * error * dataMatrix[randIndex] 12 del(dataIndex[randIndex]) 13 return weights
增加了亮出代码来进行改进。一方面,alpha在每次迭代的时候都会调整,虽然alpha会随着迭代次数不断减小,但永远不会减小到0,因为存在一个常数项。
另一方面,通过随机选取样本来更新回归系数。
>>> dataArr,labelMat=logRegres.loadDataSet() >>> weights=logRegres.stocGradAscent1(array(dataArr),labelMat) >>> logRegres.plotBestFit(weights)
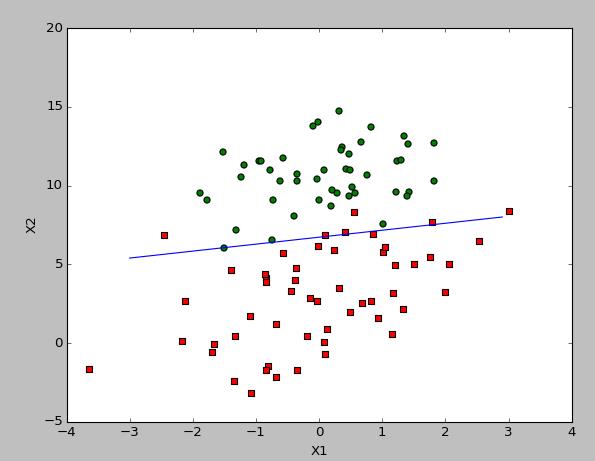
从疝气病症预测病马的死亡率
1 def classifyVector(inX, weights): 2 prob = sigmoid(sum(inX*weights)) 3 if prob > 0.5: return 1.0 4 else: return 0.0 5 6 def colicTest(): 7 frTrain = open(\'horseColicTraining.txt\'); frTest = open(\'horseColicTest.txt\') 8 trainingSet = []; trainingLabels = [] 9 for line in frTrain.readlines(): 10 currLine = line.strip().split(\'\\t\') 11 lineArr =[] 12 for i in range(21): 13 lineArr.append(float(currLine[i])) 14 trainingSet.append(lineArr) 15 trainingLabels.append(float(currLine[21])) 16 trainWeights = stocGradAscent1(array(trainingSet), trainingLabels, 1000) 17 errorCount = 0; numTestVec = 0.0 18 for line in frTest.readlines(): 19 numTestVec += 1.0 20 currLine = line.strip().split(\'\\t\') 21 lineArr =[] 22 for i in range(21): 23 lineArr.append(float(currLine[i])) 24 if int(classifyVector(array(lineArr), trainWeights))!= int(currLine[21]): 25 errorCount += 1 26 errorRate = (float(errorCount)/numTestVec) 27 print "the error rate of this test is: %f" % errorRate 28 return errorRate 29 30 def multiTest(): 31 numTests = 10; errorSum=0.0 32 for k in range(numTests): 33 errorSum += colicTest() 34 print "after %d iterations the average error rate is: %f" % (numTests, errorSum/float(numTests))
第一个函数,如果sigmoid值大于0.5函数返回1,否则返回0.
第二个函数,用于打开测试集和训练集,并对数据进行格式化处理的函数。
第三个函数,调用第二个函数10次并求结果的平均值。
.-\' _..`. / .\'_.\'.\' | .\' (.)`. ;\' ,_ `. .--.__________.\' ; `.;-\'| ./ /| | / `..\'`-._ _____, ..\' / | | | |\\ \\ / /| | | | \\ \\ / / | | | | \\ \\ /_/ |_| |_| \\_\\ |__\\ |__\\ |__\\ |__\\
以上是关于Logistic回归之基于最优化方法的最佳回归系数确定的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章