Canny边缘检测
Posted jfu22
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Canny边缘检测相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
关于Canny图像边缘检测的原理,网上有很多介绍的资料,
其中一篇介绍得比较好的文章:http://blog.csdn.net/likezhaobin/article/details/6892176
大家可以参考一下。
----------------------少废话,上代码-------------------------------------------------
/*
* CannyEdgeDetection.h
*
* 过客 && 386520874@qq.com && 2016.03.26
*
*/
#ifndef __CANNY_EDGE_DETECTION_H__
#define __CANNY_EDGE_DETECTION_H__
#include <windows.h>
#include <vector>
//----canny边缘检测-----------
class CCannyEdgeDetection
{
public:
CCannyEdgeDetection();
~CCannyEdgeDetection();
public:
int m_guid_index; //保存的图片格式,0-ImageFormatBMP,1-ImageFormatJPEG,2-ImageFormatPNG,3-ImageFormatGIF
BITMAP m_bitmap;
HBITMAP m_hBitmap;
public:
//--------图片操作---------------
int OpenImage(wchar_t* filename, BITMAP &bitmap, HBITMAP &hBitmap); //打开图片
int SaveImage(wchar_t* filename, HBITMAP &hBitmap); //保存图片,针对位图句柄
int SaveImage(wchar_t* filename, BITMAP &bitmap); //保存图片,针对内存中位图结果
int CreateEmptyImage(BITMAP &bitmap, int width, int height, int bmBitsPixel); //在内存中创建一幅空白位图
int ReleaseHandle(); //主动释放资源
int ReleaseBitmap(BITMAP &bitmap); //主动释放资源
int Canny(BITMAP &bitmap_src, BITMAP &bitmap_dst, double low_thresh, double high_thresh); //canny边缘检测
int Sobel(BITMAP &bitmap_src, BITMAP &bitmap_dst, double low_thresh, double high_thresh); //Sobel图像一阶差分梯度
};
#endif //__CANNY_EDGE_DETECTION_H__
/*
* CannyEdgeDetection.cpp
*
* 过客 && 386520874@qq.com && 2016.03.26
*
*/
#define WINVER 0x0500
#define _WIN32_WINNT 0x0500
//#include <windows.h>
#include <afx.h>
#include <atlimage.h>
#include <afxwin.h>
#include "CannyEdgeDetection.h"
CCannyEdgeDetection::CCannyEdgeDetection()
{
m_guid_index = 2; //默认输出png
m_hBitmap = NULL;
}
CCannyEdgeDetection::~CCannyEdgeDetection()
{
if(m_hBitmap != NULL)
{
::DeleteObject(m_hBitmap);
m_hBitmap = NULL;
}
}
//--------图片操作---------------
int CCannyEdgeDetection::ReleaseHandle()
{
if(m_hBitmap != NULL)
{
::DeleteObject(m_hBitmap);
m_hBitmap = NULL;
}
return 1;
}
int CCannyEdgeDetection::ReleaseBitmap(BITMAP &bitmap)
{
unsigned char* pBits = static_cast<unsigned char*>(bitmap.bmBits);
if(pBits != NULL)
{
delete [] pBits; //释放用new申请的资源
pBits = NULL;
memset(&bitmap, 0, sizeof(BITMAP));
}
return 1;
}
int CCannyEdgeDetection::OpenImage(wchar_t* filename, BITMAP &bitmap, HBITMAP &hBitmap)
{
CFileFind filefind;
BOOL IsFileFind = filefind.FindFile(filename);
if(!IsFileFind)
{
// printf("Error: Can not find file: %s;\\n", filename);
wchar_t err_str[200];
