gets()puts()函数。字符串函数。字符串排序的例子。
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了gets()puts()函数。字符串函数。字符串排序的例子。相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、实例程序:string.c的程序:
#include<stdio.h>
#define MSG "YOU MUST have many talents .tell me some."
#define LIM 5
#define LINELEN 81
int main()
{
char name[LINELEN];
char talents[LINELEN];
int i;
const char m1[40]="limit yourself to one line‘s worth.";
const char m2[]="IF you can‘t think of your anything,fake it.";
const char*m3="\nENough about me,what‘s your name?";
const char *mytal[LIM]={"adding numbers swiftly","mulityplying accurately","stashing data","flowing instructions to the letter","understanding C language"};//初始化一个字符串指针数组
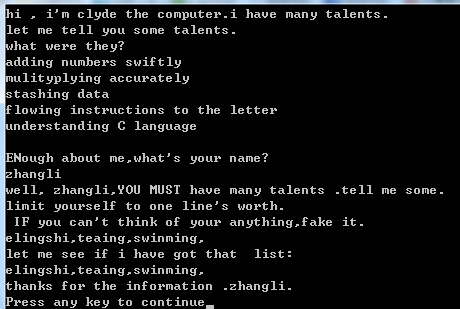
printf("hi , i‘m clyde the computer." "i have many talents.\n");
printf("let me tell you some talents.\n");
puts("what were they?");
for (i=0;i<LIM;i++)
puts(mytal[i]);
puts(m3);
gets(name);
printf("well, %s,%s\n",name,MSG);
printf("%s \n %s\n",m1,m2);
gets(talents);
puts("let me see if i have got that list:");
puts(talents);
printf("thanks for the information .%s.\n",name);
return 0;
}运行结果:
从中可以看出:定义字符串的方法有:使用字符串常量、char 数组、char指针、字符串数组、
2、把字符串看做指针:
实例程序:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
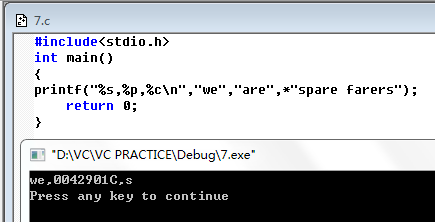
printf("%s,%p,%c\n","we","are",*"spare farers");
return 0;
}%s 格式输出字符串“we”,%p格式产生一个十六进制的地址,因此如果“are”是个地址,那么%p应该输出字符串中第一个字符的地址。最后
*"spare farers"应该产生所指向的地址中的值,即字符串*"spare farers"的第一个字符。
3、strlen() 得到字符串的长度,缩短字符串函数
示例程序:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void fit(char *,unsigned int);
int main(void)
{
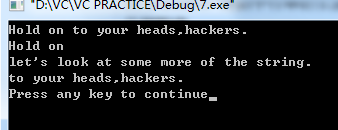
char mesg[]="Hold on to your heads,hackers.";
puts(mesg);
fit(mesg,7);
puts(mesg);
puts("let‘s look at some more of the string.");
puts(mesg+8);
return 0;
}
void fit (char *string,unsigned int size)
{
if(strlen(string)>size)
*(string+size)=‘\0‘;
}运行结果:
fit()函数在数组的第8个元素中放置了一个
‘\0‘,代替原有的空格字符,put函数输出时停在了第一个空格符处。忽略数组的其他元素,然而数组的其他元素仍然存在,mesg+8表示mesg[8]即‘t‘字符的地址,因此puts函数继续输出,直到遇到原字符串中的空字符。
4、strcat()代表(string concatenation)函数.函数接受两个字符串参数,它将第二个字符串的一份拷贝添加到第一个字符串的串尾,从而使第一个字符串称为一个新组合的字符串,第二个字符串并没有改变。该函数是char* 类型(指向char的指针),这个函数返回它的第一个参数的值,即其后添加了第二个字符串的那个字符串第一个字符的地址。
实例程序:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define size 80
int main()
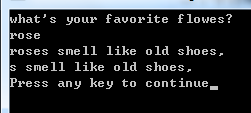
{ char flower[size];
char addon[]="s smell like old shoes,";
puts("what‘s your favorite flowes?");
gets(flower);
strcat(flower,addon);
puts(flower);
puts(addon);
return 0;
}运行结果:
5、strncat()函数,strcat函数并不检查第一个数组是否能够容纳的下第二个字符串。如果没有给第一个数组分配足够的空间,多出来的字符溢出到相邻的存储单元时就会出问题。此时用strncat()函数。这个函数需要另外的一个参数来指明最多允许添加的字符的数目,例如strncat(bugs,addon,13),函数把addon中的内容添加到bugs上,直到加到13个字符或者遇到空字符为止。
6、strcmp()函数。用户的响应和一个已有的字符串进行比较。代表(string comarison)strcmp(a,b),如果两个字符串的参数相同,则返回值为0.比较的是字符串,而不是数组。用于比较字符串而不是字符。
等等。
7、一个字符串排序的例子
我们来看一个把字符串按照字母表进行排序的例子。主要用到strcmp()
示例程序:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define size 81
#define lim 20
#define halt " "//用空字符终止输入
void start(char *string[],int num);//字符串排序函数
int main(){
char input[lim][size];
char *ptstr[lim];
int ct=0;
int k;
printf("input up to %d lines,and i will sort them.\n",lim);
printf("to stop.press the enter key at a lines start\n");
while (ct<lim&& gets(input[ct])!=NULL&&input[ct][0]!=‘\0‘)
{
ptstr[ct]=input[ct];
ct++;
}
start(ptstr,ct);
puts("\n here the soreted list:\n");
for(k=0;k<ct;k++)
puts(ptstr[k]);
return 0;
}
void start(char *string[],int num)
{
char *temp;
int top,seek;
for (top=0;top<num-1;top++)
for(seek=top+1;seek<num;seek++)
if(strcmp(string[top],string[seek])>0)
{
temp=string[top];
string[top]=string[seek];
string[seek]=temp;
}
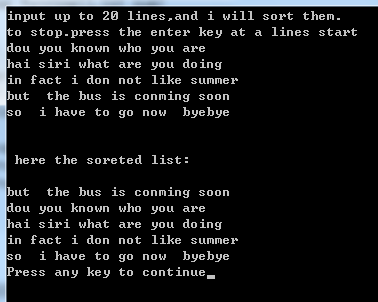
}运行结果:
以上是关于gets()puts()函数。字符串函数。字符串排序的例子。的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
scanf 与 gets ,printf 与puts 函数比较
gets()puts()函数。字符串函数。字符串排序的例子。
gets()puts()函数。字符串函数。字符串排序的例子。
我可以在不同的函数中使用相同字符串的gets()和puts()吗
输出与输出:putchar() getchar() printf() scanf() puts() gets() sscanf()