wsprintf(err_str, _T("您打开的图片文件[%s]不存在!"), filename);
MessageBox(NULL, err_str, _T("错误"), MB_OK|MB_ICONERROR);
return 0;
}
//----------------------------------------
CImage img;
img.Load(filename);
int width = img.GetWidth();
int height = img.GetHeight();
hBitmap = img.Detach(); //如果用Detach(),则CImage析构后,hBitmap仍可使用。
int nBytes = ::GetObject(hBitmap, sizeof(BITMAP), &bitmap);
return 1;
}
int CCannyEdgeDetection::SaveImage(wchar_t* filename, HBITMAP &hBitmap)
{
GUID guid[4] =
{
Gdiplus::ImageFormatBMP,
Gdiplus::ImageFormatJPEG,
Gdiplus::ImageFormatPNG,
Gdiplus::ImageFormatGIF
};
if(m_guid_index<0 || m_guid_index>3)
{
printf("Erorr: SaveImage: m_guid_index must in [0,3]\\n");
}
CImage img;
img.Attach(hBitmap);
img.Save(filename, guid[m_guid_index]); //可以从guid看出,CImage的Save()实际上是通过GDI+实现的。
hBitmap = img.Detach(); //如果用Detach(),则CImage析构后,hBitmap仍可使用。
return 1;
}
int CCannyEdgeDetection::SaveImage(wchar_t* filename, BITMAP &bitmap)
{
int width = bitmap.bmWidth;
int height = bitmap.bmHeight;
int biBitCount = bitmap.bmBitsPixel;
RGBQUAD *pColorTable = NULL;
int colorTablesize = 0; //颜色表大小,以字节为单位,灰度图像颜色表为1024字节,彩色图像颜色表大小为0
// if(biBitCount == 8){colorTablesize=1024;}
// int lineByte = (width * biBitCount/8+3)/4*4; //待存储图像数据每行字节数为4的倍数
int lineByte = bitmap.bmWidthBytes; //待存储图像数据每行字节数为4的倍数
int size_1 = sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER); // size_1 = 14
int size_2 = sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER); // size_2 = 40
int size_3 = lineByte * height; //计算位图尺寸
// int bpp = bitmap.bmBitsPixel/8; //bpp代表通道的数目,一般 bpp = 3
//--------------1. 位图文件头结构-----------------------------------------------------
BITMAPFILEHEADER fileHead;
fileHead.bfType = 0x4D42; //bmp类型
fileHead.bfSize = size_1 + size_2 + colorTablesize + lineByte * height; //bfSize是图像文件4个组成部分之和
fileHead.bfReserved1 = 0;
fileHead.bfReserved2 = 0;
fileHead.bfOffBits = 54 + colorTablesize; //bfOffBits是图像文件前3个部分所需空间之和
//--------------2. 位图信息头结构-----------------------------------------------------
BITMAPINFOHEADER head;
head.biBitCount = biBitCount; // 8,24,32
head.biClrImportant = 0;
head.biClrUsed = 0;
head.biCompression = 0; //BI_RGB = 0L
head.biHeight = height;
head.biPlanes = 1;
head.biSize = 40;
head.biSizeImage = lineByte * height;
head.biWidth = width;
head.biXPelsPerMeter = 0;
head.biYPelsPerMeter = 0;
//---------------3. 内存中的文件读写操作-------------------------------
long file_size = fileHead.bfSize; //计算位图文件尺寸
unsigned char* pBits = static_cast<unsigned char*>(bitmap.bmBits);
HGLOBAL hMem = GlobalAlloc(GMEM_MOVEABLE|GMEM_ZEROINIT, file_size);
if(hMem == NULL){printf("Erorr: GlobalAlloc: hMem == NULL\\n");return 0;}
unsigned char *pbuff = static_cast<unsigned char*>(GlobalLock(hMem)); // get the actual pointer for the HGLOBAL
memcpy(pbuff, &fileHead, size_1); //内存复制
pbuff += size_1;
memcpy(pbuff, &head, size_2); //内存复制
pbuff += size_2;
memcpy(pbuff, pBits, size_3); //内存复制
IStream *pStream = 0;
HRESULT hr = CreateStreamOnHGlobal(hMem, TRUE, &pStream); //此函数是内存数据到文件流的关键API函数
if(hr != S_OK)
{
printf("Erorr: CreateStreamOnHGlobal: hr != S_OK\\n");
return 0;
}
//--------------4. 将文件流数据正式保存到磁盘文件中----------------------------------------
GUID guid[4] =
{
Gdiplus::ImageFormatBMP,
Gdiplus::ImageFormatJPEG,
Gdiplus::ImageFormatPNG,
Gdiplus::ImageFormatGIF
};
if(m_guid_index<0 || m_guid_index>3)
{
printf("Erorr: SaveImage: m_guid_index must in [0,3]\\n");
return 0;
}
CImage img;
img.Load(pStream);
img.Save(filename, guid[m_guid_index]); //可以从guid看出,CImage的Save()实际上是通过GDI+实现的。
img.Detach();
img.Destroy();
GlobalFree(hMem); //释放GlobalAlloc(...)申请的内存
return 1;
}
/*-------------------在内存中创建一幅空白位图------------------------------
*
* 参数1: bitmap 返回的结果
* 参数2: width 位图高度
* 参数3: height 位图宽度
* 参数4: bmBitsPixel 一个像素的字节大小,一般是24字节,也可以是32字节
*
* 过客 && 386520874@qq.com && 2014.12.26
*/
int CCannyEdgeDetection::CreateEmptyImage(BITMAP &bitmap, int width, int height, int bmBitsPixel)
{
// bmBitsPixel = 32;
bitmap.bmWidth = width;
bitmap.bmHeight = height;
bitmap.bmBitsPixel = bmBitsPixel;
bitmap.bmType = 0;
bitmap.bmPlanes = 1;
bitmap.bmWidthBytes = (width * bmBitsPixel/8+3)/4*4;
printf("CreateEmptyImage: [%d x %d] memory = %d bytes;\\n", width, height, bitmap.bmHeight * bitmap.bmWidthBytes);
unsigned char *pBits = new unsigned char[bitmap.bmHeight * bitmap.bmWidthBytes]; //在堆上申请
if(pBits == NULL){printf("CreateEmptyImage: pBits == NULL\\n");return 0;}
memset(pBits, 0, sizeof(unsigned char) * bitmap.bmHeight * bitmap.bmWidthBytes); //初始化为黑色背景
bitmap.bmBits = pBits;
return 1;
}
/*-------------------图像的Canny边缘检测------------------------------
* 算法原理:
* 图像的Canny边缘检测算法,是一种理论和实际效果比较靠谱的算法,它
* 大致有下面几个步骤:
* 1. 将输入的RGB图像转换成单通道的灰度图像
* 2. 计算灰度图像的一阶梯度,该算法选择Sobel算子计算dx和dy两个方向
* 的梯度
* 3. 对图像的梯度幅值进行非极大值抑制,这一步是Canny算法的独到之处
* 经过这一步后,真正的边缘点会被暴露出来,并将其位置保存下来
* 4. 双阈值检测:将保存下来的已确认为边缘的点,以每个点为中心,将
* 相邻的8个像素由1变成2,即将曲线的轮廓进行不断的延伸。
*
* Sobel算子模板:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sobel_operator
* | -1 0 +1 | | -1 -2 -1 |
* Sx = | -2 0 +2 | Sy = | 0 0 0 |
* | -1 0 +1 | | +1 +2 +1 |
*
* 函数名称: Canny(...)
* 参数1: bitmap_src [in]输入的图像位图数据
* 参数2: bitmap_dst [out]输出的图像位图数据
* 参数3: low_thresh [in]低阈值,所有梯度幅值低于此值的点不认为是边缘点
* 参数4: high_thresh [in]高阈值,经过非极大值抑制后,所有梯度幅值高于
* 此值的点认为是边缘点
*
* 过客 && 386520874@qq.com && 2015.03.27
*/
int CCannyEdgeDetection::Canny(BITMAP &bitmap_src, BITMAP &bitmap_dst, double low_thresh, double high_thresh)
{
//-------------1. 输入参数检查-----------------------
BITMAP bitmap1 = bitmap_src;
unsigned char* pBits1 = static_cast<unsigned char*>(bitmap1.bmBits);
int bpp1 = bitmap1.bmBitsPixel/8; //bpp代表通道的数目,一般 bpp = 3
int width2 = bitmap1.bmWidth;
int height2 = bitmap1.bmHeight;
CreateEmptyImage(bitmap_dst, width2, height2, bitmap1.bmBitsPixel);
int bpp2 = bitmap_dst.bmBitsPixel/8; //bpp代表通道的数目,一般 bpp = 3
unsigned char* pBits2 = static_cast<unsigned char*>(bitmap_dst.bmBits);
BITMAP bitmap2 = bitmap_dst;
//-------------2. RGB转灰度-----------------------
int* gray = new int[width2 * height2]; //保存灰度图像数据
for(int y = 0; y < bitmap1.bmHeight; y++)
{
for(int x = 0; x < bitmap1.bmWidth; x++)
{
int B = pBits1[y * bitmap1.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp1 + 0]; //Blue
int G = pBits1[y * bitmap1.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp1 + 1]; //Green
int R = pBits1[y * bitmap1.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp1 + 2]; //Red
// int A = R * 0.299 + G * 0.587 + B * 0.114; //一般RGB2Gray公式
int A = R * 0.212671 + G * 0.715160 + B * 0.072169; //opencv的RGB2Gray公式 0.212671*R + 0.715160*G + 0.072169*B
gray[y * width2 + x] = A;
}
}
//-------------3. 计算灰度图像梯度幅值和方向-----------------------
int* dx = new int[width2 * height2]; //x向偏导数
int* dy = new int[width2 * height2]; //y向偏导数
memset(dx, 0, sizeof(int) * width2 * height2);
memset(dy, 0, sizeof(int) * width2 * height2);
//利用Sobel算子,计算x,y方向的偏导数
for(int y = 0; y < height2; y++)
{
for(int x = 0; x < width2; x++)
{
if(x < 1 || x >= width2 -1 || y < 1 || y >= height2 - 1){continue;} //3x3的算子,图像的4条边需要跳过
dx[y * width2 + x] = -(gray[(y - 1) * width2 + (x - 1)] * 1 + gray[(y + 0) * width2 + (x - 1)] * 2 + gray[(y + 1) * width2 + (x - 1)] * 1)
+ (gray[(y - 1) * width2 + (x + 1)] * 1 + gray[(y + 0) * width2 + (x + 1)] * 2 + gray[(y + 1) * width2 + (x + 1)] * 1);
dy[y * width2 + x] = -(gray[(y - 1) * width2 + (x - 1)] * 1 + gray[(y - 1) * width2 + (x + 0)] * 2 + gray[(y - 1) * width2 + (x + 1)] * 1)
+ (gray[(y + 1) * width2 + (x - 1)] * 1 + gray[(y + 1) * width2 + (x + 0)] * 2 + gray[(y + 1) * width2 + (x + 1)] * 1);
}
}
//计算梯度幅值和梯度的方向
//.......
//-------------4. 非极大值抑制-----------------------
//下面代码来自于opencv的canny.cpp修改版本
bool L2gradient = false; //采用哪种梯度的计算公式
// bool L2gradient = true; //采用哪种梯度的计算公式
// const int cn = src.channels();
const int cn = 1;
int low = low_thresh;
int high = high_thresh;
typedef unsigned char uchar;
ptrdiff_t mapstep = width2 + 2;
//注意buffer是一个二维数组,总体来说有[3 + height]行,前面3行用来不断滚动的临时计算
//和存储图像梯度|dx+dy|的幅值,后面[height]行中每个数组元素用来标记,图像中对应点是
//否是边缘点信息,只有[0,1,2]三种值,
//0-表示该像素可能是边缘
//1-表示该像素不可能是边缘
//2-表示该像素是边缘
uchar * buffer = new uchar[(width2 + 2) * (height2 + 2) + cn * mapstep * 3 * sizeof(int)]; //存储边缘信息的数组
int* mag_buf[3];
mag_buf[0] = (int*)(uchar*)buffer;
mag_buf[1] = mag_buf[0] + mapstep * cn;
mag_buf[2] = mag_buf[1] + mapstep * cn;
memset(mag_buf[0], 0, mapstep * sizeof(int));
uchar* map = (uchar*)(mag_buf[2] + mapstep * cn);
memset(map, 1, mapstep);
memset(map + mapstep * (height2 + 1), 1, mapstep);
int maxsize = max(1 << 10, width2 * height2 / 10); //栈stack用来存储标记为2的像素点指针,栈的最大尺寸为[width2 * height2]
std::vector<uchar*> stack(maxsize);
uchar **stack_top = &stack[0];
uchar **stack_bottom = &stack[0];
//----------------------------
#define CANNY_PUSH(d) *(d) = uchar(2), *stack_top++ = (d)
#define CANNY_POP(d) (d) = *--stack_top
// calculate magnitude and angle of gradient, perform non-maxima suppression.
// fill the map with one of the following values:
// 0 - the pixel might belong to an edge,0-表示该像素可能是边缘
// 1 - the pixel can not belong to an edge,1-表示该像素不可能是边缘
// 2 - the pixel does belong to an edge,2-表示该像素是边缘
for(int i = 0; i <= height2; i++) //遍历行
{
int* _norm = mag_buf[(i > 0) + 1] + 1;
if(i < height2)
{
int* _dx = dx + i * width2;
int* _dy = dy + i * width2;
if(!L2gradient)
{
for(int j = 0; j < width2 * cn; j++)
{
_norm[j] = abs(_dx[j]) + abs(_dy[j]); //梯度的幅值 |G| = |dx| + |dy|,默认使用这个公式
}
}else
{
for(int j = 0; j < width2 * cn; j++)
{
// _norm[j] = _dx[j] * _dx[j] + _dy[j] * _dy[j]; //梯度的幅值 |G| = |dx|*|dx| + |dy|*|dy|
_norm[j] = sqrt(1.0 * (_dx[j] * _dx[j] + _dy[j] * _dy[j])); //梯度的幅值 |G| = sqrt(|dx|*|dx| + |dy|*|dy|)
}
}
if(cn > 1)
{
for(int j = 0, jn = 0; j < width2; ++j, jn += cn)
{
int maxIdx = jn;
for(int k = 1; k < cn; ++k)
{
if(_norm[jn + k] > _norm[maxIdx]){maxIdx = jn + k;}
}
_norm[j] = _norm[maxIdx];
_dx[j] = _dx[maxIdx];
_dy[j] = _dy[maxIdx];
}
}
_norm[-1] = _norm[width2] = 0;
}else
{
memset(_norm - 1, 0, mapstep * sizeof(int));
}
// at the very beginning we do not have a complete ring
// buffer of 3 magnitude rows for non-maxima suppression
if (i == 0){continue;}
uchar* _map = map + mapstep * i + 1;
_map[-1] = _map[width2] = 1;
int* _mag = mag_buf[1] + 1; // take the central row
ptrdiff_t magstep1 = mag_buf[2] - mag_buf[1];
ptrdiff_t magstep2 = mag_buf[0] - mag_buf[1];
const int* _x = dx + (i - 1) * width2;
const int* _y = dy + (i - 1) * width2;
if((stack_top - stack_bottom) + width2 > maxsize)
{
int sz = (int)(stack_top - stack_bottom);
maxsize = maxsize * 3 / 2;
stack.resize(maxsize); //将栈空间扩大为原来的3/2=1.5倍
stack_bottom = &stack[0];
stack_top = stack_bottom + sz;
}
int prev_flag = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < width2; j++) //遍历列
{
#define CANNY_SHIFT 15
const int TG22 = (int)(0.4142135623730950488016887242097*(1<<CANNY_SHIFT) + 0.5); //tan(PI/8)=0.41421356...
double m = _mag[j];
if(m > low)
{
int xs = _x[j];
int ys = _y[j];
int x = std::abs(xs);
int y = std::abs(ys) << CANNY_SHIFT;
double tg22x = x * TG22;
if(y < tg22x) // PI/8 = 22.5度,tan(PI/8)
{
if(m > _mag[j-1] && m >= _mag[j+1]) goto __ocv_canny_push; //非极大值抑制:3x3模板,8邻域像素的水平方向
}else
{
double tg67x = tg22x + (x << (CANNY_SHIFT+1));
if(y > tg67x) // PI*3/8 = 67.5度,tan(PI*3/8)
{
if(m > _mag[j+magstep2] && m >= _mag[j+magstep1]) goto __ocv_canny_push; //非极大值抑制:3x3模板,8邻域像素的垂直方向
}else
{
int s = (xs ^ ys) < 0 ? -1 : 1;
if(m > _mag[j+magstep2-s] && m > _mag[j+magstep1+s]) goto __ocv_canny_push; //非极大值抑制:3x3模板,8邻域像素的两条45度对角线方向
}
}
}
prev_flag = 0;
_map[j] = uchar(1); //1-表示该像素点不是边缘
continue;
__ocv_canny_push:
if (!prev_flag && m > high && _map[j-mapstep] != 2)
{
CANNY_PUSH(_map + j); //2-表示该像素是边缘,则将其弹入栈中
prev_flag = 1;
}else
{
_map[j] = 0; //0-表示该像素可能是边缘
}
}
// scroll the ring buffer
// 滚动交换保存梯度幅值的行
_mag = mag_buf[0];
mag_buf[0] = mag_buf[1];
mag_buf[1] = mag_buf[2];
mag_buf[2] = _mag;
}
//-------------5. 双阈值检测:将8个相邻的像素由1变成2----------------------------------
// now track the edges (hysteresis thresholding)
while(stack_top > stack_bottom)
{
uchar* m;
if ((stack_top - stack_bottom) + 8 > maxsize)
{
int sz = (int)(stack_top - stack_bottom);
maxsize = maxsize * 3 / 2;
stack.resize(maxsize); //将栈空间扩大为原来的3/2=1.5倍
stack_bottom = &stack[0];
stack_top = stack_bottom + sz;
}
CANNY_POP(m);
//因为栈中保存的都是边缘点像素,现在循环检测栈中所有边缘点的
//周围8个像素是否被标记为0,如果是0,则认为该点也是边缘点,并
//将其弹入栈中,可以看出这个栈的功能实现了递归函数的功能,直
//到栈空为止,则结束循环。
if(!m[-1]) CANNY_PUSH(m - 1);
if(!m[1]) CANNY_PUSH(m + 1);
if(!m[-mapstep-1]) CANNY_PUSH(m - mapstep - 1);
if(!m[-mapstep]) CANNY_PUSH(m - mapstep);
if(!m[-mapstep+1]) CANNY_PUSH(m - mapstep + 1);
if(!m[mapstep-1]) CANNY_PUSH(m + mapstep - 1);
if(!m[mapstep]) CANNY_PUSH(m + mapstep);
if(!m[mapstep+1]) CANNY_PUSH(m + mapstep + 1);
}
//------------6. 保存算法结果到图片中----------------------
// the final pass, form the final image
const uchar* pmap = map + mapstep + 1;
for(int y = 0; y < height2; y++)
{
for(int x = 0; x < width2; x++)
{
uchar _gray = (uchar)-(pmap[y * mapstep + x] >> 1); //因为pmap[]里面的值只有0,1,2三种,而2才是边缘像素点,所以,-(2 >> 1) = 255,即用白色表示边缘
pBits2[y * bitmap2.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp2 + 0] = _gray;
pBits2[y * bitmap2.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp2 + 1] = _gray;
pBits2[y * bitmap2.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp2 + 2] = _gray;
}
}
//------------------------------
delete [] gray; gray = NULL;
delete [] dx; dx = NULL;
delete [] dy; dy = NULL;
delete [] buffer; buffer = NULL;
return 1;
}
/*-------------------Sobel图像二阶差分梯度边缘检测------------------------------
* 算法原理:
*
* Sobel算子模板:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sobel_operator
* | -1 0 +1 | | -1 -2 -1 |
* Sx = | -2 0 +2 | Sy = | 0 0 0 |
* | -1 0 +1 | | +1 +2 +1 |
*
* 函数名称: Canny(...)
* 参数1: bitmap_src [in]输入的图像位图数据
* 参数2: bitmap_dst [out]输出的图像位图数据
* 参数3: low_thresh [in]低阈值,(暂时不使用该参数)
* 参数4: high_thresh [in]高阈值,所有梯度幅值高于此值的点认为是边缘点
*
* 过客 && 386520874@qq.com && 2015.03.28
*/
int CCannyEdgeDetection::Sobel(BITMAP &bitmap_src, BITMAP &bitmap_dst, double low_thresh, double high_thresh)
{
//-------------1. 输入参数检查-----------------------
BITMAP bitmap1 = bitmap_src;
unsigned char* pBits1 = static_cast<unsigned char*>(bitmap1.bmBits);
int bpp1 = bitmap1.bmBitsPixel/8; //bpp代表通道的数目,一般 bpp = 3
int width2 = bitmap1.bmWidth;
int height2 = bitmap1.bmHeight;
CreateEmptyImage(bitmap_dst, width2, height2, bitmap1.bmBitsPixel);
int bpp2 = bitmap_dst.bmBitsPixel/8; //bpp代表通道的数目,一般 bpp = 3
unsigned char* pBits2 = static_cast<unsigned char*>(bitmap_dst.bmBits);
BITMAP bitmap2 = bitmap_dst;
//-------------2. RGB转灰度-----------------------
int* gray = new int[width2 * height2]; //保存灰度图像数据
for(int y = 0; y < bitmap1.bmHeight; y++)
{
for(int x = 0; x < bitmap1.bmWidth; x++)
{
int B = pBits1[y * bitmap1.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp1 + 0]; //Blue
int G = pBits1[y * bitmap1.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp1 + 1]; //Green
int R = pBits1[y * bitmap1.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp1 + 2]; //Red
// int A = R * 0.299 + G * 0.587 + B * 0.114; //一般RGB2Gray公式
int A = R * 0.212671 + G * 0.715160 + B * 0.072169; //opencv的RGB2Gray公式 0.212671*R + 0.715160*G + 0.072169*B
gray[y * width2 + x] = A;
}
}
//-------------3. 计算灰度图像梯度幅值和方向-----------------------
//利用Sobel算子,计算x,y方向的偏导数
for(int y = 0; y < height2; y++)
{
for(int x = 0; x < width2; x++)
{
if(x < 1 || x >= width2 -1 || y < 1 || y >= height2 - 1){continue;} //3x3的算子,图像的4条边需要跳过
int dx = -(gray[(y - 1) * width2 + (x - 1)] * 1 + gray[(y + 0) * width2 + (x - 1)] * 2 + gray[(y + 1) * width2 + (x - 1)] * 1)
+ (gray[(y - 1) * width2 + (x + 1)] * 1 + gray[(y + 0) * width2 + (x + 1)] * 2 + gray[(y + 1) * width2 + (x + 1)] * 1);
int dy = -(gray[(y - 1) * width2 + (x - 1)] * 1 + gray[(y - 1) * width2 + (x + 0)] * 2 + gray[(y - 1) * width2 + (x + 1)] * 1)
+ (gray[(y + 1) * width2 + (x - 1)] * 1 + gray[(y + 1) * width2 + (x + 0)] * 2 + gray[(y + 1) * width2 + (x + 1)] * 1);
int Grad = abs(dx) + abs(dy); //计算梯度幅值
if(Grad >= high_thresh)
{
Grad = 255;
}else
{
Grad = 0;
}
pBits2[y * bitmap2.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp2 + 0] = Grad;
pBits2[y * bitmap2.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp2 + 1] = Grad;
pBits2[y * bitmap2.bmWidthBytes + x * bpp2 + 2] = Grad;
}
}
//计算梯度幅值和梯度的方向
//.......
delete [] gray; gray = NULL;
return 1;
}
/*
* test.cpp
*
* 过客 && 386520874@qq.com && 2016.03.26
*
*/
#include "CannyEdgeDetection.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) //专门测试字体的边缘轮廓检测
{
wchar_t in[260] = TEXT("./picture/test2.png");
wchar_t out[260];
CCannyEdgeDetection ced;
BITMAP bitmap;
HBITMAP hBitmap;
BITMAP bitmap_dst;
ced.OpenImage(in, bitmap, hBitmap);
ced.Sobel(bitmap, bitmap_dst, 0, 400);
ced.SaveImage(TEXT("./picture/test2.sobel.0_400.png"), bitmap_dst);
ced.ReleaseBitmap(bitmap_dst);
ced.Canny(bitmap, bitmap_dst, 10, 100);
ced.SaveImage(TEXT("./picture/test2.canny.10_100.png"), bitmap_dst);
ced.ReleaseBitmap(bitmap_dst);
system("pause");
return 1;
}

图1.1 原始位图

图1.2canny检测[low,high]=[10,100]

图1.3 sobel检测[low,high]=[0,200]
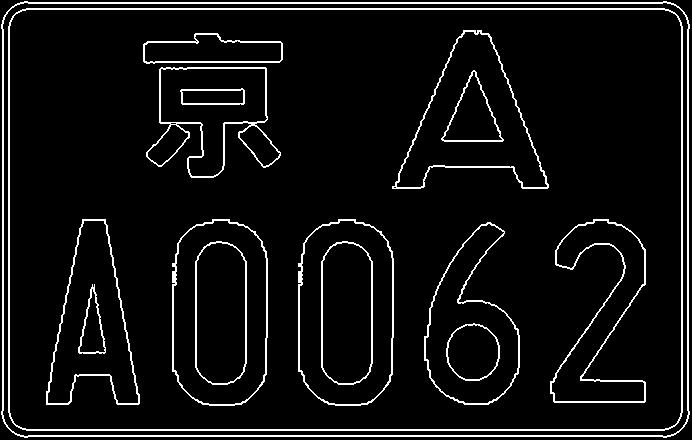
图1.4 sobel检测[low,high]=[0,400]
------------------------------------------------测试示例2----------------------------------------------------------

图2.1 原始位图

图2.2 canny检测[low,high]=[100,400]

图2.3 sobel检测[low,high]=[0,400]
--------------------------结论-------------------------------------
通过上面两个示例图片的比较,可以发现sobel的处理比较干净利落,
而canny算法的处理结果细节比较多一点,即线条的毛边比较多。
但canny的好处是它的线宽只有1个像素,而sobel则不一定。两者各
有利弊,在图像特征检测方面很难说谁好谁坏,不过听说卷积神经网络
的特征检测用了sobel算子。
以上是关于Canny边缘检测的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章